STAT6 Antibodies
Background
STAT6 is a key cytoplasmic transcription factor, mainly present in immune cells and epithelial cells. This protein plays a core role in the IL-4 and IL-13 cytokine signaling pathways and participates in immunomodulatory responses by mediating the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway, including processes such as Th2 cell differentiation, antibody class conversion, and anti-parasitic immunity. Defects in the STAT6 gene can lead to abnormal immune function and are closely related to pathological conditions such as allergic diseases and inflammatory bowel disease. Since its discovery in the 1990s, STAT6 has not only become an important target in immunological research, but also its unique structural features (such as the specific binding mechanism of the SH2 domain to phosphorylated tyrosine) have provided a molecular basis for the development of targeted drugs, significantly advancing the research on therapeutic strategies for immune-related diseases.
Structure of STAT6
STAT6 is a transcription factor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. This molecular weight is highly conserved in different mammals, mainly due to its criticality in signal transduction function.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Non-human primates |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 94 | 93.8 | 94.2 | 94.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains a dna-binding domain and 1 SH2 domain structure | The SH2 domain is highly conserved | High homology with human sequence | Amino acid sequence and humans are basically identical |
The STAT6 protein is composed of 847 amino acids and has a typical family structure of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT). Its primary structure consists of a coiled-coil domain, a central DNA-binding domain and a carboxyl-terminal transcriptional activation domain. The core function of this protein depends on its SH2 domain, which mediates the dimerization and nuclear translocation of STAT6 itself by recognizing the intracellular part of the phosphorylated IL-4 receptor. Dimerization is a necessary step to activate the transcription of downstream genes and mainly participates in the regulation of Th2 immune responses.
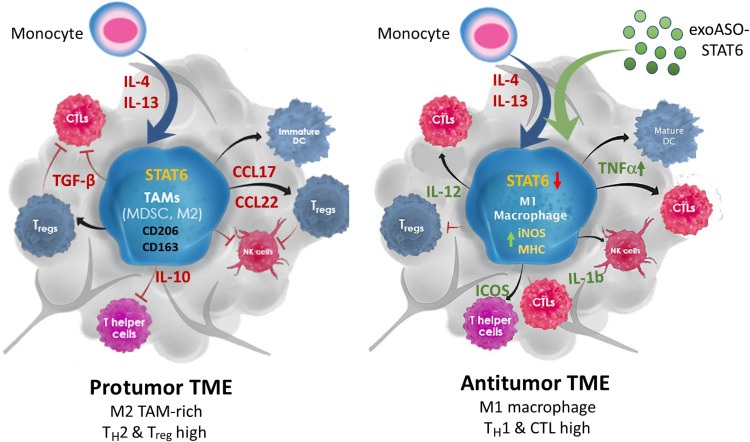 Fig. 1 exoASO-STAT6 reprograms TAMs to fight tumors.1
Fig. 1 exoASO-STAT6 reprograms TAMs to fight tumors.1
Key structural properties of STAT6:
- Contains the DNA-binding domain and SH2 domain
- SH2 domains mediate interactions with phosphorylated tyrosines
- Functional transcription factors are formed through dimerization
- Has approved a signal and the structure of transcription activation domain
Functions of STAT6
The core function of the STAT6 gene is to mediate the cytokine signal transduction of IL-4 and IL-13. In addition, it is widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes such as immune regulation, cell differentiation and inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of immune response | As a key transcription factor of Th2 immune response, it promotes the differentiation of helper T cells into Th2 subtypes and drives anti-parasitic and allergic immune responses. |
| Antibody category conversion | Regulating the category conversion of immunoglobulin heavy chains in B cells, especially promoting the production of IgE and IgG1, is closely related to allergic diseases. |
| Cell proliferation and differentiation | Participate in regulating a variety of cells (such as lymphoid cells, epithelial cells and tumor cells) of proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis process. |
| Inflammation suppression | Activate alternative activation pathways (M2-type polarization) in macrophages to exert anti-inflammatory and tissue repair functions. |
| Association with tumor progression | Abnormal activation in some cancers (such as lymphoma, breast cancer) promotes tumor cell survival, proliferation and immune escape. |
The activation of STAT6 depends on tyrosine phosphorylation mediated by JAK kinase, which then forms a homodimer and translocates to the nucleus, binding to specific response elements in the target gene promoter, thereby precisely regulating gene transcription. Its dysfunction is closely related to the development of allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases and various malignant tumors.
Applications of STAT6 and STAT6 Antibody in Literature
1. Kamerkar, Sushrut, et al. "Exosome-mediated genetic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by exoASO-STAT6 leads to potent monotherapy antitumor activity." Science advances 8.7 (2022): eabj7002. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj7002
The article indicates that for the key target of STAT6, the engineered exosome exoASO-STAT6 has been developed and researched. It can specifically silence the expression of STAT6 in tumor-associated macrophages, successfully reprogram it to the M1 phenotype, effectively activate anti-tumor immunity and significantly inhibit tumor growth.
2. Huang, Chongyang, et al. "Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization through the STAT6-dependent signaling pathway." BMC medicine 20.1 (2022): 148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-022-02352-x
Research has found that ketone body BHB can promote the polarization of macrophages to M2 type by activating the STAT6 signaling pathway, thereby alleviating intestinal inflammation and promoting tissue repair. The content of BHB in the colonic mucosa of IBD patients is decreased. Supplementing exogenous BHB can significantly improve the symptoms of experimental colitis.
3. Chao, Hua, et al. "IL-13RA2 downregulation in fibroblasts promotes keloid fibrosis via JAK/STAT6 activation." JCI insight 8.6 (2023): e157091. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.157091
Research has found that the number of M2-type macrophages in keloids increases, and the phosphorylation level of STAT6 rises. Down-regulation of IL-13RA2 promotes the fibrosis process by activating STAT6 signaling; Inhibiting STAT6 can effectively reduce cell proliferation, migration and fibrotic phenotypes, providing a basis for targeted treatment of the JAK/STAT6 pathway.
4. Zhou,and Zhengfan Jiang. "N4 DNA recognition by STAT6: structural and functional implications." Protein & cell 8.4 (2017): 240-241. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s13238-017-0380-z
Li et al. first revealed the molecular mechanism by which STAT6 specifically recognizes the N4 site in DNA. As an important transcription factor, STAT6 not only participates in the immune response mediated by IL-4/IL13, but also participates in antiviral innate immunity through the STING pathway. Its abnormal expression is closely related to inflammation and tumors, and has important clinical significance.
5. Lee, Ye-JI, et al. "STAT6 signaling mediates PPARγ activation and resolution of acute sterile inflammation in mice." Cells 10.3 (2021): 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030501
Research has found that STAT6 regulates macrophage function by activating the PPARγ signaling pathway. In acute aseptic inflammation models, the absence of STAT6 exacerbates inflammatory responses, reduces efferocytosis ability, and hinders inflammation resolution. It indicates that the STAT6-PPARγ axis plays a key role in promoting inflammatory resolution.
Creative Biolabs: STAT6 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality STAT6 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom STAT6 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our STAT6 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Kamerkar, Sushrut, et al. "Exosome-mediated genetic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by exoASO-STAT6 leads to potent monotherapy antitumor activity." Science advances 8.7 (2022): eabj7002. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abj7002
Anti-STAT6 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








