XBP1 Antibodies
Background
The XBP1 gene encodes a key transcription factor, and its protein product exists in the form of a core regulatory element of endoplasmic reticulum stress response. This protein directly maintains intracellular protein folding homeostasis by regulating the gene expression of molecular chaperone and endoplasmic reticulum-related degradation pathways. This mechanism is crucial for the function of secretory cells. When cells are in a state of stress, XBP1 mRNA undergoes atypical splicing, thereby activating its transcriptional activity. This pathway has been confirmed to be closely related to the differentiation of immune cells and the process of neural development. Researcher Hiroshi Yoshida first discovered XBP1 in the 1990s. Subsequent studies revealed that its splicing mechanism was mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane protein IRE1α. The related achievements provided a molecular basis for understanding the unfolded protein response. As a hub molecule of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway, the dynamic regulatory mechanism of XBP1 continuously provides new theoretical perspectives for the research of metabolic diseases, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
Structure of XBP1
XBP1 is a key transcription factor with a molecular weight of approximately 34 kDa. This protein belongs to the basic leucine zipper protein family, and its molecular weight varies among different splicing isomers.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 34 | 33.8 | 33.9 | 32.5 | 34.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains the basic leucine zipper domain | 83% homologous to humans | Conserved DNA binding domain | Has the similar stress response function | Highly similar to human protein |
The XBP1 protein contains 261 amino acids, and its basic structure includes the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain, the central DNA binding domain, and the C-terminal leucine zipper dimerization interface. The uniqueness of this protein lies in the atypical splicing mechanism of its mRNA mediated by IRE1α - cutting off 26 nucleotides causes the reading frame to shift, generating an active isomer composed of 376 amino acids. The C-terminal structure of the protein undergoes significant changes after splicing, forming a stable transcriptional activation conformation that can specifically bind to the DNA sequence of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response element UPRE.
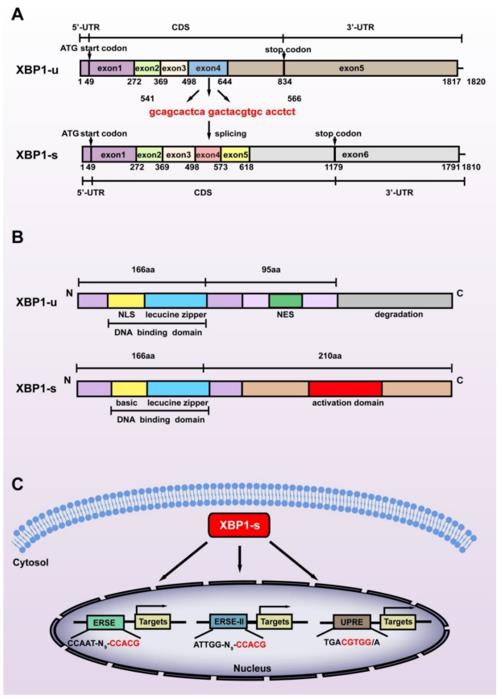 Fig. 1 Structural differences between the two splicing isoforms of XBP1.1
Fig. 1 Structural differences between the two splicing isoforms of XBP1.1
Key structural properties of XBP1:
- Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) DNA binding domain
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing activation domain
- Atypical mRNA splicing sites (26-nucleotide characteristic sequences)
- The dimerization interface at the C-end is regulated to determine the location signal
Functions of XBP1
The core function of the XBP1 gene is to regulate the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. However, this gene is also involved in a variety of cellular processes, including immune differentiation, metabolic regulation and cell fate determination.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of unfolded protein responses | As a core transcription factor of UPR, it activates the expression of genes related to molecular chaperones and endoplasmic reticulum degradation. |
| Differentiation of immune cells | Regulate plasma cell differentiation and antibody secretion, providing a molecular basis for humoral immune response. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | By regulating lipid synthesis and autophagy pathways, it affects liver metabolism and insulin sensitivity. |
| Cell survival/apoptosis determination | Under the condition of continuous endoplasmic reticulum stress, the dynamic transition from survival-promoting to apoptosis-promoting signaling pathways. |
| Regulation of inflammatory response | Through interaction with NF-κB and other signaling pathways, it is involved in the occurrence and development of chronic inflammation and related diseases. |
The activity of XBP1 is precisely regulated by its unique mRNA splicing mechanism - IRE1α -mediated atypical splicing removes 26 nucleotides, causing the coding box to shift and generating a stable transcriptional active form. This molecular switching property enables it to rapidly respond to changes in intracellular homeostasis and perform fine regulation.
Applications of XBP1 and XBP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhao, Yahui, et al. "XBP1 regulates the protumoral function of tumor-associated macrophages in human colorectal cancer." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 6.1 (2021): 357. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00761-7
The article indicates that in colorectal cancer, the activation of macrophage XBP1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis. It inhibits the phagocytic function of macrophages by up-regulating cancer-promoting factors such as IL-6 and enhancing "don't eat me" signals such as SIRPα. Targeting XBP1 can reshape macrophage activity, providing a new therapeutic strategy.
2. Lv, Wenhao, et al. "The Role of XBP1 in bone metabolism." Frontiers in Endocrinology 14 (2023): 1217579. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1217579
The article indicates that the transcription factor XBP1 is a key molecule regulating bone metabolism. It plays a significant role in bone diseases such as osteoporosis by influencing the differentiation and function of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, and regulating the intervention of immune cells in the bone remodeling microenvironment. Targeting XBP1 may offer new ideas for the treatment of bone metabolism diseases.
3. Luo X, Alfason L, et al. "Spliced or unspliced, that is the question: the biological roles of XBP1 isoforms in pathophysiology." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.5 (2022): 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052746
The article indicates that XBP1 is a key factor in endoplasmic reticulum stress, and its spliceosome XBP1-S regulates unfolded protein responses and participates in tumor progression. Its unspliced body XBP1-u is equally important and can affect autophagy and tumorigenesis through post-translational regulation. Abnormal functions of both are closely related to a variety of diseases.
4. Qu X, Li H, Hongyan Li, and Lingzhao Meng. "XBP1 regulates the transcription of HIF‐1a in BALB/c mice with chronic Rhinosinusitis without polyps." Analytical Cellular Pathology 2022.1 (2022): 3066456. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3066456
The article indicates that in chronic sinusitis (non-polypoid type), the expression of XBP1 is significantly elevated. Studies have revealed that XBP1 activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by raising or lowering the oxygen-inducible factor HIF-1α, thereby driving nasal mucosal inflammation and tissue remodeling. Targeting XBP1 may offer a new direction for the treatment of this disease.
5. Salimi, Azam, et al. "XBP1 promotes NRASG12D pre‐B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia through IL‐7 receptor signalling and provides a therapeutic vulnerability for oncogenic RAS." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 27.21 (2023): 3363-3377. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17904
The article indicates that in RAS mutant precursor B-cell leukemia, XBP1 is a key downstream factor of IL-7 receptor signaling and maintains the survival and growth of cancer cells by regulating JAK1/STAT5. Targeting XBP1 not only induces apoptosis of cancer cells but also can be combined with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235, providing a new strategy for the treatment of this type of leukemia.
Creative Biolabs: XBP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality XBP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom XBP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our XBP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Luo X, Alfason L, et al. "Spliced or unspliced, that is the question: the biological roles of XBP1 isoforms in pathophysiology." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.5 (2022): 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052746
Anti-XBP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261270) (CBMAB-C0813-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






