Glutamine Metabolism & Pathway
1. Introduction to Glutamine
Glutamine stands as a non-essential amino acid represented by the symbols Gln or Q which follows the molecular formula C5H10N2O3. Glutamine stands as the most prevalent free amino acid within human plasma and functions as a central component of multiple physiological mechanisms. The amide group in glutamine's side chain makes it both polar and hydrophilic. The linear configuration of glutamine's chemical structure makes it soluble in water. It functions as a fundamental element in protein synthesis because it is a proteinogenic amino acid. The amino acid performs dual functions by building proteins and supplying nitrogen for multiple anabolic pathways including nucleotide and amino sugar synthesis. The amino acid glutamine plays critical roles in preserving nitrogen balance while supporting immune responses and maintaining intestinal mucosa integrity. Glutamine functions as a precursor for neurotransmitter synthesis and helps maintain acid-base balance within the kidneys.
 Fig. 1 Glutamine molecule.
Fig. 1 Glutamine molecule.
2. Glutamine Metabolism Fundamentals
2.1 Glutamine vs Glutamate
Glutamine and glutamate share similar structural characteristics, but they perform distinct roles within cellular metabolism. Glutamate represents the charged form of glutamine and contains one fewer amide group in its structure. Glutamine maintains neutrality as an amino acid while glutamate becomes negatively charged when deaminated. This distinction affects their roles: The primary neurotransmitter in the central nervous system is glutamate while glutamine serves as an essential nitrogen source for protein synthesis and other metabolic pathways.
2.2 Glutamine-Glutamate Cycle
The biochemical mechanism of glutamine-glutamate conversion functions as a vital process that occurs throughout multiple tissues including brain tissue. The enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS) utilizes ATP and ammonia to transform glutamate into glutamine. The enzyme glutaminase (GLS) catalyzes the conversion of glutamine into glutamate. Neuronal neurotransmitter equilibrium relies on this cycle which concurrently facilitates nitrogen metabolism in non-neuronal tissues.
2.3 Nitrogen Metabolism
Glutamine functions as a fundamental element within nitrogen metabolic activities. Glutamine acts as the chief nitrogen transporter in human bodies while supplying nitrogen to essential biosynthetic pathways responsible for making amino acids and nucleotides. Glutaminase-mediated glutamine deamination leads to glutamate formation which then participates in metabolic pathways that generate other nitrogen-rich molecules. The maintenance of nitrogen balance depends significantly on this role during times of metabolic stress.
2.4 ATP Biosynthetic Process
The primary energy source for ATP production originates from glutamine which becomes α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) thanks to glutaminase activity. α-KG participates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and through further metabolic processes produces ATP together with NADH and FADH2. Glutamine inclusion in the TCA cycle highlights its essential function for energy production in fast-dividing cells including cancer cells and immune cells.
3. Glutamine Transport and Regulation
3.1 Transport Systems (SLC1A5)
The transport of glutamine into cells is mediated by several specialized amino acid transporters, with the SLC1A5 (ASCT2) transporter being one of the most well-characterized. The transporter belongs to the solute carrier (SLC) family and operates within the sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transport system. The brain and both kidney and intestinal tissues exhibit high levels of ASCT2 expression because they require large amounts of glutamine. Glutamine uptake via ASCT2 is sodium-dependent, meaning the transport is coupled to the movement of sodium ions into the cell, which helps drive the uptake of glutamine against its concentration gradient.
Apart from ASCT2 multiple important transporters exist:
- LAT1 (L-type amino acid transporter 1): The LAT1 transporter operates as a neutral amino acid transporter enabling glutamine passage through the plasma membrane by exchanging it with other amino acids including leucine. The LAT1 transporter is highly expressed in brain tissue and placenta along with cancer cells, where it supports amino acid and nutrient supply under nutrient-limited conditions.
