OPA1 Antibodies
Background
The OPA1 gene encodes a GTPase dynamic-related protein located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is mainly expressed in cells with high energy demands. This protein maintains the structural integrity and functional stability of the mitochondrial network by regulating the process of mitochondrial crest morphological remodeling and intimal fusion, and plays a core role in the regulation of cellular energy metabolism and apoptosis. Research has found that OPA1 mutations can cause autosomal dominant optic atrophy, which is the most common hereditary optic neuropathy, characterized by progressive degeneration of retinal ganglion cells. This gene was jointly identified by multiple research teams in 2000. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure revealed the synergistic mechanism between the GTPase domain and the membrane-binding domain. Continuous research on OPA1 has greatly advanced the understanding of the association mechanism between mitochondrial dynamics and neurodegenerative diseases, providing a new direction for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Structure of OPA1
The mitochondrial dynamin-like GTPase encoded by the OPA1 gene is a large protein with a molecular weight of approximately 112 kDa. This molecular weight may fluctuate slightly due to various isomers produced by differential splicing of transcripts.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 112 | 110 | 113 |
| Primary Structural Differences | There are more than eight splicing isomers, which are classified into long and short types | Highly homologous to humans, with a similar shearing pattern | The core functional domain is highly conservative |
This protein contains an N-terminal GTPase domain, a central kinetoprotein domain and a C-terminal transmembrane domain, which together form the functional structural basis of it. Its core function relies on the synergistic effect of soluble long L-OPA1 and the membrane-anchored short S-OPA1 after proteolysis. The two jointly complete the teaming and fusion of the mitochondrial inner membrane through trans-interaction. The dysregulation of this process directly disrupts the morphology of mitochondrial crists, leading to the release of cytochrome c and triggering apoptosis, which constitutes the core pathological mechanism of autosomal dominant optic atrophy caused by OPA1 gene mutations.
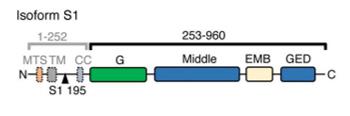 Fig. 1 Domain organization of OPA1.1
Fig. 1 Domain organization of OPA1.1
Key structural properties of OPA1:
- Modular multi-domain architecture
- Central coiled-coil domains that mediate membrane tethering
- The N-terminal GTPase domain drives conformational change and energy supply
- Proteolytic sensitive sites regulate the functional balance of long and short isomers
Functions of OPA1
The core function of the OPA1 protein is to regulate mitochondrial inner membrane fusion and maintain crest morphology. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of cellular physiological processes, including energy metabolism regulation and apoptosis inhibition.
| Function | Description |
| Endometrial fusion | The fusion of the inner mitochondrial membrane is driven by GTP hydrolysis to maintain the continuity of the mitochondrial network and ensure the exchange of contents. |
| Regulation of ridge morphology | Stabilize the tight structure of mitochondrial cristae and optimize the spatial arrangement of respiratory chain complexes to enhance the efficiency of ATP synthesis. |
| Regulation of apoptosis | By maintaining the integrity of the crest membrane to prevent the abnormal release of cytochrome c, the activation of the apoptotic pathway can be inhibited. |
| Energy metabolism balance | Coordinate mitochondrial morphology with energy demand and adapt to changes in energy supply by reconstructing ridge structure under metabolic stress. |
| Maintenance of mitochondrial DNA | By maintaining the stability of the inner membrane structure, it indirectly provides structural support for the replication and transcription of mitochondrial DNA. |
The functional activity of OPA1 is precisely regulated by proteolysis. The synergistic effect of its long and short isomers constitutes the core mechanism of mitochondrial quality control, and the disruption of this mechanism is the direct cause of hereditary optic neuropathy.
Applications of OPA1 and OPA1 Antibody in Literature
1. Zanfardino, Paola, et al. "The balance of MFN2 and OPA1 in mitochondrial dynamics, cellular homeostasis, and disease." Biomolecules 15.3 (2025): 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030433
The article indicates that OPA1 mediates mitochondrial fusion, and its mutations can lead to neurodegenerative diseases such as ADOA, affecting energy metabolism and autophagy. Therapies targeting mTOR and others to restore mitochondrial function hold great promise.
2. Herkenne, Stephanie, and Luca Scorrano. "OPA1, a new mitochondrial target in cancer therapy." Aging (Albany NY) 12.21 (2020): 20931. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.104207
The article indicates that in addressing the challenges of drug resistance and metastasis in cancer, research has found that the mitochondrial protein OPA1 is the key. Inhibiting OPA1 can effectively block tumor angiogenesis, inhibit metastasis and reverse drug resistance, opening up a new path for the development of novel anti-cancer therapies.
3. Yang, Wenbo, et al. "Empagliflozin improves renal ischemia–reperfusion injury by reducing inflammation and enhancing mitochondrial fusion through AMPK–OPA1 pathway promotion." Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters 28.1 (2023): 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-023-00457-6
Research has found that mutations in the OPA1 gene not only disrupt the structure of mitochondria but also lead to abnormal distribution of genetic material (mtDNA nucleoli) within them, with a large number of mitochondria or even complete absence of nucleoli. This provides a new mechanism for revealing the etiology of hereditary optic atrophy.
4. Weng, Jiali, et al. "TRPA1-PI3K/Akt-OPA1-ferroptosis axis in ozone-induced bronchial epithelial cell and lung injury." Science of the Total Environment 918 (2024): 170668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170668
Research has revealed that ozone activates the TRPA1 receptor and inhibits the mitochondrial fusion protein OPA1 through the PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis, leading to lung injury. Blocking TRPA1 has a protective effect.
5. Chen, Jiaqi, et al. "OPA1, a molecular regulator of dilated cardiomyopathy." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 27.20 (2023): 3017-3025. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17918
Research reveals that in dilated cardiomyopathy, the p53 gene affects the key protein OPA1 by activating Bak/Bax and OMA1, thereby leading to apoptosis, mitochondrial dynamic imbalance and ridge structure changes. OPA1 is the core mediator of this process.
Creative Biolabs: OPA1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality OPA1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom OPA1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our OPA1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhang, Danyang, et al. "Cryo-EM structures of S-OPA1 reveal its interactions with membrane and changes upon nucleotide binding." elife 9 (2020): e50294. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.50294
Anti-OPA1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-DHFR Recombinant Antibody (D0821) (CBMAB-D0821-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








