Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) Pathway
1. What is Unfolded Protein Response?
The unfolded protein response (UPR) helps maintaining protein homeostasis within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a membrane-bound organelle crucial for folding and post-translational modifications of secreted and membrane proteins. If protein folding or transport is compromised, unfolded proteins build up in the ER lumen, resulting in "ER stress". In response, the UPR mitigates the unfolded protein load by expanding the ER membrane, selectively synthesizing key folding components, eliminating slow-folding proteins, and decreasing protein entry into the ER.
2. Three Key Branches of the Unfolded Protein Response
The UPR is orchestrated by three main sensors: inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6), and protein kinase R-like ER kinase (PERK). These ER-localized transmembrane proteins become activated during ER stress to trigger UPR signaling. They consist of three domains: a single transmembrane-spanning domain, a cytosolic domain, and an ER luminal domain (LD), which senses unfolded/misfolded proteins directly or indirectly. Under normal conditions, these sensors—IRE1, ATF6, and PERK—remain inactive as they are bound to the chaperone protein BiP/GRP78, which is essential for maintaining ER homeostasis. Upon ER stress, these domains disassociate from BiP, activating the UPR. This process adjusts protein translation, transport, and degradation rates to restore normal ER function.
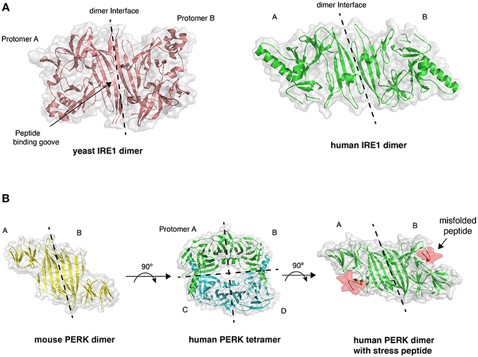 Fig.1 Crystal structures of LD.1,4
Fig.1 Crystal structures of LD.1,4
2.1 IRE1
There are two different isomers of IRE1. The more active IRE1α is expressed throughout the body, and IRE1β is specifically expressed in intestinal and lung epithelial cells. Under ER stress, IRE1α, which has protein kinase and RNA endonuclease (RNase) activities, is activated through three mechanisms. The first is the 'competition' or 'chaperone inhibition' model, suggests that BiP is the true sensor of ER stress. This model allows IRE1α dimerization and UPR activation upon IRE1 dissociation. The second is the 'allosteric' model, where BiP uses its nucleotide binding domain (NBD) to block the oligomerization of IRE1α, and triggers the dissociation of the BiP-IRE1α complex through competitive binding with unfolded proteins. The third 'direct' model indicates unfolded proteins directly interact with ScIRE1 and IRE1α, stabilizing their dimeric and higher oligomeric assemblies to facilitate UPR signaling.
Upon activation, IRE1's RNase activity enables it to specifically cleave XBP1 mRNA, splicing out a 26-bp intron and producing the transcriptionally active XBP1s protein. XBP1s upregulates genes involved in protein transport, folding, secretion, and degradation to counteract ER stress. IRE1's RNase also mediates regulated IRE1-dependent decay (RIDD), degrading specific mRNAs and precursor miRNAs to reduce ER protein load during stress. Moreover, activated IRE1 can bind to TRAF2, promoting JNK signaling and triggering apoptosis in response to severe or chronic ER stress.
