Adipokine Antibodies
Background
Adipokine is a type of multifunctional cytokine mainly secreted by adipose tissue, which is widely involved in physiological processes such as energy metabolism, inflammatory response and immune regulation. This type of protein acts on multiple target organs through autocrine, paracrine and endocrine mechanisms, coordinating the metabolic homeostasis and pathophysiological changes of the body. Leptin, as the first discovered adipokine, was identified by Jeffrey Friedman's team in 1994. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure revealed the important function of adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. The related research was recognized by the Shaw Prize in 2020. The complex mechanism of action of the Adipokine family continuously provides a key molecular basis for the research of metabolic diseases (such as diabetes and atherosclerosis), significantly promoting theoretical innovation and clinical translational research on metabolic regulatory networks.
Structure of Adipokine
Adipokines are a type of signaling protein secreted by adipocytes, with a wide molecular weight range, approximately from 4 kDa (such as leptin) to 30 kDa (such as Adiponectin), and the specific size varies by subtype and species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 16 (Leptin) | 16 (Leptin) | 16 (Leptin) |
| 30 (Adiponectin) | 30 (Adiponectin) | 30 (Adiponectin) | |
| Primary Structural Differences | Signaling peptides form dimers or polymers | Similar high homologous to human and activity | Amino acid sequences have species specificity |
This type of protein usually has a typical secretory protein structure, including signal peptide sequences and variable functional domains (such as the helical bundle structure of leptin), and exerts biological functions by forming homologous or heterologous polymers. Its activity depends on a complex spatial conformation, which can specifically bind to various cell membrane receptors and regulate physiological processes such as energy metabolism, inflammation and insulin sensitivity.
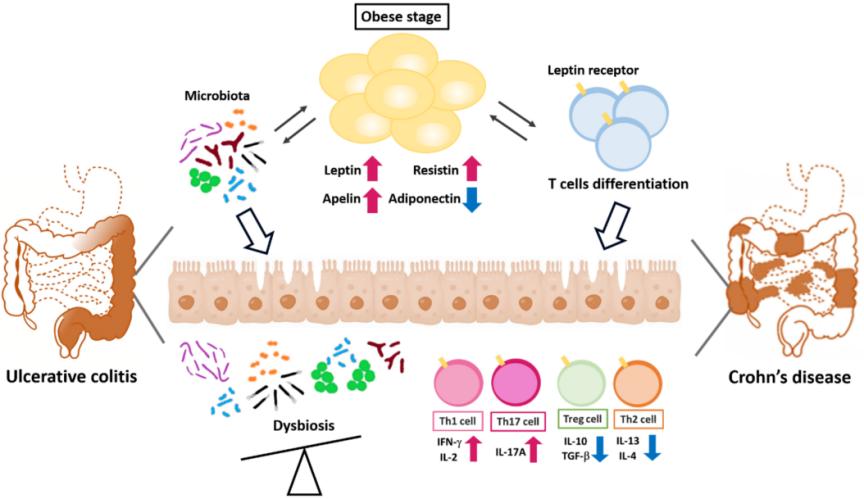 Fig. 1 Adipokines regulate the polarity of T helper cells in adipose tissue and colons.1
Fig. 1 Adipokines regulate the polarity of T helper cells in adipose tissue and colons.1
Key structural properties of Adipokine:
- Most are secretory polypeptides or proteins
- Structural diversity, containing globular, fibrous or complex polymer such as different space configurations
- Specific functional domains (such as receptor-binding domains) mediate intercellular communication
Functions of Adipokine
The main function of Adipokine is to act as a signaling molecule secreted by adipose tissue, coordinating energy metabolism throughout the body and immune inflammatory responses. However, they are also widely involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including insulin sensitivity regulation and cardiovascular function regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of energy metabolism | Regulating appetite, glycolipid metabolism and energy balance, such as leptin suppressing appetite and adiponectin enhancing insulin sensitivity. |
| Inflammatory immune regulation | Promote or inhibit inflammatory responses, such as TNF-α induced inflammation, while adiponectin has anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Insulin signaling regulation | Affect organizational response to insulin, participate in the development of the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. |
| Regulation of vascular function | Some adipokines can regulate vascular endothelial function and affect the progression of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. |
| Cell proliferation and differentiation | Involved in fat cell generation, angiogenesis and so on process, there is a close connection is associated with obesity and cancer. |
The function of Adipokine is usually achieved through autocrine, paracrine and endocrine mechanisms. Multiple factors form a complex network to jointly maintain metabolic homeostasis. Its functional disorders are closely related to metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
Applications of Adipokine and Adipokine Antibody in Literature
1. Tsai, Yi-Wen, et al. "Adipokine-modulated immunological homeostasis shapes the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.24 (2020): 9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249564
This article reviews the role of adipokines (such as adiponectin, leptin, etc.) in the immune regulation of inflammatory colon diseases, explores the mechanism by which they participate in the occurrence and development of the disease by influencing innate and adaptive immune cells, and provides new insights for related treatment strategies.
2. Carrión, Mar, et al. "The adipokine network in rheumatic joint diseases." International journal of molecular sciences 20.17 (2019): 4091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174091
The article indicates that adipokines (such as adiponectin, leptin, etc.) act as immunomodulatory mediators, secreted by adipocytes and articular cells, and are involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. They influence disease progression by regulating local and systemic inflammation, providing a new direction for treatment.
3. Mangion, Darren, Nikolai P. Pace, and Melissa M. Formosa. "The relationship between adipokine levels and bone mass—A systematic review." Endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism 6.3 (2023): e408. https://doi.org/10.1002/edm2.408
The article indicates that adipokines (such as adiponectin and leptin) are closely related to changes in bone density. Adiponectin levels are associated with decreased bone density, while leptin may have a protective effect. Existing studies show significant heterogeneity, and the results are influenced by multiple factors. Longitudinal studies need to be conducted in the future to clarify the causal relationship.
4. Goralski, Kerry B., et al. "More than an adipokine: the complex roles of chemerin signaling in cancer." International journal of molecular sciences 20.19 (2019): 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194778
The article indicates that the adipokine Chemerin has a complex role in cancer: it can accelerate tumor progression by promoting migration, proliferation and angiogenesis, and also inhibit tumors through immune regulation. Its specific effects depend on the receptor signaling pathway and may become a potential target for cancer treatment.
5. Lee, Seoyul, et al. "Effect of adipokine and ghrelin levels on BMD and fracture risk: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis." Frontiers in Endocrinology 14 (2023): 1044039. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1044039
The article indicates that adipokines (such as leptin and adiponectin) are associated with bone mineral density and fracture risk: leptin is positively correlated with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women and reduces the risk of fractures, while adiponectin is negatively correlated with bone mineral density and increases the risk of fractures, and can be used as a predictor of osteoporosis.
Creative Biolabs: Adipokine Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality Adipokine antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom Adipokine Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our Adipokine antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Tsai, Yi-Wen, et al. "Adipokine-modulated immunological homeostasis shapes the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.24 (2020): 9564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249564
Anti-Adipokine antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






