S100A9 Antibodies
Background
S100A9 is a small molecule calcium-binding protein mainly expressed in neutrophils and macrophages, and usually forms a heterodimer with S100A8 to jointly participate in the regulation of inflammatory responses. This protein plays a core role in innate immune responses and chronic inflammatory pathological processes by regulating the chemotaxis, phagocytosis of immune cells and the release of inflammatory mediators. In various autoimmune diseases and tumor microenvironments, S100A9 has been confirmed to be a key regulator of inflammatory signaling pathways, and its expression level is closely related to the severity of the disease. After being first characterized by a German research team in 1992, this protein has become an important subject in immunodiagnosis and targeted therapy research due to its outstanding role in diseases such as sepsis, arthritis and Alzheimer's disease. Its precise response mechanism to calcium ion signals and interaction patterns with other proteins continuously provide new molecular perspectives for the study of immune regulation and disease mechanisms.
Structure of S100A9
S100A9 is a calcium-binding protein with a molecular weight of approximately 13.2 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 13.2 | 13.1 | 13.3 | 13.0 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 2 EF-hand calcium-binding domains | 76% homology with human S100A9 | Conservative dimerization interface | Calcium ion binding sites are highly conserved |
This protein is composed of 114 amino acids and forms a stable dimer conformation through its primary structure. The core structure of S100A9 contains two EF-hand mods, a characteristic domain that enables it to specifically bind calcium ions. The sparse pockets on the protein surface and the zinc ion binding sites determine its interaction ability with the target protein. Two helical-ring-helical regions are connected through hinge regions. After calcium ions combine, conformational rearrangement occurs, exposing hydrophobic residues and thereby regulating their biological functions.
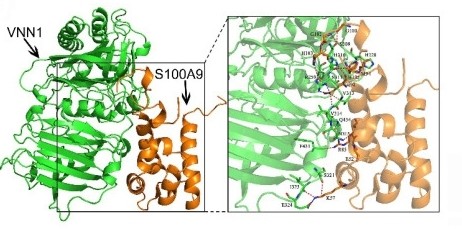 Fig. 1 Binding model between S100A9 protein and VNN1 protein.1
Fig. 1 Binding model between S100A9 protein and VNN1 protein.1
Key structural properties of S100A9:
- Stable EF-hand calcium-binding domain configuration
- Conservative polymerization interface to form two hydrophobic core
- Zinc ion binding sites regulate immune function
Functions of S100A9
The core function of S100A9 is to regulate inflammatory responses and immune responses. Meanwhile, it is also involved in various pathophysiological processes such as cell migration, tumor progression and oxidative stress.
| Function | Description |
| Inflammatory regulation | S100A8 formed calcium protein complexes, activation of TLR4 signaling pathways, and promote the release of proinflammatory factor. |
| Immunochemotaxis | As a damage-related molecular model molecule, it recruits immune cells such as neutrophils to gather at the inflammatory site. |
| Regulation of cell migration | By binding to the cell surface receptor RAGE, it regulates the transendothelial migration and movement direction of white blood cells. |
| Shaping of the tumor microenvironment | To promote angiogenesis in tumor tissues with high expression, and inhibit anti-tumor immune response. |
| Regulation of oxidative stress | Eliminate reactive oxygen species and protect immune cells from oxidative damage in an inflammatory environment. |
The calcium ion binding curve of S100A9 shows a synergistic effect, similar to calmodulin, indicating that it can serve as a key converter for intracellular calcium signals and inflammatory responses.
Applications of S100A9 and S100A9 Antibody in Literature
1. Shen, Shichun, et al. "Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals S100a9hi macrophages promote the transition from acute inflammation to fibrotic remodeling after myocardial ischemia‒reperfusion." Theranostics 14.3 (2024): 1241. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.91180
This study reveals that S100A9 highly expressing macrophages exacerbate acute inflammation through the Myd88/NFκB/NLRP3 pathway after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion, and promote fibrosis and macrophage-myofibroblast transformation through TGF-β/p-smad3 signaling. Targeted inhibition of S100A9 can effectively alleviate this pathological process.
2. Liu, Xi, et al. "S100A9 deletion in microglia/macrophages ameliorates brain injury through the STAT6/PPARγ pathway in ischemic stroke." CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 30.8 (2024): e14881. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.14881
Studies have confirmed that the high expression of S100A9 macrophages is the key to the deterioration of prognosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. It drives early inflammation and activates TGF-β signaling, directly promoting fibrosis through macrophage-myofibroblast transformation. Targeting S100A9 can effectively alleviate this process.
3. Franz, Sandra, et al. "Overexpression of S100A9 in obesity impairs macrophage differentiation via TLR4-NFkB-signaling worsening inflammation and wound healing." Theranostics 12.4 (2022): 1659. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.67174
Research has found that overexpression of S100A9 in an obese environment is the key factor leading to dysfunction of macrophages. It forms a vicious cycle with saturated fatty acids, inhibiting the differentiation of anti-inflammatory M2-type macrophages by activating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, thereby exacerbating skin inflammation and hindering wound repair. Targeted inhibition of S100A9 can effectively break this cycle.
4. Huo, Shengqi, et al. "Macrophage-derived S100A9 promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy by disturbing mitochondrial quality control via STAT3 activation." International Journal of Biological Sciences 21.7 (2025): 3061. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.111128
This study reveals that macrophage-derived S100A9 is a key mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. It causes cardiac dysfunction by activating the STAT3 signal in myocardial cells, leading to excessive mitochondrial division and disorder of the quality control system. Targeting S100A9 can effectively improve the above-mentioned pathological processes.
5. Zhang, Yanting, et al. "Deficiency of S100A9 alleviates sepsis-induced acute liver injury through regulating AKT-AMPK-dependent mitochondrial energy metabolism." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.3 (2023): 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032112
This study reveals for the first time that S100A9 aggravates liver injury by inhibiting the AMPK pathway and disrupting mitochondrial energy metabolism in acute liver injury caused by sepsis. Intervention with the S100A9 inhibitor Paquinimod can effectively improve liver function and energy metabolism, providing a new idea for clinical prevention and treatment.
Creative Biolabs: S100A9 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality S100A9 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom S100A9 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our S100A9 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Xiang, Hong, et al. "Pancreatic ductal deletion of S100A9 alleviates acute pancreatitis by targeting VNN1-mediated ROS release to inhibit NLRP3 activation." Theranostics 11.9 (2021): 4467. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.54245
Anti-S100A9 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD19 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1224) (CBMAB-C1491-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CEMIP Recombinant Antibody (3C12) (CBMAB-K0296-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD59 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2097) (CBMAB-C4421-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








