TBP Antibodies
Background
TBP (TATA box binding protein) is a core transcription factor widely present in eukaryotes. As a key component of the transcription initiation complex TFIID, TBP mediates the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to regulate gene transcription initiation by specifically recognizing and binding to the TATA box sequence in the promoter region. This protein is highly conformed in evolution and has a unique saddle-shaped three-dimensional structure. It can be embedded in DNA grooves and induce double-strand bending, providing a structural basis for the assembly of transcriptional complexes. In 1993, Nikolaus Pavletich and Carl Pabo used X-ray crystallography to resolve the high-resolution structure of the TPP-DNA complex for the first time, revealing the precise mechanism of the interaction between proteins and DNA. As a classic model for studying eukaryotic transcriptional regulation, TBP not only deepens people's understanding of gene expression regulation, the synergistic effect of transcription factors and epigenetic modifications, but also its functional abnormalities are closely related to various developmental defects and diseases, highlighting its important biological significance.
Structure of TBP
TBP (TATa-box Binding Protein) is a 38kDa nucleoprotein that specifically recognizes the TATA box sequence through its unique saddle-shaped structure and plays a core role in transcriptional initiation.
The structure-function relationship of TBP:
- DNA binding domain structure made up of two conservative repetitive structure domain (CR1 / CR2) the saddle conformation, embeddable DNA minor groove and induction of 80°bend, through the hydrophobic effect and hydrogen bond stability combined with TATA box (5 '- TATAAA - 3'), basis for transcription initiation complex assembly structure.
- The N-terminal variable region of the transcription factor interaction interface binds to transcription factors such as TFIIA and TFIIB. The upper surface groove specifically binds to TFIIB, and interacts with TFIIA on the side, jointly maintaining the stability of the transcription complex and regulating the initiation efficiency.
- C terminal control structure domain contains beta folding layer to maintain rigidity structure, some species, such as yeast C side contains phosphorylation sites, dynamic regulating transcription activity, show the evolution of conservative and diversity.
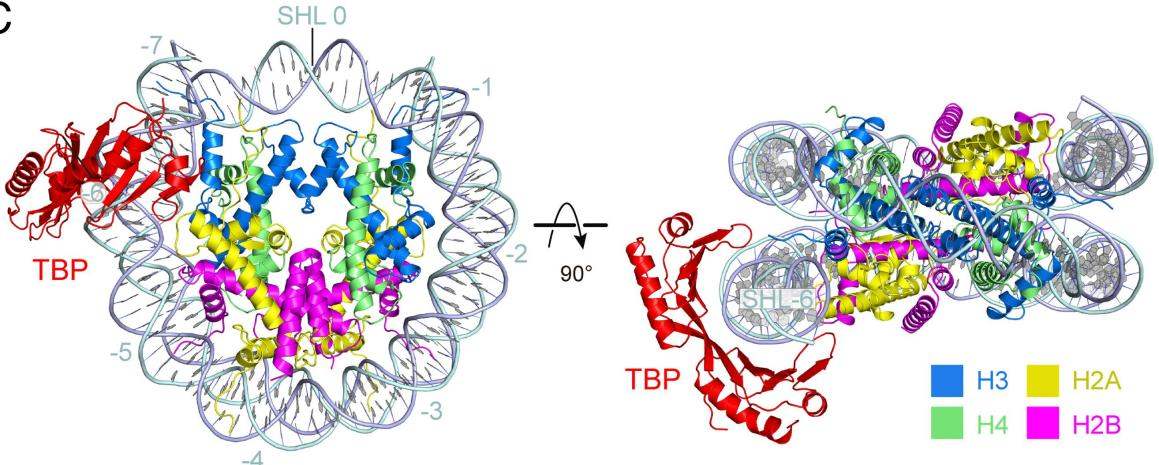 Fig. 1 Structure of the TBP–NCP complex.1
Fig. 1 Structure of the TBP–NCP complex.1
Functions of Myoglobin
The core function of TBP (TATA-box Binding Protein) is to mediate the initiation of eukaryotic transcription, and it also plays an important role in chromatin remodeling and the occurrence of diseases.
