IgG1 Antibodies
Background
IgG1 is a subtype of immunoglobulin G, encoded by the IGHG1 gene on human chromosome 14. As the most abundant antibody type in serum, it specifically recognizes pathogens through the Fab segment of its Y-shaped structure and activates the complement system and mediates macrophage phagocytosis through the Fc segment, thereby playing a core defense role in humoral immunity. Since its first identification by electrophoresis in the 1960s, IgG1 has become the main structural template for monoclonal antibody drugs due to its highly efficient neutralization ability against bacteria/viruses and placental transport characteristics. The research on the flexibility of its hinge region, disulfide bond stability and glycosylation mode has greatly promoted breakthroughs in cancer treatment (such as trastuzumab) and autoimmune disease therapy.
Structure of IgG1
IgG1 is a medium-sized protein with a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa. There are slight differences in its specific weight among different subcategories or species, mainly due to the variations in the length of the hinge region and glycosylation modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 150 | 150 | 149 |
| Primary Structural Differences | The longer hinge area enhances flexibility | The hinge area is relatively short, and flexibility is limited | Highly homologous to humans, it is often used in preclinical research |
The IgG1 molecule is composed of two heavy chains and two light chains connected by disulfide bonds, forming a typical "Y" shaped structure. Its core functional region (the constant region CH2/CH3) mediates key immune effector functions, such as activating the complement system and binding to Fcγ receptors, through conserved glycosylation sites (Asn297). The variable region located at the top of the molecule is responsible for the recognition and binding of specific antigens, forming the structural basis of its immune defense function.
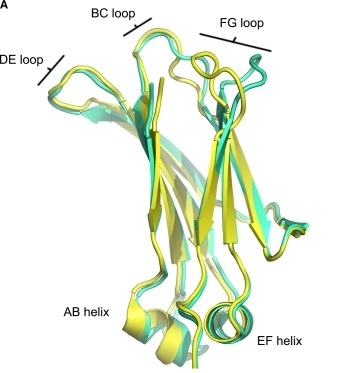 Fig. 1 Overall structure of the IgG1 (yellow) and IgG4 (green) Cγ2 domain.1
Fig. 1 Overall structure of the IgG1 (yellow) and IgG4 (green) Cγ2 domain.1
Key structural properties of IgG1:
- Typical Y symmetric structure, are connected by a disulfide bond heavy chain and light chain
- Hinge regions provide molecular flexibility and influence antigen binding range
- Conserved Fc glycosylation sites (Asn297) mediate immune function
Functions of IgG1
The core function of IgG1 lies in identifying and eliminating specific pathogens, while playing multiple roles in immune regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Pathogen identification and neutralization | Through its antigen binding fragment (Fab) accurately identify viruses, bacteria and other foreign bodies, and directly block their ability to infect cells. |
| Mediated immune effect | Antibody constant region (Fc) can activate the complement system and recruit macrophages, natural killer cells and other cells to clear the target. |
| Immune regulation | Through the interaction of its Fc segment with various Fc receptors, it participates in regulating multiple physiological processes such as inflammatory responses and cellular immune responses. |
| Long-term immune protection | Persist in the body for a long time, provide constant resistance protection for the body, is the primary antibody vaccine excitation type. |
| Passive immunity across the placenta | Is the only can transfer from mother to fetus via the placenta antibody subtypes, provide critical neonatal immune defense line. |
Unlike the multivalent high efficiency demonstrated by IgM in the early stage of anti-infection, IgG1 shows stronger targeting and long-lasting immune efficacy, and is the core executor in the body's adaptive immune response.
Applications of IgG1 and IgG1 Antibody in Literature
1. Sneed, Sunny L., et al. "An engineered immunomodulatory IgG1 Fc suppresses autoimmune inflammation through pathways shared with iv immunoglobulin." The Journal of clinical investigation 134.4 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI172980
The article indicates that the FcF241A mutant of IgG1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects through the SIGN-R1 pathway, and its efficacy does not depend on sialic acid modification, but sialic acid can increase its half-life. This mechanism is the same as that of IVIG and sialacidified Fc, and can synergistically inhibit inflammation with FcAbdeg through different pathways.
2. Yu, Jifeng, Yongping Song, and Wenzhi Tian. "How to select IgG subclasses in developing anti-tumor therapeutic antibodies." Journal of hematology & oncology 13.1 (2020): 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00876-4
The article indicates that in the development of therapeutic anti-tumor antibodies, IgG1 is often chosen as the preferred subtype due to its highest binding affinity for Fcγ receptors and its ability to effectively mediate effector functions such as ADCC and ADCP. When making an actual selection, it is also necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the characteristics of the target, the tumor microenvironment, and the mechanism of drug action.
3. Bhatti, Maryam M., Allen G. Cai, and Jan-Willem Theunissen. "Binding affinities of human IgG1 and chimerized pig and rabbit derivatives to human, pig and rabbit Fc gamma receptor IIIA." Plos one 14.7 (2019): e0219999. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219999
The article indicates that to evaluate the cross-species FcγRIIIA binding of antibodies, chimeric antibodies were constructed in the study. The results showed that the affinity of human IgG1 and rabbit IgG for this receptor in different species was similar and there were interspecific differences, while porcine IgG1 only had significant binding to porcine receptors. These findings provide tools and basis for related pharmacological research.
4. Davies, Anna M., and Brian J. Sutton. "Human IgG4: a structural perspective." Immunological reviews 268.1 (2015): 139-159. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12349
The article indicates that, unlike the highly effective IgG1, IgG4, lacking ADCC and CDC activity, has therapeutic value in scenarios such as blocking allergies, but it may also weaken IGG1-mediated anti-tumor immunity. The latest analysis of the IgG4-Fc crystal structure reveals its unique conformation, providing a new perspective for understanding its interaction with FcγRs.
5. Hui, Gar Kay, et al. "The solution structure of the human IgG2 subclass is distinct from those for human IgG1 and IgG4 providing an explanation for their discrete functions." Journal of Biological Chemistry 294.28 (2019): 10789-10806. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.007134
The article indicates that, unlike the structurally asymmetric IgG1, the study analyzed the monomer solution structure of human IgG2 through scattering techniques, revealing that it presents a symmetrical Y-shaped conformation due to its unique hinge disulfide bond. This stable structure explains the specific binding ability of IgG2 to FcγRII/III and its potential clinical application value.
Creative Biolabs: IgG1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality IgG1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom IgG1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our IgG1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Davies, Anna M., and Brian J. Sutton. "Human IgG4: a structural perspective." Immunological reviews 268.1 (2015): 139-159. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12349
Anti-IgG1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (R63) (CBMAB-C9553-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