- SNAT1 (Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1): This transporter is involved in the sodium-dependent uptake of glutamine and other neutral amino acids. It plays an essential role in maintaining cellular glutamine homeostasis.
- SLC38A1 (System A transporter): In liver and metabolic tissues the sodium-dependent transporter selectively imports glutamine to maintain cellular amino acid levels.
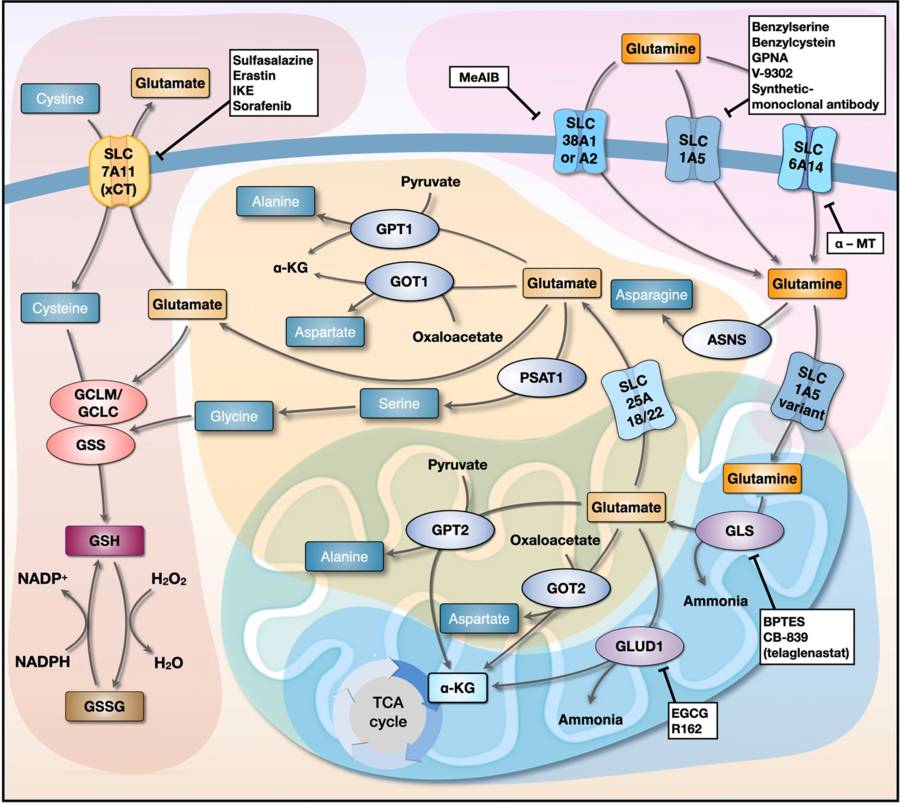 Fig. 2 Interlinked networks involved in glutamine metabolism.1, 4
Fig. 2 Interlinked networks involved in glutamine metabolism.1, 4
3.2 Cellular Uptake Mechanisms
Glutamine uptake into cells is highly regulated and occurs through sodium-coupled transport mechanisms. The process of transporting glutamine from the extracellular environment into the cytoplasm through Sodium-Coupled Neutral Amino Acid Transporters (SNATs) depends on sodium ion presence. The operation of these cellular mechanisms serves as an essential function to sustain intracellular glutamine levels especially in tissues that require high metabolic activity.
ASCT2 regulation is subject to multiple controlling elements.
- Metabolic Signals: The activity of ASCT2 becomes enhanced in cancer cells to maintain a continuous supply of glutamine which supports biosynthesis and energy production. Metabolic reprogramming makes cellular glutamine pools crucial for tissues experiencing rapid growth like tumors.
- Hormonal Regulation: Glutamine transport is directly influenced by two primary hormones which are insulin and glucagon. The hormone insulin increases the expression of glutamine transporters such as ASCT2 which results in greater glutamine uptake especially within muscle and adipose tissue. Glucagon functions as an indicator of nutrient scarcity and leads to the downregulation of transporter proteins within specific tissues.
