MITF Antibodies
Background
MITF gene encodes a key basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factor (bHLH-Zip), which is mainly involved in the development and functional regulation of melanocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cells and osteoclasts. This protein regulates the expression of downstream target genes by binding to the M-box enhancer sequence, dominates the melanin synthesis pathway (such as tyrosinase-related genes), and affects the mechanisms of cell survival and differentiation. Loss-of-function mutations in MITF can lead to genetic disorders such as Waardenburg syndrome type II and Tietz syndrome, which are characterized by auditory deficits and pigmentation abnormalities. Since Hermann Muller first discovered the mitf mutant phenotype in 1942, this gene has become a core model for studying cell fate determination, linea-specific regulation, and the molecular mechanisms of related cancers (such as melanoma), and its multifunctional function has continuously promoted the progress of cross-disciplinary research in developmental biology and disease treatment.
Structure of MITF
The molecular weight of the MITF protein is approximately 54 to 65 kDa, with specific values varying due to different splicing isomers (such as MITF-M, MITF-A, etc.) and post-translational modifications (such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination). This protein belongs to the basic helical-ring-helical leucine zipper (bHLH-Zip) family, and its structure includes conserved DNA binding regions, transcriptional activation domains, and multiple regulatory modules. The sequences and functions of MITF are highly conserved in different species, especially in mammals, where their core structures and DNA binding characteristics show significant similarities.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Pig | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 58 | 57 | ~55 | ~59 | ~56 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conserved sequence, highly similar to other mammals | Minor amino acid variations | Slightly different oxygen affinity | Adapted for prolonged oxygen storage | Similar to human myoglobin |
The MITF protein is composed of multiple functional domains, including the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain, the central bHLH-Zip domain (responsible for dimerization and DNA binding), and the C-terminal regulatory region. Its DNA binding target is the E-box or M-box sequence (5'-CATGTG-3'). The activity of this protein is strictly regulated by multiple signaling pathways (such as MAPK/ERK, WNT, cAMP), and phosphorylation modification can affect its stability, subcellular localization and transcriptional efficacy. MITF plays a core role in regulating differentiation and survival in various cell types, especially melanocytes, osteoclasts and retinal pigment epithelial cells.
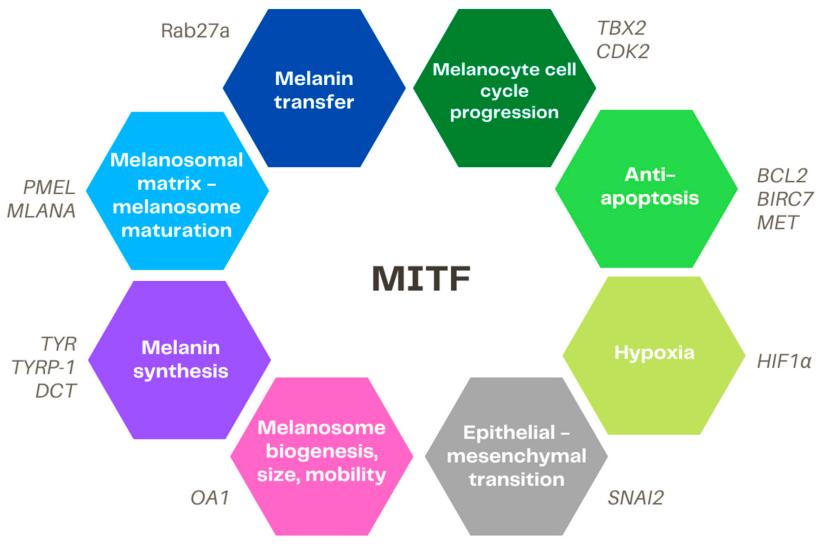 Fig. 1 Overview of the main targets of MITF.1
Fig. 1 Overview of the main targets of MITF.1
Key structural properties of MITF:
- Alkaline helical ring-helical leucine zipper (bHLH-Zip) domain
- Multiple conserved transcriptional activation domains and regulatory regions
- Specific DNA binding sequences (E-box/M-box)
- Multiple post-translational modification sites such as phosphorylation and acetylation
Functions of MITF
The main function of the MITF gene is to regulate the expression of target genes as a transcription factor, influencing cell differentiation, survival and metabolism. Meanwhile, it is also involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including pigment synthesis, immune regulation and tumorigenesis.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of melanocyte differentiation | MITF is a core regulatory factor for the development of melanocyte lineages, activating the expression of genes such as tyrosinase and dominating melanin synthesis. |
| Regulation of osteoclast function | Regulating multiple differentiation-related genes in osteoclasts affects bone resorption and bone homeostasis. |
| Cell cycle and survival regulation | By targeting and regulating genes such as BCL2 and CDK2, it inhibits apoptosis and promotes cell survival and proliferation. |
