AAV9 Antibodies
Background
AAV9 belongs to adeno-associated virus serotype 9 and is a non-pathogenic single-stranded DNA virus widely used in the field of gene therapy. Its capsid structure has the ability to efficiently cross the vascular barrier and can specifically target tissues such as myocardial muscle, skeletal muscle and the central nervous system. This virus was first isolated and identified through directed evolution technology in 2005. Its prominent feature that distinguishes it from other serotypes is its ability to achieve systemic delivery across the blood-brain barrier. This breakthrough discovery directly promoted the development of gene drugs for neurological diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy. Due to its stable long-term expression characteristics and low immunogenicity, the AAV9 vector has become one of the most clinically valuable viral vectors in the research of genetic disease treatment. The optimization research of related vectors continuously promotes the development of precision medical technology.
Structure of AAV9
AAV9 is a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector, with a capsid protein molecular weight of approximately 73 kDa. This capsid is composed of three subunits VP1/2/3. The molecular weight differences among different serotypes mainly result from the specificity of the spatial conformation of the capsid protein.
| Serotype | AAV2 | AAV8 | AAV9 | AAV-DJ | AAV-Rh74 |
| Capsid particle size (nm) | 22-26 | 25-28 | 25-28 | 24-27 | 26-29 |
| Structural features | Classic model | Enhanced hepatic tropism | The blood-brain barrier is penetrated | Chimeric optimization type | Primate specific |
The AAV9 capsid is composed of approximately 60 VP protein subunits, forming a three-dimensional icosahedral structure, with 9 unique protruding domains on its surface. These protrusions are composed of the GH ring region of the VP1 protein, containing receptor-binding epitopes, among which the circular region formed by the amino acids at positions 458-492 directly mediates cell transmembrane action. The basic amino acid clusters inside the capsid are responsible for genomic packaging, while the distribution of charged amino acids on the surface determines its characteristics and tissue orientation in crossing the blood-brain barrier.
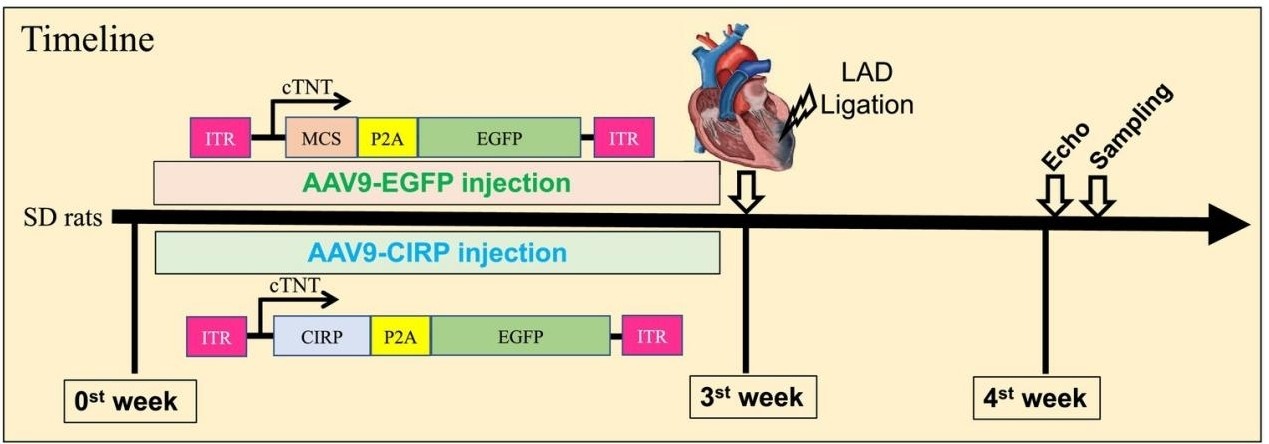 Fig. 1 AAV9 Gene Delivery Prior to Myocardial Infarction.1
Fig. 1 AAV9 Gene Delivery Prior to Myocardial Infarction.1
Key structural properties of AAV9:
- Unencapsulated icosahedral protein capsid
- Distinctive protrusion domains on the surface
- Mediated cells in film and the target function
- Single-strand DNA genome packaging within the capsid
Functions of AAV9
The main function of AAV9 is to serve as an efficient delivery vector for gene therapy. In addition, it has also participated in and inspired a variety of advanced genetic manipulation strategies.
