LBR Antibodies
Background
LBR is an integrated membrane protein mainly existing in the inner membrane of eukaryotic nuclei. This protein interacts with nuclear laminar protein B and chromatin through its amino-terminal domain, playing a key role in maintaining the nuclear membrane structure and heterochromatin anchoring. After being first identified in 1990, LBR has attracted much attention due to its unique bifunctional properties (both as a structural protein and having sterol reductase activity). Studies have found that LBR mutations are associated with a variety of human diseases, including Pelger-Huet abnormalities and Greenberg skeletal dysplasia. Its complex transmembrane structure and diverse biological functions provide an important model for the study of nuclear membrane-chromatin interactions and nuclear membrane-related diseases.
Structure of LBR
LBR is a nuclear membrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 58-60kDa, and its size varies among different species:
| Species | Human | Mice | Chicken | Yeast |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 58 | 59 | 57 | 55 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 208 aa karyoplasm domain | Nuclear mass domain slightly shorter | Homology degree: 68% | Only the transmembrane region is similar |
LBR is composed of approximately 600 amino acids and has a unique dual-domain feature. The N-terminal nucleoplasmic domain (amino acids 1-208) of this protein contains multiple functional modules, including a serine/arginine-rich sequence and nuclear localization signals. The C-terminal transmembrane domain (amino acids 209-600) contains 8 transmembrane segments, forming a hydrophobic core with sterol reductase activity.
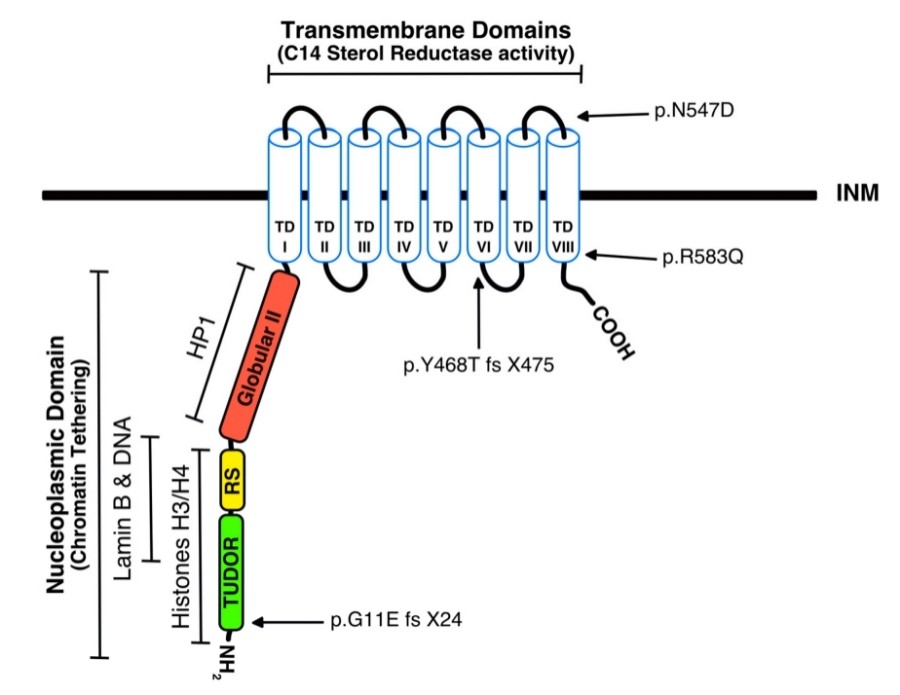 Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of full-length LBR.1
Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of full-length LBR.1
Key structural properties of LBR:
- Dual-functional domains: The core-mass domain and the transmembrane domain perform functions independently
- Amino acids 71-100: DNA binding region (containing SR-enriched sequence)
- Transmembrane region: NADPH binding site (Gly X-X-X-Gly motif)
- Nuclear plasmic domain: Binding site of nuclear lamellar protein B
- Multiple phosphorylation sites: Regulate protein function
Functions of LBR
The main function of LBR is to maintain the nuclear membrane structure and chromatin organization, and at the same time participate in various cellular physiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Nuclear fiber layer anchoring | LBR binds to type B nuclear lamellar proteins through the N-terminal domain, maintaining the structural stability of the nuclear membrane. |
| Chromatin organization | The nucleoplasmic domain interacts with the heterochromatin protein HP1, mediating the anchoring of heterochromatin in the nuclear intima. |
| Steroid metabolism | The C-terminal transmembrane domain has sterol Δ 14-reductase activity and is involved in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. |
| Mitotic regulation | Dynamic phosphorylation during cell division regulates the disintegration and recombination of the nuclear membrane. |
| Disease-related | Mutations lead to genetic diseases such as Pelger-Huet abnormalities and affect the morphology of granulocyte nuclei. |
The binding curve of LBR and chromatin shows a typical synergistic effect, indicating that its multiple binding sites can cooperatively regulate the chromatin - nuclear membrane interaction. Unlike simple DNA-binding proteins, LBR can not only recognize specific chromatin markers but also affect membrane fluidity through the sterol reductase domain, achieving dual regulation of structure and metabolic functions.