| Pigment disorders are associated with tumors | MITF mutations lead to genetic diseases such as Waardenburg syndrome, and their amplification or abnormal expression is closely related to melanoma. |
| Stress and Metabolic adaptation | In response to UV and cAMP/MAPK signaling pathways, it regulates the adaptation and pigment synthesis responses of cells under stress conditions. |
MITF exerts transcriptional regulatory effects by binding to the E-box/M-box sequence (5'-CATGTG-3'), and its activity is precisely regulated by multiple signaling pathways and post-translational modifications, demonstrating its multifunctional and core biological functions in development and disease.
Applications of MITF and MITF Antibody in Literature
1. Gelmi, Maria Chiara, et al. "MITF in normal melanocytes, cutaneous and uveal melanoma: a delicate balance." International journal of molecular sciences 23.11 (2022): 6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116001
The article indicates that MITF has a complex role in uveal melanoma (UM), and its expression deficiency is associated with the loss of BAP1 protein and poor prognosis. It may inhibit tumor invasion and inflammation, but promote local proliferation.
2. Chauhan, Jagat S., et al. "The MITF regulatory network in melanoma." Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research 35.5 (2022): 517-533. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.13053
The article indicates that MITF is a key factor in the phenotypic regulation of melanoma. It activates proliferation genes by binding to E/M-box and interacts with factors such as AP1/JUN to inhibit invasion-related genes. Low expression of MITF promotes tumor immune infiltration and treatment resistance, and its state transition directly affects the malignant evolution of tumors.
3. Abrahamian, Carla, and Christian Grimm. "Endolysosomal cation channels and MITF in melanocytes and melanoma." Biomolecules 11.7 (2021): 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071021
The article indicates that MITF is a key regulatory factor of melanoma, and its activity is regulated by the MAPK and Wnt/GSK3 pathways. Studies have revealed that endosomal lysosomal cation channels (such as TPC2 and TRPML1) affect MITF through the above-mentioned pathways, thereby regulating tumor growth and invasion.
4. Lee, Aram, Jihyun Lim, and Jong-Seok Lim. "Emerging roles of MITF as a crucial regulator of immunity." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 56.2 (2024): 311-318. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-024-01175-5
The article indicates that the MITF(E318K) variant is associated with the risk of cutaneous melanoma. Through systematic analysis, this study found that its association with the risk of non-melanoma cancer is weak, but it has a novel strong association with uterine carcinosarcoma (OR=9.24). It is recommended to update the cancer screening protocol for carriers of this variant.
5. Lai, et al. "SOX10, MITF, and microRNAs: Decoding their interplay in regulating melanoma plasticity." International Journal of Cancer (2025). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.35499
Research has found that SOX10 and MITF form a gene regulatory network through miRNA. These network motifs regulate the phenotypic transformation, treatment resistance and metastasis process of melanoma through feedforward/feedback loops, providing a new perspective for the development of mirNA-targeted therapies.
Creative Biolabs: MITF Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MITF antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MITF Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MITF antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gelmi, Maria Chiara, et al. "MITF in normal melanocytes, cutaneous and uveal melanoma: a delicate balance." International journal of molecular sciences 23.11 (2022): 6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116001
Anti-MITF antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Rat Anti-EMCN Recombinant Antibody (28) (CBMAB-E0280-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Rat Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (7G4.2E8) (CBMAB-C8725-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BBS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0253) (CBMAB-0254-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








