FGF2 Antibodies
Background
FGF2 is a widely expressed multifunctional cell growth factor protein, mainly distributed in the extracellular matrix and vascular tissues. The protein encoded by this gene binds to the fibroblast growth factor receptor and activates signaling pathways to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and migration processes, especially playing a core role in embryonic development and tissue repair. In 1974, researcher Stanley Cohen first isolated FGF2 from the pituitary gland of cattle. Its unique heparin binding property made it the first discovered member of the fibroblast growth factor family. The double-stranded polypeptide expressed by this gene has the molecular characteristics of multi-promoter regulation. The study of its structure and function has greatly advanced the development of our cognitive system in the fields of growth factor signal transduction, angiogenesis mechanism, and tumor biology.
Structure of FGF2
FGF2 is a multifunctional protein with a molecular weight of approximately 17-25 kDa. Its specific weight varies due to subtype selection and species differences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 18-25 | 17-18 | 17-18 | 17-18 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Multiple high/low molecular weight isoforms exist | Highly homologous to humans | Highly conserved amino acid sequence | Similar to the sequence of mammals |
This protein is composed of 155 amino acids (based on common subtypes) and presents a typical β -clover-shaped spatial conformation. Its three-dimensional structure contains 12 β -folds, which are connected through variable ring regions to form a functional interface for binding to the receptor. The heparin-binding domain on the surface of proteins is crucial for their binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans, and this characteristic directly affects their biological activity and stability. The active center is composed of a conserved core formed by β -folding, among which the lysine residues at positions 54 and 134 play a crucial role in maintaining its mitogenic function.
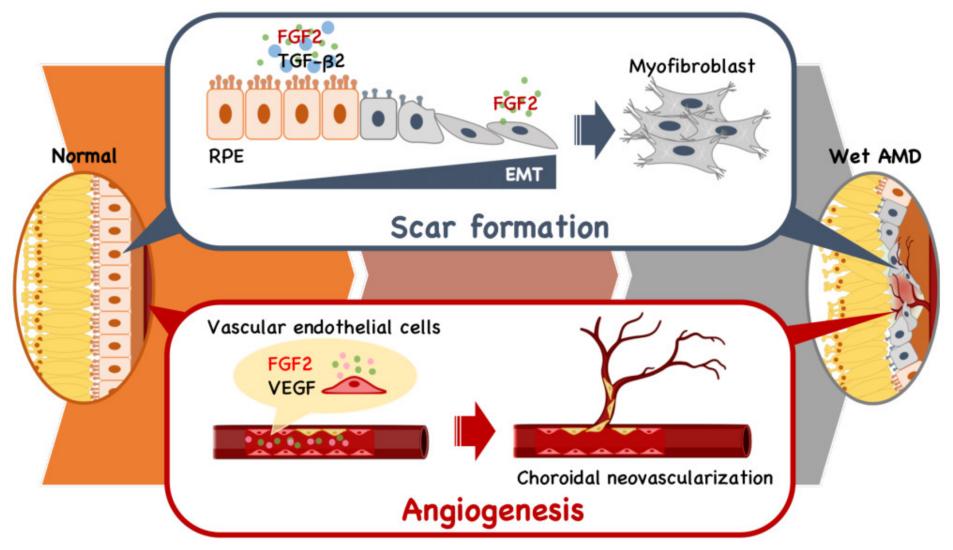 Fig. 1 FGF2's Dual Role in Retinal Angiogenesis and Fibrosis.1
Fig. 1 FGF2's Dual Role in Retinal Angiogenesis and Fibrosis.1
Key structural properties of FGF2:
- The classical β-clover shaped 3D structure is used
- Heparin binding domains are distributed on the surface to anchor the extracellular matrix
- Contains receptor binding sites that specifically activate the FGFR signaling pathway
Functions of FGF2
The main function of FGF2 is to promote cell proliferation and tissue repair, while also participating in various physiological and pathological processes such as angiogenesis and embryonic development.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of cell proliferation | By activating MAPK signaling pathways such as direct stimulation of fibroblasts, endothelial cells and other cell division and proliferation. |
| Angiogenesis induction | As an effective angiogenic factor, it induces endothelial cell migration and tubular structure formation, and establishes a neovascular network. |
| Regulation of tissue repair | Coordinate multiple repair stages such as inflammatory response, granulation tissue formation and matrix remodeling during the wound healing process. |
| Neuroprotective effect | Promote neuron survival and axon growth and neural differentiation, has important function on the central nervous system damage. |
| Embryonic development participation | In the mesoderm induction, physical development and organ formation, and many other morphogenesis, embryonic development stage play a key role. |
The signal activation of FGF2 strictly depends on its specific binding to the tyrosine kinase receptor (FGFR) on the cell surface. This characteristic endows its function with pleiotropy and it is widely involved in multiple research fields ranging from developmental biology to regenerative medicine.
Applications of FGF2 and FGF2 Antibody in Literature
1. Tan, Yuan-Yang, et al. "FGF2 is overexpressed in asthma and promotes airway inflammation through the FGFR/MAPK/NF-κB pathway in airway epithelial cells." Military Medical Research 9.1 (2022): 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-022-00366-3
This study found that the expression of FGF2 was significantly upregulated in asthma patients and model mice, and was positively correlated with IgE levels. Exogenous FGF2 can aggravate airway inflammatory cell infiltration and promote the release of IL-6/IL-8 by human lung epithelial cells through the FGFR/MAPK/NF-κB pathway, revealing that FGF2 is a potential inflammatory regulatory factor in asthma.
2. Chen, Fanfeng, et al. "FGF2 alleviates microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury by KLF2-mediated ferroptosis inhibition and antioxidant responses." International Journal of Biological Sciences 19.13 (2023): 4340. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.85692
Research has found that FGF2 upregulates KLF2 expression by activating the AMPK-HDAC5 signaling pathway in acute limb ischemia-reperfusion injury, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis and oxidative stress in microvascular endothelial cells, ultimately exerting a protective effect and reducing tissue damage.
3. Nakamura, Yoshikazu. "Multiple therapeutic applications of RBM-007, an anti-FGF2 aptamer." Cells 10.7 (2021): 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071617
Research has found that FGF2 is an important pro-angiogenic factor and plays a positive role in tissue repair and bone health. The inhibitor of FGF2, RBM-007, has completed preclinical research and is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration and achondroplasia. It also shows potential in fields such as lung cancer.
4. Wang, Rongli, et al. "FGF2 is protective towards cisplatin-induced KGN cell toxicity by promoting FTO expression and autophagy." Frontiers in Endocrinology 13 (2022): 890623. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.890623
This study reveals that in chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure, FGF2 exerts a protective effect by up-regulating the expression of the obesity-related protein FTO and activating the autophagy process of granulosa cells, thereby inhibiting cell apoptosis and promoting their proliferation.
5. Im, Jae Hong, et al. "FGF2 alters macrophage polarization, tumour immunity and growth and can be targeted during radiotherapy." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 4064. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17914-x
Studies have shown that FGF2 is a key factor regulating the programming of macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. The absence of FGF2 can promote the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages towards pro-inflammatory phenotypes, enhance anti-tumor immunity, and inhibit tumor growth. The combination of radiotherapy and FGF2 blocking antibodies can significantly enhance the therapeutic effect.
Creative Biolabs: FGF2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality FGF2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom FGF2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our FGF2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Nakamura, Yoshikazu. "Multiple therapeutic applications of RBM-007, an anti-FGF2 aptamer." Cells 10.7 (2021): 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071617
Anti-FGF2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5B-9 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYA-0216) (CBMAB-X0304-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








