MTOR Antibodies
Background
MTOR is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase, mainly present in the cytoplasm and organelle membranes of eukaryotic cells. This protein regulates key life activities such as cell growth, proliferation and autophagy by integrating nutritional, energy and growth factor signals, thereby maintaining intracellular homeostasis. In tumors and metabolic diseases, abnormal activation of the MTOR pathway often leads to uncontrolled cell growth. Its function was first discovered in the 1990s through the inhibitory effect of rapamycin, and the related research won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2019. As the core hub of the cellular signaling network, MTOR's complex regulatory mechanism continuously provides a theoretical basis for targeted therapy, promoting in-depth exploration of disease mechanisms and drug development.
Structure of MTOR
MTOR is a large serine/threonine kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 289 kDa. Its molecular weight is highly conserved among different species, but in the human body, there are minor differences due to different splicing variants.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Yeast |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 289 | 289 | ~289 | ~280 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Including HEAT, FAT, FRB, kinase domain structure | Highly homologous with humans, the structure of domain are basically identical | Highly conservative kinase domain structure | Homologous genes only contain core conserved domains |
This protein is composed of over 2,500 amino acid residues, and its primary structure folds into a complex multi-domain three-dimensional conformation. The core of the MTOR protein is the kinase domain at the C-terminal, and its activity is regulated by the sensitivity of the upstream FRB domain to rapamycin. Multiple HEAT repeat sequences form superhelical structures at the N-terminal, mediating protein-protein interactions and complex assembly. Its functional exertion depends on the formation of two different complexes, mTORC1/2, and the specific adaptor proteins of both (such as Raptor and Rictor) determine the substrate specificity and the differences in signaling pathways.
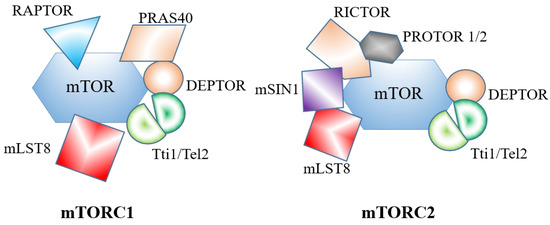 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of mTORC1 and mTORC2 structures.1
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of mTORC1 and mTORC2 structures.1
Key structural properties of MTOR:
- Made up of multiple linear array HEAT repeat sequence superhelix stents
- With a conservative FRB structure domain for rapamycin mediated allosteric inhibition
- The C-terminal contains a typical kinase domain to catalyze substrate phosphorylation
- mTORC1/mTORC2 complexes with different functions were dynamically assembled by Raptor/Rictor
Functions of MTOR
The core function of MTOR kinase is to integrate intracellular and extracellular signals to regulate cell growth. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including metabolic reprogramming, autophagy regulation and immune response.
| Function | Description |
| Cell growth regulation | As a central regulator, it promotes protein synthesis and cell proliferation by phosphorylating downstream substrates such as 4E-BP1 and S6K. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Sense the nutritional and energy status (such as amino acid and glucose levels), and coordinate the balance between anabolism and catabolism. |
| Inhibition of autophagy | Inhibit autophagy initiation when nutrients are adequate to maintain intracellular homeostasis and prevent unnecessary degradation of substances. |
| Activation of immune cells | By regulating metabolic pathways, it affects the activation, differentiation and function of immune cells such as T cells and B cells. |
| Cell cycle advancement | By integrating growth factor signals, it provides the necessary licensing signals for cells to transition from the G1 phase to the S phase. |
The function of MTOR is achieved by forming two different complexes (MTORC1/2). mTORC1 is sensitive to rapamycin and is mainly responsible for regulating anabolism and autophagy. However, mTORC2 is not sensitive to rapamycin and mainly regulates cytoskeletal recombination and cell survival. The synergistic effect of the two determines the ultimate fate of cells.
Applications of MTOR and MTOR Antibody in Literature
1. Gargalionis, Antonios N., et al. "mTOR signaling components in tumor mechanobiology." International journal of molecular sciences 23.3 (2022): 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031825
The article indicates that mTOR, as a core hub integrating nutritional and metabolic signals, is abnormally activated in tumors. Recent studies have found that the mTOR pathway is interrelated with the mechanical and biological mechanisms of tumors. It regulates tumor growth, invasion and drug efficacy by sensing mechanical signals, providing a new perspective for cancer treatment.
2. Marafie, Sulaiman K., Fahd Al-Mulla, and Jehad Abubaker. "mTOR: its critical role in metabolic diseases, cancer, and the aging process." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.11 (2024): 6141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116141
The article indicates that mTOR is the core hub for regulating cell growth and metabolism, and its abnormal signals are closely related to cancer, metabolic diseases and aging. This article reviews the role of the mTOR pathway in diseases, explores the efficacy of existing inhibitors, and looks forward to the research and development prospects of the next generation of bifunctional targeted drugs.
3. Gao, Yuan, and Tian Tian. "mTOR signaling pathway and gut microbiota in various disorders: mechanisms and potential drugs in pharmacotherapy." International journal of molecular sciences 24.14 (2023): 11811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411811
The article indicates that mTOR, as a core regulatory factor of cellular metabolism, its abnormal signal is associated with various diseases. This review explores the mechanism by which the gut microbiota and its metabolites affect the functions of multiple organs such as the gastrointestinal tract and liver through the mTOR pathway, and looks forward to new strategies for treating related diseases by regulating the microbiota-mTOR axis.
4. Catena, Valeria, and Maurizio Fanciulli. "Deptor: not only a mTOR inhibitor." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 36.1 (2017): 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0484-y
The article indicates that Deptor is a key inhibitory protein of the mTOR complex and affects tumor development by regulating processes such as cell growth, autophagy and transcription. It plays a dual role in causing and inhibiting cancer. This review explores potential new therapeutic strategies targeting the Deptor-mTOR interaction.
5. Zeng, Chudai, et al. "The coordination of mTOR signaling and non-coding RNA in regulating epileptic neuroinflammation." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 924642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.924642
The article indicates that the mTOR signaling pathway is a core regulatory factor of neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Non-coding Rnas participate in this process by interfering with the mTOR pathway, influencing neuroinflammatory cells and mediators, and thereby promoting the occurrence and development of epilepsy. This article reviews the interaction mechanism between the two in epilepsy and their potential therapeutic value.
Creative Biolabs: MTOR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MTOR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MTOR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MTOR antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gao, Yuan, and Tian Tian. "mTOR signaling pathway and gut microbiota in various disorders: mechanisms and potential drugs in pharmacotherapy." International journal of molecular sciences 24.14 (2023): 11811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411811
Anti-MTOR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-261270) (CBMAB-C0813-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