| Function | Description |
| Gene delivery | Through its capsid structure, it mediates cell infection and effectively introduces therapeutic genes into target cells. |
| In vivo transduction | Achieving long-lasting gene expression in living animals is particularly adept at penetrating the blood-brain barrier to target the central nervous system. |
| Tissue targeting | The unique domains on its capsid surface endow it with a natural affinity for tissues such as the heart muscle, skeletal muscle and liver. |
| Immune regulation | Compared with other serotypes, AAV9 can trigger relatively mild host immune responses in some cases, which is beneficial for long-term efficacy. |
| Therapeutic application | As the core carrier of approved drugs such as Zolgensma, it offers hope for a radical cure for genetic diseases like spinal muscular atrophy. |
The transduction characteristics of AAV9 exhibit broad tissue tropism. Its capsid structure interacts with various cell surface receptors, which enables it to efficiently infect target organs even after systemic administration and makes it one of the most widely used vectors in in vivo gene therapy.
Applications of AAV9 and AAV9 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhong, Peng, et al. "AAV9‐mediated CIRP gene transfer protects against cardiac dysfunction and remodelling in a rat model of myocardial infarction." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 28.19 (2024): e70084. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70084
This study mediated the overexpression of cold-induced RNA-binding protein (CIRP) in the heart through AAV9 and found that it could improve the cardiac function of rats with myocardial infarction, inhibit cardiac inflammatory responses and adverse remodeling, indicating that CIRP has a protective effect on the heart.
2. Abeliovich, Asa, Franz Hefti, and Jeffrey Sevigny. "Gene therapy for Parkinson's disease associated with GBA1 mutations." Journal of Parkinson's Disease 11.s2 (2021): S183-S188. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-212739
This study, through the AAV9 gene therapy PR001, aims to deliver the functional GBA1 gene to the brain to restore the activity of glucocerebellase, thereby slowing down the disease progression of GBA1-mutated Parkinson's disease. It is currently in the clinical trial stage.
3. Danquah, Bright D., et al. "Mass Spectrometric analysis of antibody—Epitope peptide complex dissociation: Theoretical concept and practical procedure of binding strength characterization." Molecules 25.20 (2020): 4776. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI146286
In this study, through intrathecal injection of AAV9 gene therapy, the MFSD8 gene can be effectively delivered, significantly improving the pathological characteristics and behavioral defects of CLN7 disease mouse models and prolonging their lifespan. Preclinical studies have confirmed that this therapy is safe and effective.
4. Huang, Pianpian, et al. "Redd1 knockdown prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiac senescence." Aging (Albany NY) 13.10 (2021): 13788. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202972
Research has found that Redd1 protein promotes the aging of myocardial cells. In vivo experiments, the delivery of shRNA using the AAV9 vector to knock down Redd1 could significantly alleviate doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction and aging-related phenotypes in mice.
5. Bozoglu, Tarik, et al. "Endothelial retargeting of AAV9 in vivo." Advanced Science 9.7 (2022): 2103867. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202103867
In this study, the G2CNN-modified AAV9 vector was successfully used to achieve efficient targeted gene transduction on vascular endothelial cells in mice and pigs. This carrier can respectively mediate the specific adhesion of white blood cells, anti-inflammation and blood pressure regulation, providing a new tool for the research of vascular diseases and atherosclerosis.
Creative Biolabs: AAV9 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality AAV9 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom AAV9 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our AAV9 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhong, Peng, et al. "AAV9‐mediated CIRP gene transfer protects against cardiac dysfunction and remodelling in a rat model of myocardial infarction." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 28.19 (2024): e70084. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70084
Anti-AAV9 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








