GNAS Antibodies
Background
GNAS gene encoding the G protein alpha subunit is a core component of G protein signal transduction pathways, mainly distributed in multiple tissues inside of the cell membrane. This protein participates in the synthesis of cAMP second messengers by regulating the activity of adenylate cyclase, thereby influencing key physiological processes such as cell proliferation and differentiation. In mammalian development, the imbalance in the expression of GNAS imprinted genes can lead to skeletal abnormalities and metabolic defects, which are closely related to various genetic diseases in humans. This locus was first located in 1988 through G protein function studies. Its complex alternative splicing and genomic imprinting phenomena have made it a classic model for epigenetic research. The related mechanism research has greatly promoted our understanding of cell signal transduction, imprinted gene regulation and disease occurrence mechanisms.
Structure of GNAS
The G protein α subunit (Gαs) encoded by the GNAS gene is a key signal transduction protein, with a molecular weight of approximately 44.7 kDa. This molecular weight may vary due to different transcripts and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Zebrafish | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 44.7 | 44.8 | 44.6 | 45.1 | 44.7 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Activation of cAMP, maternal mark | Highly homologous to humans, it is used in disease models | Important models for signal transduction research | Functionally conserved in early development | Highly conserved in function in mammals |
This protein contains 394 amino acids and forms its core functional structure through its GTPase domain. The protein structure contains a key GTP binding site, which enables it to switch between active (GTP binding) and inactive (GDP binding) states. Its signal transduction ability precisely stems from this conformational change. GNAS proteins are arranged in a classic alternating α -helix and β -fold pattern, with the Ras domain responsible for GTP hydrolysis and the helical domain involved in the interaction. The key "switch I" and" Switch II" regions undergo conformational rearrangement after GTP binding, thereby exposing their binding interfaces with effectors (such as adenylate cyclase), and ultimately initiating the downstream cAMP signaling pathway.
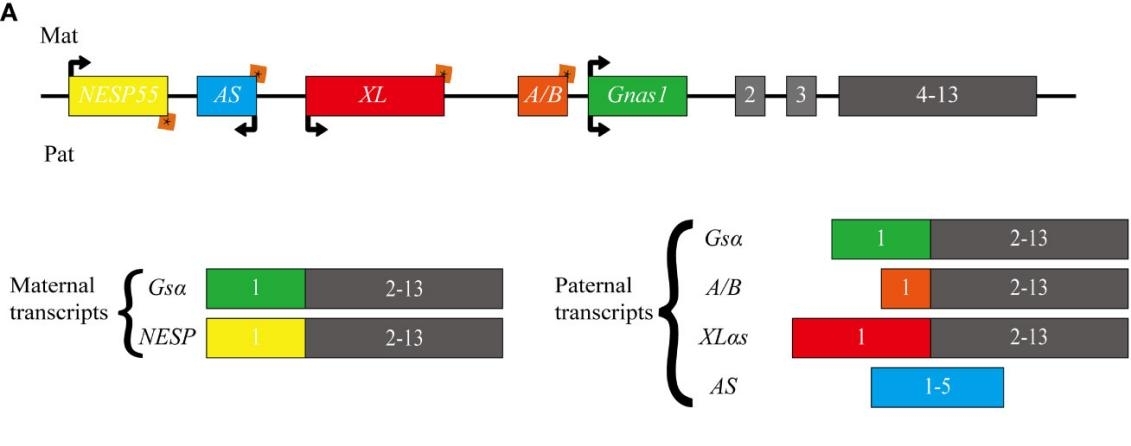 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the human GNAS locus.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the human GNAS locus.1
Key structural properties of GNAS:
- The classic Ras-like domain is chimed with the helical domain
- Three molecular Switch area (the Switch I/II/III) is in charge of conformational changes
- GTP binds the pocket to realize the molecular switch function of signaling
Functions of GNAS
The core function of the GNAS gene-encoded protein (Gαs) is to mediate the cAMP signaling pathway downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRS). In addition, it is also involved in a variety of key cellular physiological processes, including cell proliferation regulation, differentiation determination and hormone response.
