MUC16 Antibodies
Background
MUC16 is a large transmembrane glycoprotein that mainly exists on the surface of human epithelial cells, especially being highly expressed in the ovaries, respiratory tract and ocular surface tissues. This protein forms a mucus barrier through its extracellular domain, participates in cell protection, lubrication and signal transduction functions, and plays a key role in immune regulation. Because the extracellular segment of MUC16 can shed and enter the bloodstream, its fragment CA125 has become an important tumor marker for monitoring the progression and recurrence of ovarian cancer in clinical practice. This gene was first identified in ovarian cancer research in the 1980s. Its complex highly glycosylated structure and abnormal expression mechanism remain a hot area in cancer diagnosis and targeted therapy research to this day, providing important clues for understanding the tumor microenvironment and immune escape.
Structure of MUC16
MUC16 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with an extremely high molecular weight. Its core polypeptide has a molecular weight of approximately 550-600 kDa, and after highly glycosylated modification, the total protein molecular weight can exceed 2,000 kDa. This huge molecular weight difference mainly stems from the abundance of serine/threonine repeat sequences in its extracellular segment, which are the main sites for O-glycosylation and N-glycosylation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | >2,000 (whole protein) | Approximately 1,800 (predicted) | Approximately 1,900 (predicted) |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conserved sequence, highly similar to other mammals | Minor amino acid variations | Slightly different oxygen affinity |
The extracellular domain of this protein is composed of a large number of tandem "SEA" functional modules, which have self-lysis properties and form the basis for the formation of the mucus barrier and the production of soluble CA125 antigen. Its transmembrane domain anchors the protein to the cell membrane, while the shorter intracellular tail region may be involved in intracellular signal transduction. The vast glycosylated structure of MUC16 forms a physical barrier, and the CA125 fragment produced by its abnormal shedding is a key biomarker for the clinical diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
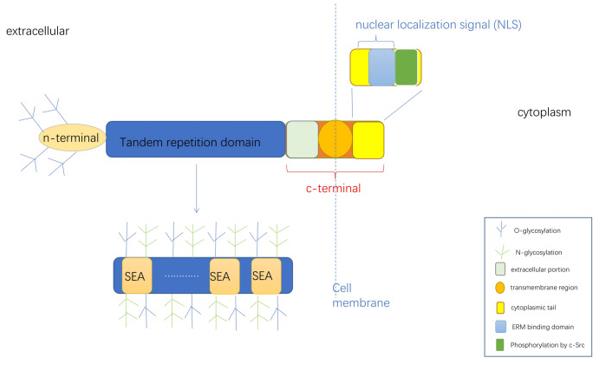 Fig. 1 Structure diagram of MUC16.1
Fig. 1 Structure diagram of MUC16.1
Key structural properties of MUC16:
- Large and highly glycosylated extracellular domains
- Transmembrane domains and intracellular short tails
- Characteristic SEA function module
Functions of MUC16
The core function of MUC16 protein (also known as CA125) is to form a physical barrier and mediate cellular signal transduction, and it is also directly involved in tumorigenesis and immune regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Physical barriers and lubrication | Its large and highly glycosylated extracellular domain forms a hydrophilic gel layer on the cell surface, providing physical protection, lubrication and moisture retention for epithelial cells. |
| Intercellular signal transduction and adhesion | Through the interaction of the extracellular segment with other membrane proteins or receptors (such as mesothelin), it is involved in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, and intercellular recognition and adhesion. |
| Immune regulation | Can be used as immune barrier limit pathogen contact epithelial cells, and its loss of fragment (e.g., CA125) can adjust the function of natural killer cells and other immune cells, affect the immune surveillance. |
| Tumor markers and metastasis | CA125 is abnormally highly expressed in various cancers such as ovarian cancer. After its extracellular segment detach, it enters the bloodstream and becomes a serum marker for clinical diagnosis and monitoring. Meanwhile, MUC16 is also involved in promoting the peritoneal metastasis and invasion of tumor cells. |
Unlike myoglobin, which mainly performs a single oxygen storage/transport function, MUC16 has a highly complex function. Its huge glycosylated structure directly determines its multiple biological functions. Its dysfunction is not only closely related to the malignant progression of tumors, but also involves various pathological processes such as mucosal immune deficiency.
Applications of MUC16 and MUC16 Antibody in Literature
- Zhang, Xin-Yu, Lian-Lian Hong, and Zhi-qiang Ling. "MUC16: clinical targets with great potential." Clinical and experimental medicine 24.1 (2024): 101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-024-01365-5
The article indicates that MUC16 is abnormally expressed in various tumors, promoting tumor progression by regulating signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT, and mediating T cell and NK cell inhibition to assist tumor immune escape. Targeting MUC16 has become a new direction in clinical treatment.
- Ruyun, G. A. O., et al. "MUC16: The Novel Target for Tumor Therapy." Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer 25.7 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.31
The article indicates that MUC16 (CA125) is a key biomarker for tumors such as ovarian cancer. It activates signaling pathways by binding to multiple ligands, driving tumor proliferation, invasion and immune escape. Targeted therapy for MUC16 has made progress and has become a highly promising new direction in tumor treatment.
- Chen, Xinyi, et al. "MUC1 and MUC16: critical for immune modulation in cancer therapeutics." Frontiers in immunology 15 (2024): 1356913. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1356913
The article indicates that MUC1 and MUC16 are abnormally expressed in tumor cells and drive tumor progression by regulating mechanisms such as proliferation, apoptosis resistance, and immune escape. As a key biomarker and therapeutic target, it provides a new direction for the development of targeted drugs and immunotherapies.
- Felder, Mildred, et al. "MUC16 (CA125): tumor biomarker to cancer therapy, a work in progress." Molecular cancer 13.1 (2014): 129. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-129
The article indicates that MUC16 (CA125) is a key serum marker for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer, and its expression level is closely related to tumor progression and metastasis. At present, therapies targeting MUC16 are emerging as a new research direction in the treatment of ovarian cancer and are expected to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment.
- Saad, Hebatallah M., et al. "The potential role of MUC16 (CA125) biomarker in lung cancer: a magic biomarker but with adversity." Diagnostics 12.12 (2022): 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122985
The article indicates that CA125 (MUC16) is an important supplementary marker of CEA in the diagnosis of lung cancer, and its elevated serum level is associated with advanced lung cancer, pleural effusion and liver metastasis. In addition to ovarian cancer, tumors such as lung cancer can also produce CA125, but its use as a screening marker remains controversial.
Creative Biolabs: MUC16 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MUC16 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MUC16 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MUC16 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhang, Xin-Yu, Lian-Lian Hong, and Zhi-qiang Ling. "MUC16: clinical targets with great potential." Clinical and experimental medicine 24.1 (2024): 101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-024-01365-5
Anti-MUC16 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






