TNFAIP3 Antibodies
Background
TNFAIP3 is a zinc finger protein widely present in the cytoplasm and mainly plays a key role in immune and inflammatory responses. The A20 protein encoded by this gene can simultaneously regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway and the apoptosis process through its unique OTU domain and zinc finger motifs, thereby maintaining immune homeostasis. In autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, the functional abnormality of TNFAIP3 is closely related to pathological development. This gene was first identified by a research team in 1990 during a tumor necrosis factor induction experiment. Its unique dual deubiquitinating enzyme and ubiquitin ligase activity mechanism provides an important molecular basis for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies and deepens people's understanding of the immune regulatory network.
Structure of TNFAIP3
TNFAIP3 is a zinc finger protein with a molecular weight of approximately 89 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies depending on the species and the splicing method of the transcript.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 89.2 | 88.7 | 88.9 | 89.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 7 zinc finger domains of type A20 | There are two amino acid substitutions in the structure of the C-terminal zinc finger | 95% homology with human sequence | Completely conservative OTU structure domain |
This protein is composed of 790 amino acids, and its primary structure includes the N-terminal OTU deubiquitinating enzyme domain and the C-terminal A20 zinc finger module. The OTU domain constitutes the core catalytic center of proteins, among which the conserved cysteine residues are crucial for enzyme activity. The zinc finger array at the C-end forms the functional region of ubiquitin ligase. These two domains work in synergy through an α -helical linker peptide to jointly achieve bidirectional regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
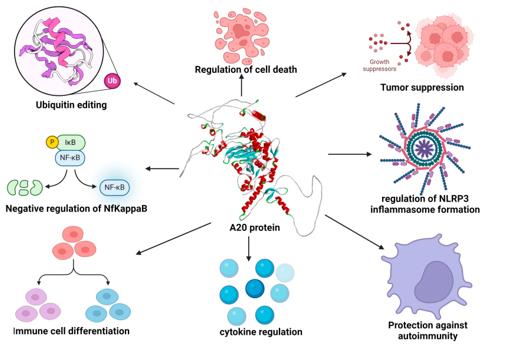 Fig. 1 Functions of TNFAIP3 (A20) protein.1
Fig. 1 Functions of TNFAIP3 (A20) protein.1
Key structural properties of TNFAIP3:
- Unique OTU catalytic domain and synergy of A20 type zinc finger module
- Bifunctional active centers regulate enzyme activity through allosteric effects
- Specific zinc finger motifs recognize the K63/K48 ubiquitin chain topology
- Conserved cysteine residues constitute the deubiquitination active site
- Molecular surface there are multiple phosphorylation control site
Functions of TNFAIP3
The core function of protein A20 encoded by the TNFAIP3 gene is to maintain the balance of immune homeostasis. Its specific mechanisms of action include:
| Function | Description |
| Negative regulation of inflammatory signals | Clearing the K63 ubiquitin chain through the OTU domain terminates the activation of inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB. |
| Regulation of apoptosis | Intervene in the assembly of death receptor signaling complexes to inhibit programmed death caused by excessive immune responses. |
| Innate immune balance | Negative feedback regulates pattern recognition receptor (such as TLR) signals to prevent excessive activation of antiviral responses. |
| Autoimmunity prevention | The zinc finger structure mediates the ubiquitination of K48, degrading key signaling molecules to prevent the occurrence of autoimmune diseases. |
| Participation in tissue repair | Promote the reconstruction of tissue homeostasis and coordinate the injury repair process during the stage when inflammation subsides. |
The unique dual-enzyme activity of A20 enables it to simultaneously edit both activating and inhibitory ubiquitin modifications. This "molecular switch" characteristic makes it play a core regulatory role in immune responses, and its functional abnormalities are closely related to the occurrence of various autoimmune diseases and lymphomas.
Applications of TNFAIP3 and TNFAIP3 Antibody in Literature
1. Bagyinszky, Eva, and Seong Soo A. An. "Genetic Mutations Associated With TNFAIP3 (A20) Haploinsufficiency and Their Impact on Inflammatory Diseases." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.15 (2024): 8275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158275
The article indicates that mutations in the TNFAIP3 (A20) gene can lead to various autoimmune diseases such as Behcet's disease, causing immune disorders. It is recommended that patients with autoinflammation undergo this genetic test to guide diagnosis and treatment.
2. Zammit, Nathan W., et al. "TNFAIP3 reduction-of-function drives female infertility and CNS inflammation." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 811525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.811525
The article indicates that the Tnfaip3 loss-of-function variant causes reproductive problems such as ebony cycle disorders and insulin resistance in mice by triggering neuroinflammation and hormonal imbalances, suggesting that hyperimmunity may come at the expense of fertility.
3. Wang, Ming-Jie, et al. "TNFAIP3 gene rs10499194, rs13207033 polymorphisms decrease the risk of rheumatoid arthritis." Oncotarget 7.50 (2016): 82933. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12638
The article indicates that the polymorphisms of rs10499194 and rs13207033 in the TNFAIP3 gene can reduce the risk of rheumatoid arthritis, and this protective effect is particularly significant in the white population, but not observed in the Asian population.
4. Yang, Jiajia, et al. "TNFAIP3 genetic polymorphisms reduce ankylosing spondylitis risk in Eastern Chinese Han population." Scientific Reports 9.1 (2019): 10209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46647-1
Studies have shown that the T allele of the rs10499194 polymorphism of the TNFAIP3 gene may reduce the risk of ankylosing spondylitis, especially in specific subgroups such as males and HLA-B27 positive individuals, where the protective effect is more significant.
5. Chen, Cunte, et al. "TNFAIP3 mutation is an independent poor overall survival factor for patients with T‐cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Cancer medicine 12.4 (2023): 3952-3961. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.5196
Studies have shown that TNFAIP3 gene mutations are more common in adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and are significantly associated with poor prognosis in patients, serving as an independent prognostic risk biomarker.
Creative Biolabs: TNFAIP3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality TNFAIP3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom TNFAIP3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our TNFAIP3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Bagyinszky, Eva, and Seong Soo A. An. "Genetic Mutations Associated With TNFAIP3 (A20) Haploinsufficiency and Their Impact on Inflammatory Diseases." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.15 (2024): 8275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158275
Anti-TNFAIP3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0790) (CBMAB-0793-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTG1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179597) (CBMAB-A0916-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FeLV g27 Recombinant Antibody (1) (CBMAB-V208-1714-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








