MMAA Antibodies
Background
MMAA genes encode proteins as key factors involved in energy metabolism in the mitochondria, mainly distributed in vertebrate cells, responsible for regulating the vitamin B12 transformation and transport, in order to maintain mitochondrial function and cellular energy steady-state. This gene indirectly supports aerobic respiration and energy supply by participating in the metabolic process of cobalamin, especially playing a significant role in high-energy-consuming tissues such as the heart and liver. Its mutation is closely related to the autosomal recessive genetic disorder methylmalonic aciduria, leading to metabolic disorders and developmental abnormalities. Since its function was discovered, the research on the structure and mechanism of the MMAA gene has deepened people's understanding of the molecular basis of metabolic diseases and provided an important basis for the development of related treatment strategies.
Structure of MMAA
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the MMAA gene is approximately 42 kDa. The molecular weight of this protein varies among different species, mainly due to variations in its nuclear localization signal and mitochondrial targeting sequence.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 42.0 | 41.8 | 41.5 | 42.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains classical nuclear localization sequence | Verification with a sequence of one amino acid replacement | Lack of a complete mitochondrial targeting domain | The C-terminal sequence differs by three amino acids from that of other species |
The MMAA protein is composed of 385 amino acids, and its three-dimensional structure includes a GTP-binding domain and a cobalamin binding region. The GTPase activity of this protein depends on its conserved G1-G5 motif, which together form the active center. The arginine residue at position 123 directly participates in the hydrolysis of GTP, while the glutamic acid at position 289 plays a key role in maintaining the stability of cobalamin.
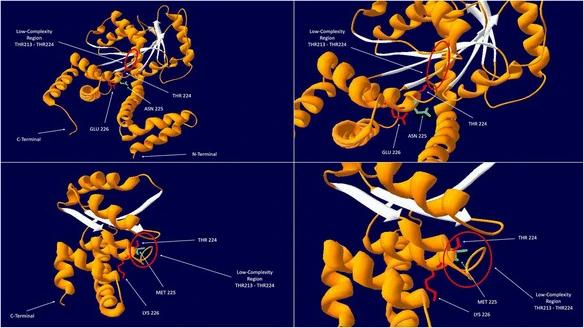 Fig. 1 MMAA Protein Structure and the p.N225M Mutation.1
Fig. 1 MMAA Protein Structure and the p.N225M Mutation.1
Key structural properties of MMAA:
- Contains GTP-binding and cobalamin binding dual functional domains
- Highly conserved core motifs of GTPase activity
- Multiple helical structures form the vitamin B12 binding pocket
- Specific amino acid residues are involved in maintaining cobalamin stability
Functions of MMAA
The core function of the protein encoded by the MMAA gene is to participate in the metabolism and transport of vitamin B12 within cells. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Cobalamin activation | In mitochondria, it mediates the conversion of vitamin B12 to its active form, adenosine cobalamin, which is an essential cofactor for methylmalonyl-coa mutase. |
| Metabolic regulation | By maintaining the normal operation of the methylmalonyl-CoA metabolic pathway, preventing the accumulation of toxic metabolites, and ensuring the homeostasis of energy metabolism. |
| Maintenance of mitochondrial function | Ensure the normal operation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to support cellular energy supply. |
| Metabolic balance of organic acids | dysfunction can lead to methylmalonic aciduria, characterized by abnormally elevated levels of methylmalonic acid in the blood and urine. |
This protein precisely regulates cobalamin metabolism through the GTP hydrolysis mechanism, and its functional defect will directly cause energy metabolism disorder and abnormal development.
Applications of MMAA and MMAA Antibody in Literature
1. Jafari, Mahboobeh, et al. "Identification of novel mutations in the MMAA and MUT genes among methylmalonic aciduria families." Iranian biomedical journal 27.6 (2023): 397. https://doi.org/10.61186/ibj.3782
This study conducted genetic analysis on 12 Iranian families with methylmalonic aciduria. Through homozygous localization and sequencing techniques, two novel mutations were identified in the MMAA and MUT genes. Some patients were not detected with known pathogenic mutations, suggesting the existence of other genetic mechanisms. This discovery expands the gene mutation spectrum of MMA.
2. Zhang, Yiyin, et al. "ESR1 regulates the obesity-and metabolism-differential gene MMAA to inhibit the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma." Frontiers in oncology 12 (2022): 899969. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.899969
Research has found that the MMAA gene plays a tumor suppressor role in liver cancer. It inhibits tumor growth by damaging mitochondrial function and maintaining REDOX balance. Especially in obese female patients, the highly expressed estrogen receptor can upregulate MMAA, thereby exerting a protective effect, indicating that obesity may be a protective factor.
3. Lin, Yiming, et al. "Mild clinical features of isolated methylmalonic acidemia associated with a novel variant in the MMAA gene in two Chinese siblings." BMC medical genetics 19.1 (2018): 114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-018-0635-4
In this study, a novel homozygous missense mutation c.365T>C of the MMAA gene was discovered in a Chinese MMA family. This mutation may lead to unstable protein structure and is associated with the relatively mild clinical manifestations of CBLA-type methylmalonic acidemia in two fellow patients. The research confirmed the diagnosis through screening of the affected children and genetic verification of the family.
4. Keyfi, Fatemeh, et al. "Identification of a novel deletion in the MMAA gene in two Iranian siblings with vitamin B12-responsive methylmalonic acidemia." Cellular & molecular biology letters 21.1 (2016): 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-016-0005-1
In this study, a homozygous deletion of c.674delA was found in exon 4 of the MMAA gene in a family with methylmalonic acidemia. This mutation causes premature termination of protein translation through frameshift, resulting in truncated protein, and has been confirmed as a pathogenic allele. Both of the sick children carried this mutation.
5. Wesół-Kucharska, Dorota, et al. "Clinical picture and treatment effects in 5 patients with Methylmalonic aciduria related to MMAA mutations." Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports 22 (2020): 100559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100559
This study retrospectively analyzed 5 patients with CBLA-type methylmalonic aciduria caused by MMAA gene mutations. All patients were sensitive to hydroxycobalamin treatment and had good metabolic control. However, complications such as neurodevelopmental delay and chronic kidney disease still occurred during the long-term course of the disease, suggesting that early treatment failed to completely prevent long-term damage.
Creative Biolabs: MMAA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MMAA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MMAA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MMAA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Jafari, Mahboobeh, et al. "Identification of novel mutations in the MMAA and MUT genes among methylmalonic aciduria families." Iranian biomedical journal 27.6 (2023): 397. https://doi.org/10.61186/ibj.3782
Anti-MMAA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCL5 Recombinant Antibody (R0437) (CBMAB-R0437-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






