USP40 Antibodies
Background
The USP40 gene encodes a deubiquitinating enzyme belonging to the ubiquitin-specific protease family. This protein is mainly present in the cytoplasm and regulates key physiological activities such as cell cycle progress and DNA damage repair by precisely hydrolyzing the ubiquitin chains on substrate proteins. Studies have shown that USP40 ensures accurate chromosome separation by maintaining the stability of mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint proteins. The loss of its function may lead to genomic instability. This gene was first identified in 2003 through sequence homology analysis. The protease it encodes has typical characteristics of the USP family catalytic domain, with a hydrolyzed active center formed by conserved cysteine and histidine residues. As an important member of the deubiquitinating enzyme system, the functional study of USP40 provides an important molecular basis for revealing the regulatory mechanism of post-translational modifications of proteins and the cellular stress response pathway.
Structure of USP40
USP40 is a deubiquitinating enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 128 kDa. There are certain differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to sequence variations in the regulatory domain.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 128.1 | 127.8 | 126.5 | 105.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the complete USP and UBL structural domains | Highly conserved structure of catalytic domain | There is a sequence missing in the UBL domain | Only the core USP domain is retained |
This protein is composed of 1102 amino acids, with a highly conserved USP catalytic domain at its core. This domain is formed by multiple α -helicles and β -folds to create a hydrophilic active pocket. The catalytic center is composed of a "catalytic triplet" made up of cysteine, histidine and aspartic acid, and is responsible for the precise hydrolysis of ubiquitin chains. Its N-terminal usually contains a ubiquitin-like domain, which regulates the recognition and binding process between the enzyme and the substrate through allosteric effects.
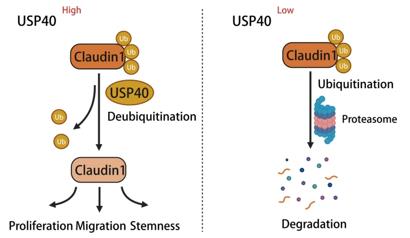 Fig. 1 Scheme for the regulatory mechanism of USP40 on Claudin1.1
Fig. 1 Scheme for the regulatory mechanism of USP40 on Claudin1.1
Key structural properties of USP40:
- Contains the typical USP catalytic domain core
- Hydrophilic active pockets are formed for identifying ubiquitin chains
- The catalytic triple (Cys-His-Asp/Asn) is responsible for the hydrolysis function
- The C-terminal zinc finger domain stabilizes the ubiquitin binding channel
Functions of USP40
The core function of the protein encoded by the USP40 gene is to participate in the regulation of protein stability within cells. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Cell cycle regulation | By deubiquitinating and modifying mitose-related proteins (such as CDC20), the normal function of spindle assembly checkpoints is ensured, and the accurate separation of chromosomes is maintained. |
| DNA damage response | Repair factors are recruited and stabilized at the double-strand break sites of DNA, and the homologous recombination repair process is coordinated through the deubiquitination mechanism. |
| Maintenance of genomic stability | Eliminate abnormal ubiquitination markers of key regulatory proteins to prevent chromosomal aneuploidy changes caused by incorrect protein degradation. |
| Cellular stress adaptation | In response to stress signals such as oxidative stress, it helps cells maintain internal environmental homeostasis by regulating the ubiquitination levels of stress pathway proteins. |
The catalytic efficiency of this enzyme is regulated by the allosteric configuration of its N-terminal regulatory domain. Compared with other members of the USP family, USP40 has a significantly higher recognition ability for K63 linked ubiquitin chains than K48 linked types, suggesting that it may have specific functions in the signal transduction pathway. Current research has found that its functional deficiency is closely related to the occurrence and development of certain tumors.
Applications of USP40 and USP40 Antibody in Literature
1. Wu, Qingsong, et al. "USP40 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and stemness by deubiquitinating and stabilizing Claudin1." Biology Direct 19.1 (2024): 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-024-00456-3
This study reveals that the deubiquitinating enzyme USP40 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and predicts a poor prognosis. USP40 stabilizes the protein by binding to Claudin1 and inhibiting its ubiquitination, thereby promoting the proliferation, migration and stem cell characteristics of HCC. Targeting USP40 may become a new treatment strategy for HCC.
2. Miao, Jiaxing, et al. "The deubiquitinase USP40 preserves endothelial integrity by targeting the heat shock protein HSP90β." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 56.2 (2024): 395-407.https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-024-01160-y
Research reveals that the deubiquitinating enzyme USP40 plays a key protective role in vascular endothelium. It can stabilize the endothelial barrier, inhibit inflammation and alleviate experimental lung injury. The mechanism is to deubiquitinate and inhibit HSP90β, thereby suppressing the downstream RhoA and NF- κ B signaling pathways.
3. An, Wentao, et al. "Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 (GMEB1) interacts with the de-ubiquitinase USP40 to stabilize CFLARL and inhibit apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 38.1 (2019): 181.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1182-3
Research has found that the catalytic mechanisms of different deubiquitinating enzymes (USPs) vary. Unlike USP7, which relies on a "third key residue", the catalytic activity of enzymes such as USP40 mainly depends on a "fourth key residue". This diversity in mechanism provides new ideas for the development of inhibitors specifically targeting USP40.
4. Keijzer, Niels, et al. "Variety in the USP deubiquitinase catalytic mechanism." Life Science Alliance 7.4 (2024). https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202302533
This study reveals that the catalytic mechanisms of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP family are diverse. Unlike USP7, the catalytic activity of USP40 does not rely on a "third key residue", but mainly depends on a conserved "fourth key residue". This unique mechanism provides a new target for the development of drugs specifically targeting USP40.
5. Wu, Wei, et al. "Whole-exome sequencing identified four loci influencing craniofacial morphology in northern Han Chinese." Human genetics 138.6 (2019): 601-611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02008-6
This study, through whole exome sequencing, found that a specific mutation site of the USP40 gene was significantly associated with the craniofacial morphology of the northern Han population, especially the width of the piriform foramen. This provides new clues for revealing the genetic basis of facial shapes.
Creative Biolabs: USP40 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality USP40 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom USP40 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our USP40 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wu, Qingsong, et al. "USP40 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and stemness by deubiquitinating and stabilizing Claudin1." Biology Direct 19.1 (2024): 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-024-00456-3
Anti-USP40 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








