PTGS2 Antibodies
Background
Prostaglandin peroxidase 2 (PTGS2), also known as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), is a membrane-bound heme protease that mainly exists in the inflammatory sites, endothelial cells and specific tissues of mammals. This enzyme catalyzed the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandin precursors and played a core role in mediating inflammatory responses, pain signal transmission, and maintaining the stability of the internal environment of tissues. Unlike the structural isoenzyme PTGS1, the expression of PTGS2 can be rapidly induced by the stimulation of cytokines, growth factors, etc., and thus is regarded as a key regulatory factor in inflammatory and pathological processes. Since its identification in the 1990s, its three-dimensional structure and functional mechanism have been clarified through techniques such as X-ray crystallography. The related research not only promotes the targeted development of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs but also provides an important foundation for a deeper understanding of the association between cell signal transduction and diseases.
Structure of PTGS2
PTGS2 (prostaglandin endoperoxidase 2) is an enzyme protein with a molecular weight of approximately 70 kDa. This molecular weight is relatively constant among different mammalian species because its key enzyme functional domain is highly conserved.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 69-71 | 69-71 | 69-71 | 69-71 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 604 amino acids, with epidermal growth factor like structure is combined with membrane domains | Completely conservative sequence is highly homologous, active site | Shares more than 85% sequence similarity with human PTGS2 | The core catalytic domain is consistent with that of humans |
This protein contains approximately 600 amino acids, and its primary structure folds to form a typical three-part structure: an epidermal growth factor-like domain at the N-terminal, a transmembrane anchoring domain, and a large spherical catalytic domain at the C-terminal containing a heme cofactor. The secondary structure of PTGS2 is mainly composed of α -helices and β -folds, which together form a long hydrophobic channel. The key catalytic sites in its tertiary structure are composed of tyrosine-385 residues located deep in the channel and adjacent heme cofactors. The proximal histidine -388 residue coordinates with heme iron, while the distal arginine -120 and other residues are involved in stabilizing the substrate and regulating the specific synthesis of prostaglandin precursors.
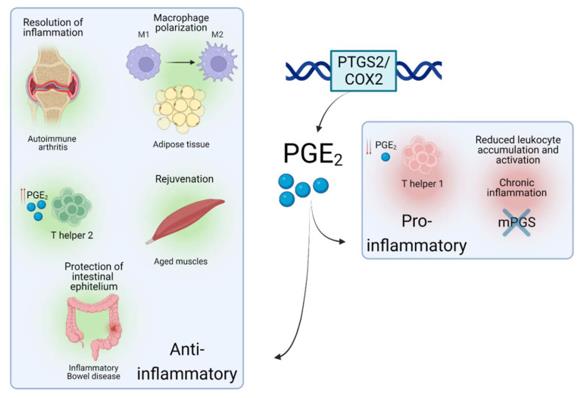 Fig. 1 Roles of PTGS2/COX2-PGE2 in different inflammatory situations.1
Fig. 1 Roles of PTGS2/COX2-PGE2 in different inflammatory situations.1
Key structural properties of PTGS2:
- Compact spherical catalytic domain
- Contains long hydrophobic channels as substrate binding sites
- Epoxidation reaction relies on heme excipients
Functions of PTGS2
The main function of the PTGS2 gene (prostaglandin peroxidase 2) is to catalyze a key step in prostaglandin biosynthesis. However, it also plays a core role in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including inflammatory responses, pain perception and cell proliferation regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Synthesis of prostaglandins | Catalyzing the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 is a key rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of all series of prostaglandins. |
| Inflammation mediation | Prostaglandins (such as PGE2) that are rapidly induced to express at the site of inflammation are key inflammatory mediators, causing vasodilation, pain and fever. |
| Pain signal transmission | Prostaglandins generated in damaged or inflamed tissues directly sensitize the surrounding pain neurons and amplify pain signals. |
| Tissue repair and protection | In tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, its basal expression has a protective effect on maintaining mucosal integrity and regulating renal blood flow. |
| Cell proliferation and differentiation | Involved in regulation of cell growth, differentiation of certain organization, and is associated with tumor development. |
The enzymatic activity kinetics of PTGS2 exhibits typical characteristics of Mie enzymes, and its catalytic efficiency is strictly regulated by the concentration of the substrate (arachidonic acid) and the REDOX state of heme. Compared with the constitutive expression of PTGS1, the induced expression of PTGS2 and its specific upregulation under pathological conditions make it an important target for anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.
Applications of PTGS2 and PTGS2 Antibody in Literature
- Martín-Vázquez, Eugenia, et al. "The PTGS2/COX2-PGE2 signaling cascade in inflammation: Pro or anti? A case study with type 1 diabetes mellitus." International journal of biological sciences 19.13 (2023): 4157. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.86492
The article indicates that prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is produced by the induced cyclooxygenase PTGS2/COX2 and plays a complex role in type 1 diabetes. It may not only promote pancreatic β -cell damage but also have a protective effect. Targeting this signaling pathway may provide new strategies for treatment.
- Yan, Suyan, et al. "ADAM17/PTGS2 Facilitates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Regulating Ferroptosis." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 29.5 (2025): e70466. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70466
Research has found that ADAM17 promotes pulmonary fibrosis by up-regulating PTGS2 and inducing ferroptosis in pulmonary fibroblasts. Inhibiting ADAM17 can effectively alleviate the fibrosis process in mouse models, providing a new target for the treatment of this disease.
- Jiang, Yun, et al. "LCN2 depletion aggravates sepsis-induced liver injury by regulating PTGS2-dependent ferroptosis." International journal of medical sciences 21.14 (2024): 2770. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.98246
Studies have revealed that lipocalin 2 (LCN2) exerts a protective effect in septic liver injury by inhibiting the expression of PTGS2 to alleviate ferroptosis. The deficiency of LCN2 will aggravate liver damage.
- Li, Zhao-Cheng, and Fu An. "ERBB2-PTGS2 axis promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating senescence of nucleus pulposus cells." BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 24.1 (2023): 504. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-023-06625-1
Research has found that the aging and degeneration of intervertebral disc cells are closely related. The ERBB2 gene alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting the expression of PTGS2 and delaying the aging of nucleus pulposus cells. The ERBB2-PTGS2 axis provides a new target for the treatment of this disease.
- Tan, Cheng, et al. "Activation of PTGS2/NF‐κB signaling pathway enhances radiation resistance of glioma." Cancer medicine 8.3 (2019): 1175-1185. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1971
Research has found that PTGS2 enhances radiotherapy tolerance in gliomas by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway, and its overexpression can promote tumor proliferation and reduce DNA damage. This pathway provides a new target for the treatment of glioma.
Creative Biolabs: PTGS2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality PTGS2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom PTGS2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our PTGS2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Martín-Vázquez, Eugenia, et al. "The PTGS2/COX2-PGE2 signaling cascade in inflammation: Pro or anti? A case study with type 1 diabetes mellitus." International journal of biological sciences 19.13 (2023): 4157. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.86492
Anti-PTGS2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CASQ1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0863) (CBMAB-C0918-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 (Phospho-Ser3) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1770) (CBMAB-C1832-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0435) (CBMAB-0437-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






