ISG15 Antibodies
Background
ISG15 is a small ubiquitin-like modified protein that is widely present in various cell types of vertebrates. The protein encoded by this gene can participate in key biological processes such as intracellular immune regulation, antiviral response and signal transduction by covalently binding to target proteins. During the process of viral infection, ISG15 can be rapidly induced to express and enhance the host's innate immune defense ability by interfering with viral replication and transmission. This gene was discovered by researchers in interferon-treated cells in 1984 and is the first identified ubiquitin-like modification molecule. Its unique double domain and specific binding mechanism provide an important model for studying post-translational modifications of proteins. The in-depth exploration of the structure and function of ISG15 at present continuously promotes the research progress in fields such as immune response mechanisms and host-pathogen interactions.
Structure of ISG15
Myoglobin is a relatively small protein with a molecular weight of approximately 16.7 kDa. This weight may slightly vary between species due to minor differences in amino acid sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 15.8 | 15.9 | 16.1 | 15.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Consists of 157 amino acids, containing two ubiquitin sample structure domain | High homologous to human ISG15 and C terminal sequence has nuances | The amino acid sequence is relatively conserved | The structure is highly similar to that of mouse ISG15 |
The primary structure of this protein contains two tandem ubiquitin-like domains and covalently binds to the target protein through the LRLRGG sequence at its C-terminal. The tertiary structure of ISG15 forms a compact spherical conformation, and its secondary structure is mainly composed of α -helicles and β -folds. These elements jointly shape the functional surface for its interaction with specific E1/E2/E3 enzyme systems. The glycine residue at the C-terminal is crucial for its conjugated connection with the target protein, while the specific hydrophobic core maintains its structural stability, thereby performing a key function in the interferon-induced immune response.
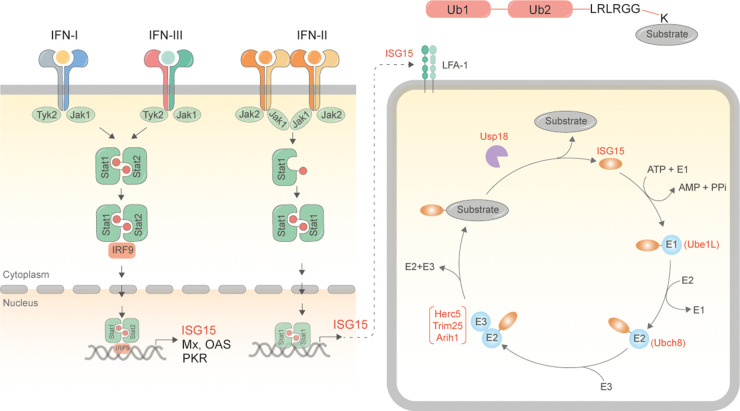 Fig. 1 Schematic for synthesis of ISG15 and ISGylated proteins.1
Fig. 1 Schematic for synthesis of ISG15 and ISGylated proteins.1
Key structural properties of ISG15:
- Compact 3D structure consisting of two tandem ubiquitin-like domains
- Hydrophobic core to maintain structural stability
- The C-terminal LRLRGG motif serves as a covalent binding site
Functions of ISG15
The core function of ISG15 is to act as an interferon-induced ubiquitin-like modifier and participate in intracellular immune regulation. However, it also involves many other physiological and pathological processes, including antiviral defense and cellular signal transduction.
| Function | Description |
| Immune regulation | ISG15 is released outside the cell as a signaling molecule and regulates the activity of immune cells through autocrine or paracrine means. |
| Antiviral defense | By ISG modification (covalently binding to target proteins) to modify viral or host proteins, the replication and assembly of the virus can be directly inhibited. |
| Intracellular signal | Through covalent or non-covalent interactions with key signaling proteins, JAK-STAT and other immune-related signaling pathways are finely regulated. |
| Protein stability | By binding and modifying specific newly synthesized or stress-state proteins, their stability is enhanced to prevent their degradation. |
| Cellular stress response | Under the condition of oxidative stress and genotoxic stress is induced, assist to maintain homeostasis and promote survival. |
Unlike ubiquitin, which mainly mediates protein degradation, the modification spectrum of ISG15 is more diverse. Its modification behavior does not directly lead to the degradation of substrate proteins, but exerts its extensive regulatory functions by altering the activity, localization or interaction of target proteins, highlighting its unique role in innate immunity.
Applications of ISG15 and ISG15 Antibody in Literature
1. Mirzalieva, Oygul, et al. "ISG15 and ISGylation in human diseases." Cells 11.3 (2022): 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030538
The article indicates that ISG15 is an interferon-induced protein with a ubiquitin-like structure that can participate in protein ISG modification. It is abnormally expressed in pathological processes such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and inflammation, playing a "double-edged sword" role and has now become a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
2. Cui, Na, et al. "ISG15 accelerates acute kidney injury and the subsequent AKI-to-CKD transition by promoting TGFβR1 ISGylation." Theranostics 14.11 (2024): 4536. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.95796
The article indicates that ISG15 plays a key role in acute kidney injury (AKI) and its transformation into chronic kidney disease (CKD). Research has found that ISG15 aggravates renal fibrosis and injury by promoting the ISG modification of TGFβR1 and inhibiting its ubiquitination. This indicates that ISG15 is a potential therapeutic target in the process of AKI-CKD.
3. Munnur, Deeksha, Adrianna Banducci-Karp, and Sumana Sanyal. "ISG15 driven cellular responses to virus infection." Biochemical Society Transactions 50.6 (2022): 1837-1846. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20220839
The article indicates that ISG15 is a key protein induced by interferon, possessing both intracellular ISG modification and extracellular cytokine functions. Its role in antiviral immunity is complex, capable of regulating autophagy, inflammation and metabolism, and can also be antagonized by viruses. Moreover, there are differences in studies between human and mouse models, and its exact antiviral mechanism remains to be clarified.
4. Yerra, Veera Ganesh, et al. "Pressure overload induces ISG15 to facilitate adverse ventricular remodeling and promote heart failure." The Journal of Clinical Investigation 133.9 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI161453
The article indicates that ISG15 is significantly upregulated in pathological ventricular remodeling. The ISG-mediated modification it mediates targets the myofibrin Filamin-C, inhibits autophagy in cardiomyocytes and leads to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, thereby promoting the development of heart failure.
5. Qu, Tongyuan, et al. "ISG15 targets glycosylated PD-L1 and promotes its degradation to enhance antitumor immune effects in lung adenocarcinoma." Journal of Translational Medicine 21.1 (2023): 341. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-04135-1
The article indicates that ISG15 promotes the degradation of PD-L1 protein through ubiquitination modification and inhibits the progression of lung cancer. This effect can enhance CD4+ T cell infiltration and anti-tumor immunity, improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors, and suggest its potential as a new target for tumor immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: ISG15 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ISG15 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ISG15 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ISG15 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Munnur, Deeksha, Adrianna Banducci-Karp, and Sumana Sanyal. "ISG15 driven cellular responses to virus infection." Biochemical Society Transactions 50.6 (2022): 1837-1846. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20220839
Anti-ISG15 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








