APOA1 Antibodies
Background
APOA1 gene encoding apolipoprotein A1, is the core of the human body high-density lipoprotein (HDL) composition. This protein plays a key role in the reverse transport of cholesterol. It can combine with phospholipids and cholesterol to form complexes, transporting excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver for metabolism, thereby maintaining lipid homeostasis and having anti-atherosclerotic functions. Since its discovery in the 1970s, APOA1 has not only been an important biomarker for cardiovascular disease research, but its tertiary structure analysis has also revealed the molecular mechanism of the interaction between apolipoproteins and lipids. Synthetic peptide mimics developed based on their functions have become a new direction in cardiovascular drug research and development, continuously driving in-depth studies on lipid metabolism and the treatment of related diseases.
Structure of APOA1
APOA1 is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 28.3 kDa, and its molecular weight varies slightly among different species. This protein is composed of 243 amino acids and has a typical apolipoprotein structure, forming an amphiphilic α -helix that enables it to bind and transport lipids. APOA1 is a major structural component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and plays a core role in cholesterol reverse transport and cardiovascular protection.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 28.3 | 28.1 | 28.0 | 28.2 | 28.4 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 6 to 8 amphipathic α-helices | 83% homology with humans | 80% homology with humans | Unique C-end structure | Highly conservative helical structure |
APOA1 combines with phospholipids through its amphiphilic α -helical structure to form disc-shaped HDL particles. Its N-terminal domain is responsible for lipid binding, while the C-terminal domain mediates protein interactions. The α -helix formed by amino acids at positions 44-65 and 66-87 is particularly crucial for the efflux function of cholesterol. Multiple regions of proteins contain characteristic repeat sequences of apolipoproteins, which maintain the stability of lipoprotein particles through hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces.
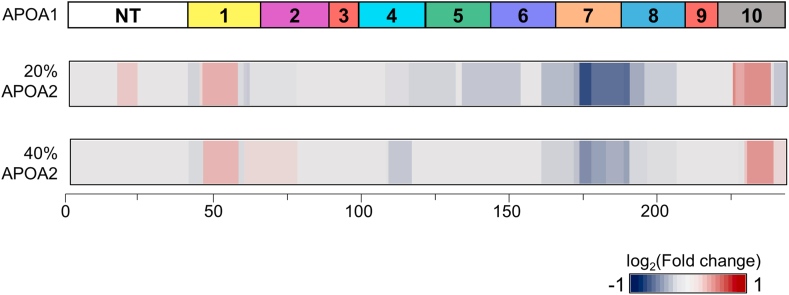 Fig. 1 Structural changes in APOA1 in the presence of exogenous APOA2.1
Fig. 1 Structural changes in APOA1 in the presence of exogenous APOA2.1
Key structural properties of APOA1:
- Amphiphilic α-helical structure
- Can bind to lipids to form a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) complex
- With cholesterol combining with domain
Functions of APOA1
The main function of the APOA1 gene is to mediate the reverse transport of cholesterol and participate in the assembly of high-density lipoprotein (HDL). It is also involved in a variety of physiological processes, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and endothelial protection functions.
| Function | Description |
| Reverse transport of cholesterol | As a core component of HDL, it transports cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver for metabolism and resists atherosclerosis. |
| Lipoprotein assembly | Combined with phospholipid form new HDL particles, promote the dissolution of lipid and transport. |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | Inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors in endothelial cells and alleviate vascular inflammatory responses. |
| Antioxidant protection | Prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and reduce the formation of foam cells. |
| Improvement of endothelial function | Promote the production of nitric oxide (NO), improve vascular dilation function, and protect the vascular endothelial barrier. |
APOA1 achieves lipid binding and transport functions through its amphiphilic α-helical structure. Its binding to cholesterol has high affinity and specificity, which is of great clinical significance in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Applications of APOA1 and APOA1 Antibody in Literature
1. Liu, Zhenzhen, et al. "APOA1 is a novel marker for preeclampsia." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.22 (2023): 16363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216363
This study explored the role of apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia (PE). Research has found that the plasma APOA1 level in patients with PE increases in the late stage of pregnancy and is positively correlated with systolic blood pressure. APOA1 can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells, and this effect may be achieved through the PPARγ signaling pathway, suggesting that APOA1 may become a new target for the prevention and treatment of PE.
2. He, Yi, et al. "Flipped C-terminal ends of APOA1 promote ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux by small HDLs." Circulation 149.10 (2024): 774-787. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065959
Research has found that the C-terminal structure of apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) in small and dense high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles is more likely to detach from the lipid surface, thereby enhancing its ability to reverse cholesterol transport mediated by the ABCA1 pathway. This mechanism has been verified in both LCAT-deficient patients and model systems, suggesting that small-sized HDL particles and their conformational changes in APOA1 play an important role in cardiovascular protection.
3. Zeng, Wei, et al. "APOA1 mRNA and protein in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma correlate with the disease outcome." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 12406. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16434-6
This study explored the clinical significance of apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (KIRC). Studies have found that the mRNA and protein expressions of APOA1 in KIRC tissues and serum are significantly decreased, and the low expression is associated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival of patients. The expression of APOA1 is also negatively correlated with immune cell infiltration and PD-L1, suggesting that it may serve as a novel prognostic indicator for KIRC.
4. He, Yue, et al. "Role of APOA1 in the resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy in squamous cervical cancer." BMC cancer 22.1 (2022): 411. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09528-x
This study explored the mechanism by which apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) enhances platinum-based chemotherapy resistance in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Experiments have found that overexpression of APOA1 can significantly enhance the resistance of cells to carboplatin. Sixty-four differentially expressed proteins were screened out by mass spectrometry analysis, and it was preliminarily revealed that they might promote platinum resistance through multiple pathways such as STAT1/p38 MAPK, CD81/C3/PI3K and TOP2A.
5. Ghaemi, Farzaneh, et al. "ApoA1/HDL-C ratio as a predictor for coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a matched case-control study." BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 24.1 (2024): 317. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-024-03986-w
This study explored the relationship between the ratio of apolipoprotein A1/ high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (ApoA1/HDL-C) and coronary heart disease (CAD) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). The results showed that the ApoA1/HDL-C ratio of CAD patients was significantly increased, and the higher this ratio was, the greater the risk of CAD (OR=3.41). When the ratio is ≥2.66, it can effectively predict CAD (AUC=0.885), suggesting its potential as an indicator for coronary heart disease risk assessment in patients with T2D.
Creative Biolabs: APOA1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality APOA1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom APOA1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our APOA1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Sarkar, Snigdha, et al. "APOA2 increases cholesterol efflux capacity to plasma HDL by displacing the C-terminus of resident APOA1." Journal of Lipid Research 65.12 (2024): 100686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100686
Anti-APOA1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCND2 Recombinant Antibody (DCS-3) (CBMAB-G1318-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