| Function | Description |
| Transcription Initiation | Specifically recognize and bind to the TATA box sequence, recruit RNA polymerase II and universal transcription factors to form transcription initiation complexes. |
| Chromatin Remodeling | By interacting with histone modification enzymes, it regulates local chromatin structure and gene accessibility. |
| Transcriptional Regulation | Enhances oxygen availability in tissues during low-oxygen conditions, supporting survival in hypoxic environments. |
| Developmental Regulation | Selectively activate specific gene expression programs during embryonic development. |
| Disease Association | Abnormal expression is associated with the occurrence and development of various cancers and neurodegenerative diseases. |
The binding of TBP to DNA presents a unique saddle-shaped conformation, inducing DNA curvature of approximately 80°. This structural feature enables it to interact with multiple transcription factors simultaneously, forming a highly specific transcriptional regulatory network. Compared with the synergistic mode of general transcription factors, TBP shows a more complex interaction spectrum in the regulation of tissue-specific expression.
Applications of TBP and TBP Antibody in Literature
1. Kim, Joseph L., and Stephen K. Burley. "1.9 Å resolution refined structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of TATAAAAG." Nature structural biology 1.9 (1994): 638-653. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0994-638
This study analyzed the three-dimensional structure of the TBP complex with the 14bp TATA element of the main late promoter of adenovirus (R factor 19.4%), revealed the molecular mechanism by which the monomer maroon α/β protein induced unique conformational changes in DNA, and focused on clarifying the molecular basis of DNA deformation, TATA element recognition and transcription initiation complex assembly.
2. Wang, Haibo, Le Xiong, and Patrick Cramer. "Structures and implications of TBP–nucleosome complexes." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118.30 (2021): e2108859118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2108859118
This study found through cryo-electron microscopy that yeast TBP can bind to specific sites of nucleosomes with the assistance of TFIIA. The spatial steric hindrance formed explains the structural basis that promoter nucleosomes must be displaced to initiate transcription.
3. Burley, Stephen K. "The TATA box binding protein." Current opinion in structural biology 6.1 (1996): 69-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-440X(96)80097-2
Studies have shown that TBP, as a key factor for the transcription initiation of three eukaryotic RNA polymerases, has recently made significant breakthroughs in the research on the structure of the complex formed with TATA elements and the transcription factor IIB, revealing the molecular mechanism of transcription initiation.
4. Bauer, Andreas, Otmar Huber, and Rolf Kemler. "Pontin52, an interaction partner of β-catenin, binds to the TATA box binding protein." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95.25 (1998): 14787-14792. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.25.14787
This study identified a new type of protein interactions beta catenin Pontin52, it not only with beta 2-5 - catenin Armadillo repeat area, also can connect TATA box binding protein (the TBP), The in vivo multiprotein complex composed of Pontin52, β-catenin and lymphocyte enhancer factor-1 /T cytokine was confirmed, revealing the regulatory role of Pontin52 in the nuclear function of β-catenin.
5. Metz, Richard, et al. "c-Fos-induced activation of a TATA-box-containing promoter involves direct contact with TATA-box-binding protein." Molecular and cellular biology 14.9 (1994): 6021-6029.https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.14.9.6021-6029.1994
This study reveals that c-Fos activates transcription by directly interacting with TATA box-binding protein (TBP) through its unique TBP binding motif (TBM), while Fra-1 lacks this function, indicating that the activation mechanism mediated by TBP is a key feature of the functional differentiation of FOS-related proteins.
Creative Biolabs: TBP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in manufacturing high-quality TBP (TATA box-binding protein) antibodies, which are suitable for both scientific research and industrial fields. We offer product lines of monoclonal antibodies for techniques such as Western blot, co-immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunofluorescence to meet the diverse needs of basic research and clinical diagnosis.
- Custom TBP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TBP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at info@creative-biolabs.com.
Reference
- Wang, Haibo, Le Xiong, and Patrick Cramer. "Structures and implications of TBP–nucleosome complexes." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118.30 (2021): e2108859118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2108859118
Anti-TBP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (D9S6V) (CBMAB-CP0017-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-A2M Recombinant Antibody (V2-178822) (CBMAB-A0036-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (61-3E7) (CBMAB-1183-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