| Function | Description |
| cAMP signal activation | After being activated by GPCR, Gαs stimulates adenylate cyclase to synthesize cAMP, which acts as a key second messenger to amplify extracellular signals. |
| Hormone signal transduction | Transducing signals of various hormones (such as adrenaline and thyroid stimulating hormone) to coordinate metabolism and endocrine balance of the body. |
| Regulation of cell proliferation | By regulating the cAMP level to affect gene expression, it bidirectionally regulates cell growth and division. |
| Developmental differentiation determines | During embryonic development, its imprinting expression pattern plays a decisive role in tissue-specific differentiations such as bone formation and energy metabolism. |
| Tumorigenesis association | Gain-of-function mutations, such as R201, consistently activate the cAMP pathway and become a direct driver of various endocrine tumors. |
The signaling activity of Gαs is strictly regulated by its GTP hydrolysis cycle. This "molecular switch" mechanism ensures the instantaneous and controllable nature of the signal, which contrasts sharply with single-function signaling proteins and demonstrates its core integration role in complex cellular communication.
Applications of GNAS and GNAS Antibody in Literature
1. Yang, Wan, et al. "GNAS locus: bone related diseases and mouse models." Frontiers in endocrinology 14 (2023): 1255864. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1255864
The article indicates that GNAS is a gene locus with complex imprinting effects, capable of generating various transcripts such as Gsα and XLas, and regulating physiological activities through multiple signaling pathways. Its mutations are associated with various bone diseases such as fibrous dysplasia and Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. Researchers have used mouse models to deeply explore its mechanism.
2. He, Michael Y., et al. "GNAS knockout potentiates HDAC3 inhibition through viral mimicry-related interferon responses in lymphoma." Leukemia 38.10 (2024): 2210-2224. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-024-02325-4
Studies have shown that the expression level of the GNAS gene is the key to the sensitivity of lymphoma to HDAC3 inhibitors. The absence of GNAS activates the "viral mimics" response, triggering interferon signals and thereby significantly enhancing the tumor's sensitivity to drugs. Therefore, low GNAS expression may serve as a biomarker for predicting the efficacy of HDAC3 inhibitors.
3. Afolabi, Hafeez Abiola, et al. "A GNAS gene mutation's independent expression in the growth of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Cancers 14.22 (2022): 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225480
Studies have shown that GNAS gene mutations are associated with a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. A meta-analysis covering tens of thousands of patients showed that the overall incidence of this mutation in colorectal cancer was 4.8%, among which R201C and R201H were the main mutation types. These mutations are more common in men and advanced tumors and can serve as potential prognostic biomarkers.
4. Cipriano, Lorenzo, et al. "Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of GNAS Gene: Review and Disease Management of a Hotspot Mutation." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.20 (2024): 10913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010913
Studies have shown that the hotspot mutation c.565_568delGACT in the GNAS gene is associated with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia. Research has found that compared with other GNAS mutations, patients with this specific mutation are more likely to present clinical features such as short fingers, round face, intellectual disability and ectopic ossification, suggesting a unique genotype-phenotypic association.
5. Lemos, Manuel C., and Rajesh V. Thakker. "GNAS mutations in Pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a and related disorders." Human mutation 36.1 (2015): 11-19. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22696
Studies have shown that inactivated mutations in the GNAS gene can lead to pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia and related diseases. The mutation types are mainly frameshift mutations. Different genetic sources and mutation types are closely related to complex clinical manifestations such as parathyroid hormone resistance, special body types and ectopic ossification.
Creative Biolabs: GNAS Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GNAS antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GNAS Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GNAS antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yang, Wan, et al. "GNAS locus: bone related diseases and mouse models." Frontiers in endocrinology 14 (2023): 1255864. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1255864
Anti-GNAS antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








