BMP2 Antibodies
Background
BMP2 is an important member of the transforming growth factor -β (TGF-β) superfamily, mainly involved in bone formation and embryonic development processes. This protein binds to cell surface receptors in the form of dimers, activates the downstream SMAD signaling pathway, and thereby regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone matrix formation. Clinically, BMP2 has been approved for bone regeneration treatments such as spinal fusion and fracture repair. As the first growth factor drug to pass the FDA certification, BMP2 was approved for marketing in 2002. Its unique structural and functional mechanisms provide important models for the study of cell signal transduction, tissue regeneration and developmental biology, and have significant value in both basic research and clinical application fields.
Structure of BMP2
BMP2 is a dimer glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 30-38kDa. This protein shows high conservation among different species, but there are subtle differences.
| Species | Human | Mice | Bovine | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 38 | 36 | 37 | 32 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conservative sequence | Glycosylation sites are different | Active area highly conservative | Early evolutionary homologues |
BMP2 is composed of approximately 400 amino acids and forms a characteristic "cysteine junction" structure through disulfide bonds. Its three-dimensional structure contains a core domain composed of 7 β -folded sheets and 1 α -helix. Similar to myoglobin, BMP2 also maintains its biological activity through specific structural features (such as the hydrophobic core formed by β -folding), but its functional mechanism is more complex, involving the dimerization of cell surface receptors to activate the SMAD signaling pathway. This structure-function relationship makes it an important target for bone regeneration therapy.
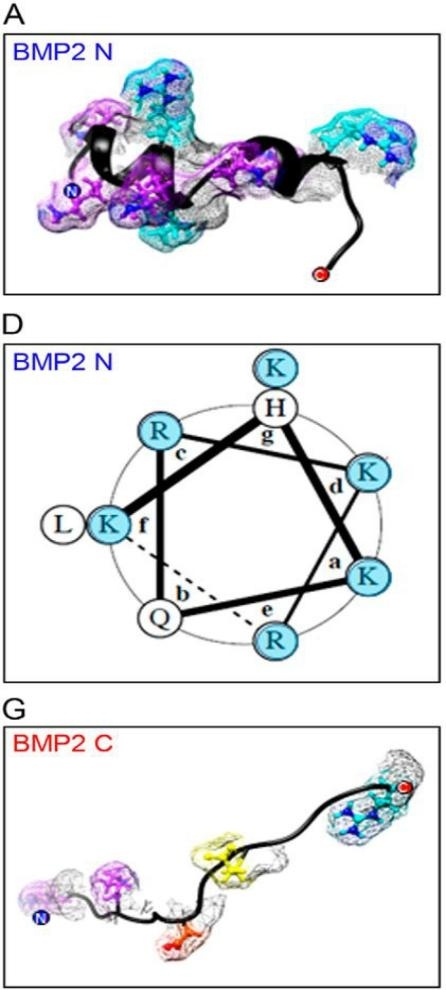 Fig. 1 Structural basis of BMP2 N-terminal electropositive helix for HS binding.1
Fig. 1 Structural basis of BMP2 N-terminal electropositive helix for HS binding.1
Key structural properties of BMP2:
- Receptor binding region (β4-β5 ring)
- Heparin binding site (N-terminal basic region)
- Dimerization interface (cysteine residue)
Functions of BMP2
The core function of BMP2 is to regulate bone development and tissue regeneration, and it plays an important role in various physiological and pathological processes at the same time.
| Function | Description |
| Bone formation | Induce mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into osteoblasts and promote bone matrix mineralization (clinically applied in spinal fusion surgery). |
| Embryo development | Regulate the formation of mesoderm tissues and affect the development process of organs such as the heart and kidneys. |
| Cartilage metabolism | Involved in chondrocyte differentiation and joint maintenance through the SOX9 pathway. |
| Damage repair | In express high fracture, activate the SMAD pathway promote callus formation. |
| Tumorigenesis | Abnormal expression is associated with the progression of tumors such as osteosarcoma and prostate cancer. |
The signal activation of BMP2 shows a typical "all or none" feature (different from the gradient response of other members of the TGF-β family), and its dose-effect curve is steep S-shaped, indicating the existence of a co-receptor activation mechanism. This characteristic makes it necessary to precisely control the concentration in clinical applications to avoid side effects such as ectopic ossification.
Applications of BMP2 and BMP2 Antibody in Literature
1. Valera, Elvira, et al. "BMP-2/6 heterodimer is more effective than BMP-2 or BMP-6 homodimers as inductor of differentiation of human embryonic stem cells." PloS one 5.6 (2010): e11167. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011167
The article indicates that BMP-2/6 heterodimer can more effectively induce the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into trophoblast and endodermal cells than BMP-2 or BMP-6 homologous dimer, significantly up-regulate the expression of markers such as CDX2 and SOX17, and more strongly activate Smad and non-Smad signaling pathways.
2. Le Page, Cécile, et al. "BMP-2 signaling in ovarian cancer and its association with poor prognosis." Journal of ovarian research 2 (2009): 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-2215-2-4
The article indicates that BMP-2 is overexpressed in ovarian cancer cells, promoting cancer cell migration and inhibiting intercellular adhesion by activating the Smad1/5/8 and ERK signaling pathways, and its expression level is negatively correlated with the survival rate of patients.
3. Feng, Peng-Cheng, et al. "BMP2 secretion from hepatocellular carcinoma cell HepG2 enhances angiogenesis and tumor growth in endothelial cells via activation of the MAPK/p38 signaling pathway." Stem cell research & therapy 10 (2019): 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1301-2
The article indicates that BMP2 is highly expressed in liver cancer and promotes tumor proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis by activating the MAPK/p38 signaling pathway. Inhibiting BMP2 can block this pathway and slow down the progression of liver cancer.
4. Blaney Davidson, Esmeralda N., et al. "Elevated extracellular matrix production and degradation upon bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) stimulation point toward a role for BMP-2 in cartilage repair and remodeling." Arthritis research & therapy 9 (2007): 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2305
The article indicates that BMP-2 promotes cartilage repair by stimulating proteoglycan synthesis and collagen expression, while increasing the activity of matrix-degrading enzymes. In the IL-1 injury model, BMP-2 can enhance the self-repair ability of cartilage, indicating that it has a dual regulatory effect.
5. Hauff, Kristin, et al. "Matrix-immobilized BMP-2 on microcontact printed fibronectin as an in vitro tool to study BMP-mediated signaling and cell migration." Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 3 (2015): 62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2015.00062
The article indicates that by immobilizing BMP-2 on cellular fibronectin (cFN), the study confirmed that immobilized BMP-2(iBMP-2) and soluble BMP-2(sBMP-2) can both activate the Smad1/5 signaling pathway, inhibit the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts, and promote cell migration. This strategy provides a new method for studying the signal transduction of growth factors.
Creative Biolabs: BMP2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality BMP2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom BMP2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our BMP2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference
- Billings, Paul C., et al. "Domains with highest heparan sulfate–binding affinity reside at opposite ends in BMP2/4 versus BMP5/6/7: Implications for function." Journal of Biological Chemistry 293.37 (2018): 14371-14383. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.003191
Anti-BMP2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






