NLK Antibodies
Background
NLK gene encoding a protein kinase called Nemo samples, belongs to the family of serine/threonine protein kinase. This protein, as an evolutionarily conserved signaling molecule, mainly participates in the regulation of multiple key signaling pathways such as Wnt/β-catenin, influencing the processes of cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Studies have shown that NLK plays a significant role in neurodevelopment, immune regulation and tumorigenesis, and its abnormal expression is associated with various cancers and developmental diseases. Since its discovery in the late 1990s, NLK has become a hot topic in molecular biology research due to its cross-regulatory function in multiple signaling pathways, providing an important perspective for understanding the complexity of cellular signaling networks.
Structure of NLK
NLK is a serine/threonine protein kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 85-90 kDa, which varies by species and transcriptional variant. This protein structurally contains a highly conserved kinase domain, which is responsible for phosphorylating substrates and participating in the regulation of multiple signaling pathways.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 87 | 86 | 89 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Participate in the regulation of pathways such as Wnt and Notch | Affect neural development and immunity | Signal transduction during embryonic development |
The NLK protein is composed of approximately 700 amino acids, and its tertiary structure shows a typical kinase folding. The ATP-binding pocket is located between the N-terminal and C-terminal lobes of the kinase domain. The phosphate transfer reaction is completed through conserved catalytic residues (such as lysine and aspartic acid), and it can specifically interact with various signaling proteins (such as LEF1 and STAT3) through the N-terminal domain, thereby negatively or positively regulating the expression of downstream genes.
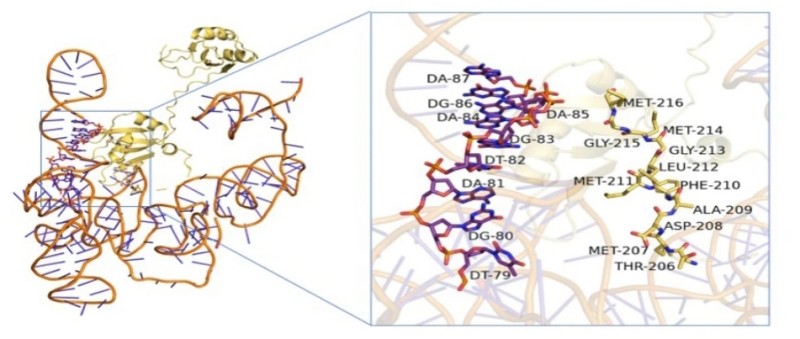 Fig. 1 Molecular docking predictions performed the interaction between MSI2 and NLK.1
Fig. 1 Molecular docking predictions performed the interaction between MSI2 and NLK.1
Key structural properties of NLK:
- Contains the typical serine/threonine kinase domain
- N end with C end leaf form ATP combined with pockets
- Conserved catalytic lysine and magnesium ion binding rings participate in phosphoric acid transfer
Functions of NLK
The main function of NLK is to act as a signal transduction regulator, participating in cell proliferation, differentiation and stress response. In addition, it also extensively involves a variety of pathophysiological processes, including tumorigenesis and neurodevelopmental abnormalities.
| Function | Description |
| Wnt signal regulation | Inhibiting the activity of the Wnt pathway by phosphorylating transcription factors such as TCF/LEF affects cell fate determination and tissue homeostasis. |
| Regulation of the NF-κB pathway | It can interact with IKK and NF-κB subunit and participate in the negative regulation of inflammation and immune response. |
| Cell cycle influence | By acting on the CDK and cyclin complex, it can prevent excessive cell proliferation and has potential anti-cancer effects. |
| Neuron development support | In the developing brain can regulate the differentiation and migration of neural precursor cells, influence the formation of cortex and synaptic function. |
| Tumor suppression and promotion | Depending on the environment, it can play a dual role of inhibiting or promoting tumors and is associated with various types of cancer. |
NLK is an evolutionarily conserved kinase whose activity is precisely regulated by upstream signals such as MAPK and Notch pathways, and is widely expressed in various tissues, especially in the nervous system and malignant tumors.
Applications of NLK and NLK Antibody in Literature
1. Song, Jialin, et al. "Hsa_circ_0009092/miR-665/NLK signaling axis suppresses colorectal cancer progression via recruiting TAMs in the tumor microenvironment." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 42.1 (2023): 319. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02887-8
This study found that circ_0009092 upregulates NLK expression by adsorbing miR-665, thereby inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and hindering the progression of colorectal cancer. NLK directly binds to STAT3, reduces the expression of CCL2, decreases the infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages, and affects the tumor microenvironment. NLK may become a potential therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.
2. Huang, Long, et al. "MSI2 regulates NLK-mediated EMT and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to promote pancreatic cancer progression." Cancer Cell International 24.1 (2024): 273. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03444-9
Research has found that MSI2 directly binds to NLK mRNA and enhances its translation, upregulates NLK expression, and thereby activates the EMT and PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathways, promoting the invasion, migration and liver metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Both MSI2 and NLK are independent adverse prognostic indicators for patients, and this axis provides a new target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
3. Chen, nyan, et al. "The expression of NLK is functionally associated with colorectal cancers (CRC)." Journal of Cancer 12.23 (2021): 7088. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.62526
Research has found that the NLK gene polymorphism locus rs2125846 is a susceptibility locus for colorectal cancer in the Chinese population. Interfering with NLK expression can inhibit the proliferation and migration of cancer cells and promote apoptosis. LncRNA XIST may upregulate NLK by inhibiting miR-92b-3p, thereby promoting the development of colorectal cancer. This mechanism provides a new target for clinical prevention and treatment.
4. Suwei, Dong, et al. "NLK functions to maintain proliferation and stemness of NSCLC and is a target of metformin." Journal of hematology & oncology 8.1 (2015): 120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-015-0203-8
Research has found that NLK is significantly highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and is associated with tumor stage. Inhibiting NLK can suppress cell proliferation, tumor formation and stem cell characteristics by regulating JUN protein. Metformin can selectively inhibit the expression of NLK and reduce the levels of tumor stem markers, indicating that targeting NLK may be a potential therapeutic strategy.
5. Szaluś-Jordanow, Olga, et al. "A primary multiple pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the heart in an adult dog." BMC Veterinary Research 19.1 (2023): 137. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00774-9
Research has found that NLK enhances the binding of SRF to ELK by phosphorylating serine at positions 101/103 of the SRF protein, thereby promoting the SRF/ELK signaling pathway and inhibiting the SRF/MKL pathway, which hinders the differentiation of myoblasts. Mice with muscle-specific Nlk knockout showed muscle fiber hypertrophy and weight gain, indicating that NLK plays a key role in regulating muscle development in vivo.
Creative Biolabs: NLK Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality NLK antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom NLK Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our NLK antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Huang, Long, et al. "MSI2 regulates NLK-mediated EMT and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to promote pancreatic cancer progression." Cancer Cell International 24.1 (2024): 273. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-024-03444-9
Anti-NLK antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