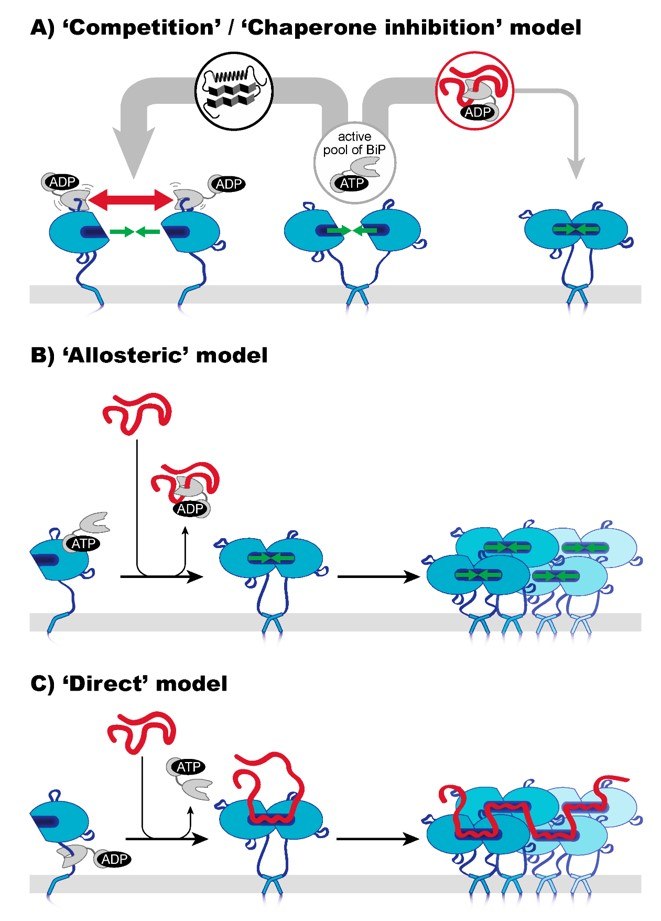 Fig.2 Three models of how IRE1α might sense ER stress. 2,4
Fig.2 Three models of how IRE1α might sense ER stress. 2,4
2.2 ATF6
ATF6, a transmembrane protein encoding a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor, is localized to the ER under normal conditions through its association with BiP. Upon ER stress, ATF6 disengages from BiP and translocates to the Golgi apparatus, where it undergoes sequential proteolytic cleavage by the site-1 protease (S1P) and site-2 protease (S2P). This cleavage process liberates a fragment containing the bZIP domain, termed 'ATF6p50', which then translocates to the nucleus to exert its transcriptional activity. Along with XBP1s, it regulates genes involved in protein transport, folding, secretion, and degradation of unfolded proteins.
2.3 PERK
Upon ER stress, PERK phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), curbing protein synthesis and easing the ER's protein-folding burden. This process involves upregulated transcription factors ATF4 and CHOP. They drive the transcription of genes in amino acid metabolism, antioxidant responses, and autophagy, while also boosting GADD34 expression to dephosphorylate eIF2α. Since PERK isn't the only kinase affecting eIF2α phosphorylation, other kinases can perform similar roles when cells encounter different stresses. While PERK activation is an adaptive response to ER stress, it can also trigger apoptotic signaling through various means, like upregulating pro-apoptotic factors downstream of CHOP.
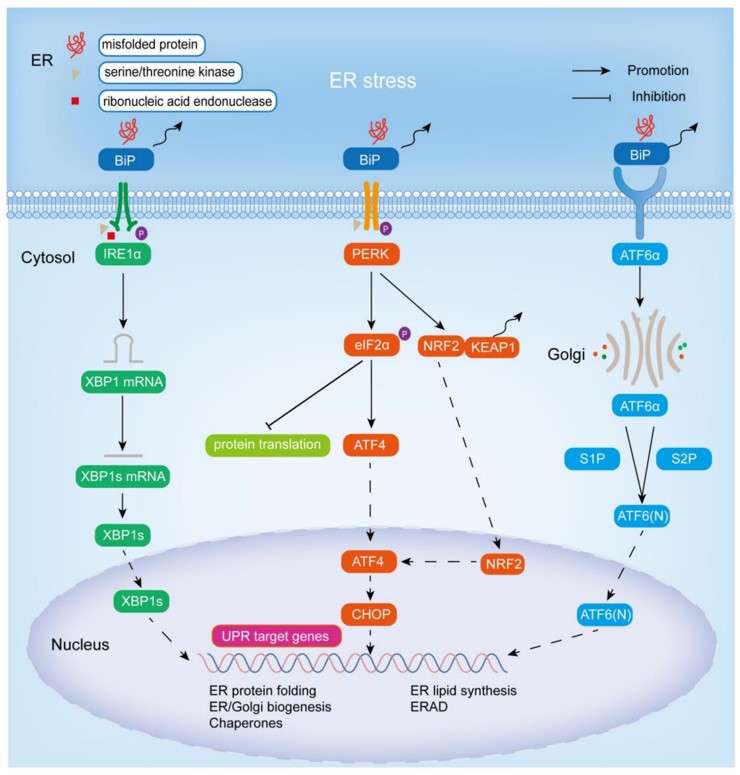 Fig.3 Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the adaptive UPR signaling pathway.3,4
Fig.3 Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the adaptive UPR signaling pathway.3,4
3. Selective Regulation of Unfolded Protein Response Sensors
The three UPR sensors are regulated by different factors, with IRE1 being the most conserved and sole sensor in lower eukaryotes, hence its extensive research. Various proteins modulate IRE1α signaling at different stages, such as dimerization, oligomerization, and phosphorylation, by forming complexes with IRE1α.