Applications of LBR and LBR Antibody in Literature
1. Ye, Qian, and Howard J. Worman. "Primary structure analysis and lamin B and DNA binding of human LBR, an integral protein of the nuclear envelope inner membrane." Journal of Biological Chemistry 269.15 (1994): 11306-11311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)78126-5
This article indicates that the human nuclear membrane protein LBR interacts with laminin B and DNA. Its amino terminal contains a Ser-ArG-rich region, which can be recognized by autoantibodies and can bind to DNA (the key amino acids of 71-100). LBR plays an important role in the anchoring of the nuclear lamina and chromatin.
2. Schuler, Ekkehard, Feng Lin, and Howard J. Worman. "Characterization of the human gene encoding LBR, an integral protein of the nuclear envelope inner membrane." Journal of Biological Chemistry 269.15 (1994): 11312-11317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)78127-7
The research found that the human nuclear membrane protein LBR gene spans 35kb and contains 13 exons (1-4 encode the nucleoplasmic domain, and 5-13 encode the transmembrane region). Its 5' end contains multiple transcription factor binding sites, and the transmembrane region is homologous to yeast protein, suggesting that this gene may have evolved from the recombination of nuclear protein and membrane protein genes.
3. Ye, Qian, and Howard J. Worman. "Interaction between an integral protein of the nuclear envelope inner membrane and human chromodomain proteins homologous to Drosophila HP1." Journal of Biological Chemistry 271.25 (1996): 14653-14656. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.25.14653
Research has found that the nuclear membrane protein LBR can bind to the heterochromatin protein HP1, revealing that it mediates the adhesion of heterochromatin to the nuclear intima through the amino-terminal domain. LBR, as a bidirectional anchoring protein between the nuclear lamina and chromatin, plays a key role in maintaining the structural integrity of the nuclear membrane.
4. Tsai, Pei-Ling, et al. "The Lamin B receptor is essential for cholesterol synthesis and perturbed by disease-causing mutations." Elife 5 (2016): e16011. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16011
Studies have found that the nuclear membrane protein LBR is crucial for cholesterol synthesis. LBR mutations can lead to poor skeletal development and Pelger-Huet abnormalities in Greenberg. The mechanisms are divided into two categories: Sterol reductase domain mutations reduce NADPH affinity, while truncation mutations cause rapid protein degradation. These mutants provide a new model for the study of endonuclear protein metabolism.
5. Simos, George, Christèle Maison, and Spyros D. Georgatos. "Characterization of p18, a component of the lamin B receptor complex and a new integral membrane protein of the avian erythrocyte nuclear envelope." Journal of Biological Chemistry 271.21 (1996): 12617-12625. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.21.12617
Studies have found that mutations in the nuclear membrane protein LBR gene can induce lupus-like autoimmune responses. F1 female mice carrying Lbr mutations (NZW×B6.Lbric) showed splenomegaly, renal injury and high-titer anti-chromatin antibodies (mainly IgG2 subtype), and their antinuclear antibodies presented a complex reaction pattern of nuclear membrane and histone, suggesting that abnormal nuclear structure can promote the occurrence of lupus under the background of genetic susceptibility.
Creative Biolabs: LBR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LBR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for Western Blot, IF, IHC, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LBR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our myoglobin antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference
- Nikolakaki, Eleni, Ilias Mylonis, and Thomas Giannakouros. "Lamin B receptor: interplay between structure, function and localization." Cells 6.3 (2017): 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030028
Anti-LBR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






