THBS1 Antibodies
Background
THBS1 (thrombospondin-1) is a multi-domain glycoprotein secreted by various cells, mainly existing in the extracellular matrix and platelet alpha granules. This protein participates in regulating processes such as cell adhesion, migration, proliferation and apoptosis by interacting with cell surface receptors, cytokines and matrix components, and plays a key role in angiogenesis, tissue repair and immune regulation. THBS1 was first identified in 1971. Its complex modular structure and multiple biological functions make it a typical model for the study of extracellular matrix proteins. The bidirectional regulatory mechanism of this protein in tumor progression, fibrotic diseases and thrombosis has been widely studied, significantly deepening people's understanding of the cellular microenvironment signaling network and pathophysiological processes.
Structure of THBS1
THBS1 is a relatively large multi-domain glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 145 kDa. Its molecular weight may vary within a certain range under the influence of post-translational modifications such as glycosylation and polymerization.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~145 | ~140 | ~142 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing N, before the end of the collagen with source area, three repetition of type I, II, III structure domain, the C ball area | Domain structure of highly conservative, amino acid sequence homology of about 90% | With the human THBS1 this similarity in functional domain structure |
This protein is composed of approximately 1,152 amino acids, and its complex tertiary structure is mainly made up of multiple independently folded functional domains. The structural core of THBS1 contains a trimer formed by three identical subunits linked by disulfide bonds. Its structural features include a heparin-binding domain at the N-terminal, a procollagen homologous region, three type I repeat sequences (responsible for binding to cell surface receptors such as CD36 and integrin), three type II repeat sequences (related to collagen binding), and a globular calcium-binding domain at the C-terminal. This modular structure enables it to interact simultaneously with extracellular matrix components, growth factors and multiple cell surface receptors, thereby precisely regulating cell behavior.
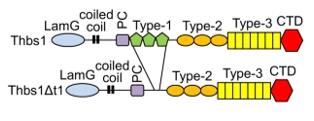 Fig. 1 Domain Structures of WT Thbs1 and the ΔT1 Mutant.1
Fig. 1 Domain Structures of WT Thbs1 and the ΔT1 Mutant.1
Key structural properties of THBS1:
- Modular multi-domain trimer structure
- Stable conformation of multiple calcium ion binding sites
- Three type I repeat sequences mediate cell receptor recognition
- The C-terminal globular domain is involved in cell signaling
Functions of THBS1
The primary function of THBS1 is to act as a multifunctional regulatory protein in the extracellular matrix, participating in cell communication and tissue remodeling. However, it also extensively involves a variety of pathophysiological processes, including angiogenesis, tumor development and immune regulation.
| Function | Description |
| Anti-angiogenesis | By binding to receptors such as CD36 through its type I repeat sequence, it inhibits the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells, thereby suppressing the formation of new blood vessels. |
| Regulation of cell adhesion and migration | By interacting with various cell surface receptors such as integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans, it bidirectionally regulates the adhesion, spreading and migration behaviors of cells. |
| Tissue repair and fibrosis | By activating TGF-β and other pathways, it promotes fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix deposition, and participates in wound healing and fibrosis. |
| Immune regulation | Interact with receptors on the surface of macrophages, adjust its polarization state and secretion of cytokines, inflammatory reaction process. |
| Regulation of tumor progression | Play a complex role in tumor microenvironment, early may inhibit tumor growth, terminal, often by promoting the transformation of epithelial - interstitial and immune escape mechanism to accelerate the tumor invasion and metastasis. |
The function of THBS1 shows a high degree of environmental dependence. Its specific role in tissue homeostasis, repair and disease development depends on the spatiotemporal specificity of its expression, the state of proteolytic processing and the combination of cellular microenvironment signals in which it is located.
Applications of THBS1 and THBS1 Antibody in Literature
- Vanhoutte, Davy, et al. "Thbs1 induces lethal cardiac atrophy through PERK-ATF4 regulated autophagy." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 3928. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24215-4
Research has found that thrombin sensitive protein-1 (Thbs1) specifically activates the endoplasmic reticulum stress protein PERK, driving ATF4-mediated autophagy, which leads to myocardial atrophy and fatal heart failure. This mechanism is independent of other Thbs members and receptors and directly regulates the size of cardiomyocytes under stress conditions.
- Omatsu, Mayuki, et al. "THBS1-producing tumor-infiltrating monocyte-like cells contribute to immunosuppression and metastasis in colorectal cancer." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 5534. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41095-y
Studies have found that the high expression of THBS1 in tumor-associated monocytes is a key driver of the stromal activation phenotype in colorectal cancer. It promotes metastasis and immunosuppression by inducing T-cell exhaustion and damaging angiogenesis, leading to a poor prognosis.
- Shen, Jie, et al. "Hippo component YAP promotes focal adhesion and tumour aggressiveness via transcriptionally activating THBS1/FAK signalling in breast cancer." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 37.1 (2018): 175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0850-z
This study reveals that YAP regulates THBS1 expression through TEAD transcription, thereby activating FAK phosphorylation, promoting the formation of adhesion spots in breast cancer cells and enhancing their invasion and metastasis capabilities. The YAP/THBS1/FAK axis provides a new mechanism for the interaction between the Hippo pathway and adhesion signals.
- Zhang J, Chen W, et al. "M1-like tumor-associated macrophages activated by exosome-transferred THBS1 promote malignant migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 37.1 (2018): 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0815-2
This study reveals that THBS1 is enriched in exosomes of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and can induce tumor-associated macrophages to polarize into M1-like phenotypes. The cytokines secreted by the latter instead promote the migration of cancer cells, forming a positive feedback loop that promotes cancer.
- Corbella, Eleonora, et al. "THBS1 and THBS2 enhance the in vitro proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.3 (2024): 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031782
The article indicates that THBS1 and THBS2 not only promote lymphatic metastasis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, but also directly act on cancer cells, enhancing their proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion abilities. The effect of THBS2 in inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition is particularly significant, further exacerbating the malignant progression of tumors.
Creative Biolabs: THBS1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality THBS1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom THBS1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our THBS1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Vanhoutte, Davy, et al. "Thbs1 induces lethal cardiac atrophy through PERK-ATF4 regulated autophagy." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 3928. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24215-4
Anti-THBS1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Antibody (V2-502280) (CBMAB-C1055-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