Table 1. Selected IRE1α-binding partners and regulators.
| Protein | Function | In Vitro Binding | Overexpressed Interactor (Tagged) | Overexpressed IRE1α (Tagged) |
| AIP1 | MAPK signalling | – | – | – |
| ABL1 | Regulates cell signaling pathways, DNA damage responses, and apoptosis | – | No | Yes |
| CHIP | Ubiquitin system | – | – | – |
| Fortilin | Cell survival | Yes | – | – |
| cABL1 | Regulation of the cell cycle | Yes | NO | Yes |
| HSP90 | Chaperone | – | – | – |
| BIM | Apoptosis | Yes | – | – |
| BI-1 | Apoptosis | Yes | – | – |
| BID | Apoptosis | Yes | Yes | No |
| BiP | Chaperone | Yes | – | – |
| ER protein-targeting machineries | Protein synthesis | – | – | Yes |
| BAK | Apoptosis | Yes | – | – |
| BAX | Apoptosis | Yes | – | – |
| Filamin A | Regulates actin cytoskeleton | Yes | – | – |
| HSP47 | Facilitates collagen folding and trafficking | Yes | – | – |
| HRD1 | ERAD | – | – | – |
| HSP70 | Chaperone | Yes | No | Yes |
| PKA | Kinase | – | – | – |
| PKC | Kinase | Yes | – | – |
| IP3R1–IP3R3 | Calcium channel | Yes | No | Yes |
| JAB1 | MAPK signalling | – | Yes | Yes |
| JIK | MAPK signalling | – | Yes | Yes |
| Myosin heavy chain IIB | Regulates actin cytoskeleton | – | Yes | Yes |
| NMI | Cell signalling | – | Yes | No |
| Optineurin | Autophagy | – | – | – |
| PARP16 | Protein modification | – | Yes | Yes |
| PDIA1 | Catalyzes disulfide bond formation | Yes | – | – |
| PDIA6 | Catalyzes disulfide bond formation | Yes | – | – |
| PPM1L | Phosphatase | – | Yes | Yes |
| SIG-1R | Chaperone | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| TRAF2 | Acts as an adapter protein | – | – | – |
| PSEN1 | Protein processing | – | No | Yes |
| PUMA | Apoptosis | Yes | – | – |
| RACK1 | Cell signalling | – | – | – |
| Sec61 | Translocon | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UFBP1 | UFM1 conjugation system | – | Yes | Yes |
| Ubiquitin D | Ubiquitin system | – | – | – |
| USP14 | Ubiquitin system | – | – | – |
| Yip1A | ER–Golgi apparatus trafficking | – | – | – |
4. New Physiological Functions of Unfolded Protein Response
Beyond its role in unfolded protein-related conditions, the UPR plays essential roles in diverse physiological processes, including lipid and cholesterol metabolism, energy homeostasis, inflammation, and cell differentiation. This is largely attributed to the complex crosstalk between different stress and metabolic pathways, enabling the UPR to integrate dynamic signaling networks and maintain organelle homeostasis across various environments.
4.1 TLR Signaling and XBP1
Activating Toll-like receptors (TLRs) specifically triggers the splicing of XBP1 mRNA, enhancing the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. This TLR-mediated splicing of XBP1 mRNA is dependent on IRE1α and is regulated through a specific signaling branch involving TIR domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP), TRAF6, adaptor proteins like myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MYD88), and NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2), highlighting the UPR's crucial role in inflammatory responses.
4.2 Glucose Metabolism
The UPR targets chaperones and foldases of the glucose-regulated protein (GRP) family and is crucial for monitoring glucose level fluctuations. When cells are exposed to physiological glucose concentrations, IRE1α undergoes phosphorylation, enabling it to regulate insulin levels. Glucose fluctuations phosphorylate IRE1α at Ser724 without the classical electrophoretic activation pattern, and they do not trigger XBP1 mRNA splicing, JNK phosphorylation, or BIP release from IRE1α.
