TCF7 Antibodies
Background
TCF7 (T-cell factor 7) is a transcription factor involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, mainly existing in various vertebrate tissues, especially playing a key role in the immune system and development process. This protein affects biological processes such as T cell development, differentiation, and stem cell self-renewal by binding to β -catenin and regulating the expression of downstream target genes. TCF7 was first identified in T cells in the 1990s. Its structure contains a highly conserved HBG-box DNA-binding domain, which can specifically recognize DNA sequences and regulate transcriptional activity. As one of the core mediators of the Wnt pathway, the function and structure of TCF7 have become important models for the study of cell signal transduction, immune regulation and cancer mechanisms, profoundly promoting our understanding of the association between transcriptional regulatory networks and diseases.
Structure of TCF7
The TCF7 (T-cell factor 7) gene encodes a variable-length transcription factor protein, and the molecular weight of its main subtype is approximately 50-60 kDa. The molecular weight varies among different species, mainly due to the differences in amino acid sequence length and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 440-495 | About 430 | About 520 | About 450 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the conserved β-catenin binding domain and HMG-box | Structure similar to human height, function of interchangeable | With additional regulatory regions, adapted to early developmental needs | Structure is simplified, but the core of conservative dna-binding domain function |
The core structure of the TCF7 protein includes an amino-terminal domain responsible for binding to β -catenin, as well as a highly conserved HBG-box DNA binding domain. This HMG-box domain can specifically recognize and bind to specific sequences on the DNA double helix (such as 5 '-CCTTTGATC-3'), causing significant DNA bending, thereby altering the local chromatin structure and recruiting other transcriptional regulatory factors. Its tertiary structure is stabilized through hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bond networks, forming a conformation suitable for interaction with DNA and co-activators/co-inhibitors.
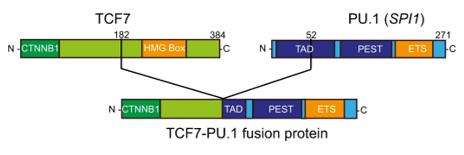 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the resulting TCF1-PU.1 (TCF7-SPI1) fusion protein.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the resulting TCF1-PU.1 (TCF7-SPI1) fusion protein.1
Key structural properties of TCF7:
- Highly conserved HMG-box DNA binding domain
- Modular protein structure
- Key amino acid residues regulate DNA binding and signal integration
Functions of TCF7
The transcription factor encoded by the TCF7 gene has the core function of acting as a downstream effector of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, regulating the transcriptional expression of target genes. This function is mainly reflected in the determination of cell fate and the maintenance of homeostasis.
| Function | Description |
| Transcriptional regulation | TCF7 binds to β-catenin that enters the nucleus to form a complex and binds to a specific DNA sequence (Wnt reactive element), activating the transcription of downstream target genes (such as c-Myc, Cyclin D1). |
| Cell fate determination | In embryonic development and stem cell biology, it dominates the differentiation of cells into specific lineages (such as T-cell lineages) by regulating specific genetic programs. |
| Regulation of the immune system | In the thymus, TCF7 is crucial for the survival and proliferation of early T cell precursors, as well as the transition from CD4+/CD8+ double-negative to double-positive phases. |
| Signal integration and conversion | When the Wnt signal is absent, TCF7 can bind to transcriptional suppressors (such as Groucho), actively inhibiting the transcription of target genes and converting the presence or absence of extracellular signals into precise gene switches. |
| Maintenance of tissue homeostasis | In adult tissues (such as intestinal crypts), it maintains the continuous renewal and repair of tissues by regulating genes related to the self-renewal and proliferation of stem cells. |
The activity of TCF7 is not constant but is precisely regulated. Its own expression is induced by multiple signals, and its protein activity can be regulated by various post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation and acetylation), and depends on competitive binding to β-catenin or inhibitors, thereby forming a dynamic, environment-dependent transcriptional regulatory switch in cells.
Applications of TCF7 and TCF7 Antibody in Literature
- Duan, Yang, et al. "TCF7/SNAI2/miR-4306 feedback loop promotes hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum." Journal of Translational Medicine 20.1 (2022): 468. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03677-0
This study first discovered that TCF7 is highly expressed in ligamentum flavum hypertrophy and confirmed that it can promote cell proliferation and fibrosis. Mechanistically, TCF7 exerts its effect by activating the SNAI2/miR-4306 feedback loop, suggesting that this pathway can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
- Ghosh, Rituparna, and Matthew J. Yousefzadeh. "TCF7‐Linked Immune Resilience: A Salutogenic Biological Warranty for Longevity." Aging Cell 24.6 (2025): e70090. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.70090
Research has found that high expression of TCF7 is key to maintaining immune resilience, as it can enhance immune capacity and suppress chronic inflammation. This feature has a weak correlation with age and is a new target for promoting healthy aging.
- Rong, Haixu, et al. "Correlation between TCF7+ T cells and prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2022): 782058. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.782058
This study confirmed that TCF7-positive T cells are an independent predictor of postoperative survival in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Incorporating it into existing predictive models (such as TNM staging) can significantly enhance the predictive accuracy and clinical application value of the models.
- Ma, Zhongnan, et al. "TCF7 is highly expressed in immune cells on the atherosclerotic plaques, and regulating inflammatory signaling via NFκB/AKT/STAT1 signaling." Bioscience Reports 42.7 (2022): BSR20212064. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20212064
This study confirmed that single-cell sequencing revealed that genes such as TCF7 are involved in the continuous activation of T cells and macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques through the AKT/NFκB signaling pathway, and are potential therapeutic targets.
- Van Thillo, Quentin, et al. "Oncogenic cooperation between TCF7-SPI1 and NRAS (G12D) requires β-catenin activity to drive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Nature Communications 12.1 (2021): 4164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24442-9
This study found that the TCF7-SPI1 fusion gene needs to co-induce T-cell leukemia with NRAS mutations, and its carcinogenesis depends on the interaction of TCF/β-catenin. Blocking this effect can induce the differentiation of cancer cells, providing a new strategy for targeted therapy.
Creative Biolabs: TCF7 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TCF7 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TCF7 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TCF7 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Van Thillo, Quentin, et al. "Oncogenic cooperation between TCF7-SPI1 and NRAS (G12D) requires β-catenin activity to drive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Nature Communications 12.1 (2021): 4164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24442-9
Anti-TCF7 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTCF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2371) (CBMAB-C2443-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