4.3 Cell Differentiation Programs
XBP1 promotes plasma cell differentiation by inhibiting transcriptional repressors such as interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) and B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-6 (BLIMP1). XBP1 deficiency inhibits immunoglobulin secretion. IRE1α also contributes to B cell differentiation through immunoglobulin gene recombination. This enables early UPR activation to prepare cells for future high secretory demands post-differentiation.
4.4 Other Physiological Outcomes
ATF6 negatively regulates the activity of CREB regulated transcriptional coactivator 2 (CRTC2). XBP1 positively regulates hepatic lipid synthesis by activating key metabolic pathway genes, influencing cholesterol and triglyceride levels. XBP1 negatively regulates forkhead box O1 (FOXO1), a key transcription factor in energy regulation. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) can activate XBP1 mRNA splicing, promoting neurite growth and cell differentiation. When BDNF signals through TRKB or p75, components downstream of these receptors may modulate IRE1α.
5. Related Products
Creative Biolabs is a trusted provider of high-quality UPR-related antibodies for research applications. We offer custom antibodies targeting key components of the IRE1, PERK, and ATF6 signal pathways. Our products are optimized for various techniques, including Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, supporting researchers in advancing their studies.
| CAT# | Products | Specificity | Antibody Isotype |
| CBMAB-V208-0518-FY | Mouse Anti-E. coli GroEL Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H0466) | E. coli | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-E1057-FY | Mouse Anti-EIF2AK3 (AA 530-850) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0645) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-E1058-FY | Mouse Anti-EIF2AK3 (AA 665 -764) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0646) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-E1059-FY | Mouse Anti-EIF2AK3 (AA 530-850) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0647) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-P0301-YC | Mouse Anti-EIF2AK3 Recombinant Antibody (5G5) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-P0302-YC | Rabbit Anti-EIF2AK3 Recombinant Antibody (C33E10) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-P0303-YC | Rabbit Anti-EIF2AK3 Recombinant Antibody (D11A8) | Human | IgG |
| PTM-CBMAB-0889LY | Rabbit Anti-EIF2AK3 (Phosphorylated T980) Recombinant Antibody | Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-A2520-LY | Mouse Anti-EIF2AK3 Recombinant Antibody (7B10) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-EN1200-LY | Rabbit Anti-EIF2AK3 Recombinant Antibody (EG1017) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-EN1251-LY | Rabbit Anti-EIF2AK3 (Phospho-Thr981) Recombinant Antibody (EG1060) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-E1768-FY | Rabbit Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-1198) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-E1769-FY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 (AA 401-500) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-1199) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-E1770-FY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 (AA 401-500) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-1200) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-E1771-FY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-1201) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-I1836-YY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (9F2) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-R4461-CN | Rabbit Anti-ERN1 (phosphorylated Ser724) Recombinant Antibody (CBNH-136) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-A2707-LY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (4D12) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A2710-LY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (8D12) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-CS193LY | Mouse Anti-ERN1 Recombinant Antibody (CB193) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-V208-1011-CQ | Mouse Anti-GroEL Recombinant Antibody (9A1/2) | E. coli | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-V208-1675-CQ | Mouse Anti-GroEL Recombinant Antibody (P2E4AT) | M. tuberculosis | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-V208-C0346-YY | Mouse Anti-GroEL Recombinant Antibody (CBMY-C0337) | M. bovis | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-V208-C0347-YY | Mouse Anti-GroEL Recombinant Antibody (CBMY-C0338) | M. bovis | IgM |
| CBMAB-V208-C0348-YY | Mouse Anti-GroEL Recombinant Antibody (CBMY-C0339) | M. tuberculosis | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H1868-FY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0935) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H1869-FY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 (AA 1-391) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0936) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H1870-FY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 (AA 74-180) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0937) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H1871-FY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 (AA 1-392) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0938) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A3827-LY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 Recombinant Antibody (3E10) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A3829-LY | Mouse Anti-HERPUD1 Recombinant Antibody (2G7) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H0450-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2048) | Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0451-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2052) | Mouse, Rat, Sheep, Rabbit, Guinea pig, Hamster, Cattle, Dog, Human, Pig, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-H0786-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2051) | Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3060-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF2 (AA 1-230) Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3214) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3061-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 (AA 1-517) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2043) | Human, Mouse, Monkey | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3062-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF2 (AA 74-324) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2044) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3063-FY | Rabbit Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2045) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3067-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2053) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3070-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2056) | Mouse, Human, Monkey | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3071-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2057) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3072-FY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2058) | Cattle, Dog, Guinea pig, Hamster, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Pig, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-A4106-LY | Mouse Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (1F11-A3) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-AP9917LY | Rat Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (A283) | Cattle, Dog, Guinea pig, Hamster, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Pig, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep | IgG |
| CBMAB-EN1869-LY | Rabbit Anti-HSF2 Recombinant Antibody (EG1567) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-H0651-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 (AA 121-221) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2066) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3075-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 (AA 309-463) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2062) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3076-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2063) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3077-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2064) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3081-FY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2069) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-A4108-LY | Mouse Anti-HSF4 Recombinant Antibody (1A4) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H0032-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (6H4.2G7) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0473-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3238) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H0478-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 (AA 20-650) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2269) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H0571-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3239) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3278-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3240) | Human, Rat, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3279-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2265) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3281-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2267) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3283-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 (AA 420-654 ) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2270) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3284-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2271) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H3285-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 (AA 649-654) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2272) | Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3289-FY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 (C-terminus) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2276) | Human, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3290-FY | Rabbit Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2277) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3291-FY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2278) | Mouse | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3294-FY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 (AA 497-581) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2281) | Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3295-FY | Human Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2282) | Mouse, Human | |
| CBMAB-G1060-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (10C3) | Rat, Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G1061-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (15B165) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G1063-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (3C5-1A4) | Rat, Human, Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G1064-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (3D2) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G1066-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (474421) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-G1067-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (4E87) | Rat, Yeast | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G1068-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (4E88) | Cattle, Cat, Chicken, Human, Monkey, Mouse, Pig, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep, Frog | IgG |
| CBMAB-G1069-LY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (5K23) | Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G1070-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (6H4-2G7) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Cattle, Monkey, Hamster, Frog | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G1071-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (C38) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-G6088-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (10C9) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G6091-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (13k16) | Human, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6092-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (42773) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6093-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (4E3) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6095-LY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (76-E6) | Mouse, Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6096-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (8G3) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G6099-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (AT3D2) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6100-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (C9-9) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6102-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2297) | Human, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6103-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2298) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6104-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2299) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-G6105-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2300) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G6107-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2302) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-H4146-FY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-3593) | Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0644-FY | Rat Anti-HSPA5 (AA 497-581) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-3373) | Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-Z0210-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (3B4-H11-C9) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-A4128-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (4E11) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-CS254LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CB254) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-CA085LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CB85A) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-AP2712LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CAP899) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP2721LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (5F8) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP2722LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (CAP900) | Human, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP3209LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (A300) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP10553LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (A301) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-EN1734-LY | Mouse Anti-HSPA5 Recombinant Antibody (EG1453) | Human, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1573-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (0.N.354) | Human, Cat, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1575-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (13H299) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1576-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (1H6) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-K1577-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (6A400) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1578-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (8J1167) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1579-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (AE20) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-K1582-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (DE-K10) | Human, Cat, Dog | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1585-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (KRT10/844) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-K1586-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (LH2) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-K1587-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (RKSE60) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-K1589-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (SPM261) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-K1590-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (SPM262) | Human, Cat | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-K1591-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (SPM623) | Human, Dog, Cat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-K1592-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (VIK-10) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-A4536-YC | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (AE1) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-A4537-YC | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CK 210) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Chicken, Cattle, Pig, Monkey | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C6575-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (4A27) | Human, Dog, Ferret | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C7606-LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (5F302) | Human, Cattle, Dog, Rabbit, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C0097-YY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0035) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C4256-YY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2815) | Dog, Cat, Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C4257-YY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2816) | Cattle, Dog, Human, Rabbit, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C4258-YY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2817) | Human, Pig | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C3130WJ | Rabbit Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2268) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-C3132WJ | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2269) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C5285WJ | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3975) | Human, Monkey, Cattle, Dog, Rabbit, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Turtle | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C5287WJ | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3976) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-C5289WJ | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3978) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C5290WJ | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3979) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C3775-CN | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1028) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C3776-CN | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (5F187) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-C3780-CN | Rabbit Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (CBCNC-619) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-R0048-FY | Rabbit Anti-KRT10 Monoclonal Antibody (SP99) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP2822LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (4D1) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-AP4113LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 Recombinant Antibody (A783) | Human, Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-AL184LY | Mouse Anti-KRT10 (Concentrate) Antibody (CB184) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A4573-YC | Mouse Anti-MANF Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A998) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-M1526-FY | Mouse Anti-MANF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1367) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-M1527-FY | Mouse Anti-MANF (AA 116-185) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1368) | Human | IgG1, k |
| CBMAB-M1528-FY | Rabbit Anti-MANF Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1369) | Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-M0730-FY | Mouse Anti-MBTPS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0598) | Human | IgG1, k |
| CBMAB-M2011-FY | Mouse Anti-MBTPS2 (AA 312-418) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1843) | Human | IgG1, k |
| CBMAB-S1078-CQ | Mouse Anti-MBTPS2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-3807) | Human | |
| CBMAB-A5336-LY | Mouse Anti-MBTPS2 Recombinant Antibody (1A3) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G0535-LY | Mouse Anti-NOP53 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-134) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G3905-LY | Mouse Anti-NOP53 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1314) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G3906-LY | Mouse Anti-NOP53 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1315) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3908-LY | Mouse Anti-NOP53 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1317) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-G6398-LY | Mouse Anti-NOP53 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2390) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-CP1933-LY | Rabbit Anti-Phospho-EIF2AK3 (Thr980) Recombinant Antibody (16F8) | Rat, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-1180-YY | Mouse Anti-SIL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1176) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-1181-YY | Mouse Anti-SIL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1177) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-2270-YY | Mouse Anti-SIL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1921) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S1185-CQ | Mouse Anti-SIL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-3917) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S1989-CQ | Mouse Anti-SIL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-4760) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S2329-CQ | Mouse Anti-SYVN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-5111) | Mouse, Rat, Human | |
| CBMAB-S3838-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SYVN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0923) | Human, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-S4089-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SYVN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-1226) | Mouse, Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP2675-LY | Rabbit Anti-SYVN1 Recombinant Antibody (D3O2A) | Human, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-T2190-YJ | Mouse Anti-THBS4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2949) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-T2191-YJ | Rat Anti-Thbs4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2950) | Mouse | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-X0081-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (8C357) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0083-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCX-114) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-X0084-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCX-115) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0085-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (XBP1H6E5) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0086-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (8F6.11) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0087-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCX-116) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-X0088-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCX-117) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0089-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCX-118) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0090-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (1C4) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0091-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (143F) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-X0092-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (3H1G4) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0093-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (9B7E5) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0094-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (F-4) | Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0095-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (13B804) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0096-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (2D9) | Human | IgG2a, Κ |
| CBMAB-X0097-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (13L31) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-X0098-YC | Rabbit Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (D2C1F) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-X0099-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (Q3-695) | Human, Mouse | IgG1, Κ |
| CBMAB-X0100-YC | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (9D11A43) | Human, Mouse | IgG2a, Κ |
| CBMAB-A9962-LY | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (1E3) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-A9963-LY | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (4E4) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-A9965-LY | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (3F5) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-CP3024-LY | Rabbit Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (D2C1F) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP3025-LY | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (E8C2Z) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP3026-LY | Mouse Anti-XBP1 Recombinant Antibody (E7M5C) | Human | IgG1 |
References
- Adams, Christopher J et al. "Structure and Molecular Mechanism of ER Stress Signaling by the Unfolded Protein Response Signal Activator IRE1." Frontiers in molecular biosciences vol. 6 11. 12 Mar. 2019. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00011.
- Radanović, Toni, and Robert Ernst. "The Unfolded Protein Response as a Guardian of the Secretory Pathway." Cells vol. 10,11 2965. 31 Oct. 2021. DOI:10.3390/cells10112965.
- Wu, Tingyu et al. "Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis." Journal of translational medicine vol. 21,1 480. 18 Jul. 2023. DOI:10.1186/s12967-023-04328-8.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