3.3 Regulatory Pathways
Glutamine metabolism and transport are tightly regulated by a combination of hormonal, nutrient sensing, and metabolic signals. These regulatory pathways ensure that glutamine uptake and utilization are adapted to the cell's metabolic state.
- mTORC1 Pathway
The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway functions as the primary regulator of cellular metabolism based on nutrient availability. The mTORC1 pathway requires amino acids like glutamine for activation which leads to the synthesis of transport proteins including ASCT2. Glutamine binding to Rag GTPases receptors activates mTORC1 which prompts protein synthesis while stimulating cellular growth mechanisms. Cancer cells need the mTORC1 signaling pathway since it allows for more glutamine absorption and increased biomass generation when active.
- AMPK Pathway
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) functions as a cellular energy sensor to maintain energy balance. The AMPK pathway becomes active in response to insufficient cellular ATP levels which then leads to mTORC1 inhibition and diminished glutamine transporter expression. Energy stress conditions activate AMPK which then increases the function of specific transporters such as SNAT1 to preserve proper glutamine concentrations.
- Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) Pathway
Hypoxia leads to the stabilization of HIF-1α among hypoxia-inducible factors which then activates genes that help cells adapt metabolically by upregulating glutamine transporter proteins. Increased HIF-1α activity stimulates ASCT2 transcription alongside other amino acid transporters to boost glutamine uptake which supports cell survival and proliferation within hypoxic tumor settings.
- Glucocorticoid Signaling
The metabolic processing and transportation of glutamine face disruption from glucocorticoids which include cortisol. Glucocorticoid hormones attach themselves to receptors which leads to modifications in the genetic expression of glutamine transporter genes. Cortisol triggers ASCT2 gene activation in liver and muscle tissues during stress and extended fasting to ensure adequate glutamine availability for vital processes like gluconeogenesis and protein synthesis.
3.4 Mitochondrial Transport
Once glutamine is taken up into the cell, it needs to be transported into the mitochondria for further metabolism, particularly in tissues with high energy demands. The transport of glutamine into mitochondria is facilitated by specific mitochondrial glutamine transporters, which belong to the SLC25 family of mitochondrial solute carriers.
The SLC25A22 protein operates as a confirmed transporter, and it allows glutamine to cross the mitochondrial membrane. Within mitochondria the enzyme glutaminase (GLS) acts on glutamine to produce α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), and α-KG subsequently enters the TCA cycle to support energy production and anaplerosis. Mitochondrial glutamine transport is especially important in tissues like the brain, heart, and muscles, where high mitochondrial activity is required for processes like ATP generation, protein synthesis, and neurotransmitter production. Both SLC25A12 and SLC25A13 as well as SLC25A22 make up the mitochondrial glutamine transport system with SLC25A22 showing greater specificity for transporting glutamine.
4. Key Metabolic Pathways of Glutamine
4.1 Glutaminolysis
Glutaminolysis refers to the conversion of glutamine to glutamate by the enzyme glutaminase (GLS). Glutamate can then undergo further metabolism to produce important intermediates like α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), which is a key substrate in the TCA cycle for ATP production and anaplerosis.
- Regulation of Glutaminolysis
Glutaminase (GLS) is the first and rate-limiting enzyme in the glutaminolysis pathway. GLS activity is regulated by several factors:
- Cytokines and Growth Factors: In cancer cells, growth factors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) or insulin-like growth factor (IGF) activate the PI3K-AKT pathway, which enhances GLS expression and activity.
- Tumor Suppressors: In some cancer types, p53 suppresses GLS activity. p53 inhibition of GLS promotes glutamine's use for biosynthetic processes like nucleotide production, preventing excess α-KG production in specific cellular contexts.
- Regulation by Acetylation: GLS can be post-translationally modified through acetylation, affecting its activity. This regulation is particularly important in metabolically stressed cells, such as in hypoxia.
- Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH)
Once glutamine is converted to glutamate by GLS, glutamate can be deaminated by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) to form α-KG. This reaction is regulated by the energy status of the cell, with ATP acting as an inhibitor and ADP or AMP acting as activators of GDH.
4.2 TCA Cycle Integration
The integration of glutamine into the TCA cycle is a key metabolic pathway for energy production. Glutamine-derived α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) is an essential intermediate in the TCA cycle. It contributes to energy production, anaplerosis, and biosynthesis of amino acids and nucleotides.
- Regulation of TCA Cycle Integration
Once α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG) is generated from glutamine metabolism, it enters the TCA cycle. The entry of α-KG into the TCA cycle is highly regulated:
- Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC): The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is tightly regulated by the PDC complex, which can be inhibited by acetyl-CoA (feedback inhibition) and activated by ADP.
- Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH): IDH catalyzes the conversion of isocitrate to α-KG. IDH activity is regulated by NADH (which inhibits) and NAD⁺ (which activates). Mutations in IDH can lead to metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells, where α-KG is diverted into pathways that promote cell growth and survival.
- Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) and Fumarase: These enzymes also modulate the TCA cycle through their activity in the interconversion of metabolic intermediates, impacting the flow of α-KG.
- Regulation by Acetylation and Methylation
Acetylation of α-KG dehydrogenase and other TCA cycle enzymes can influence the activity and efficiency of the cycle. Similarly, histone modifications and DNA methylation can alter gene expression patterns for enzymes involved in glutamine metabolism and TCA cycle integration.
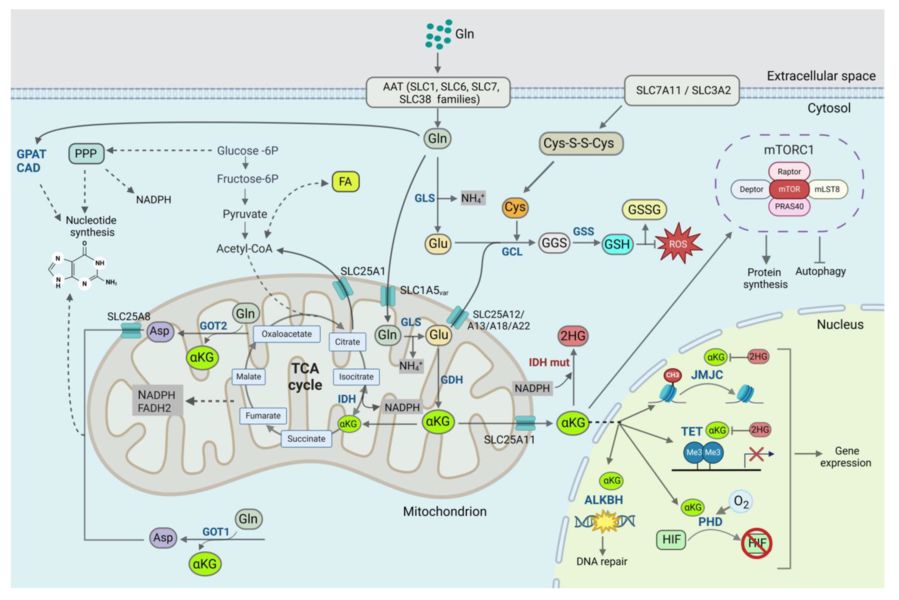 Fig. 3 The role of glutamine (Gln) supply in cell metabolism.2, 4
Fig. 3 The role of glutamine (Gln) supply in cell metabolism.2, 4
4.3 Alpha-Ketoglutarate Production
α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG) is a key metabolite derived from glutamine and involved in various anabolic and catabolic pathways. In addition to its role in energy production via the TCA cycle, α-KG plays a central role in amino acid synthesis, redox balance, and the regulation of cell signaling.
- Glutaminolysis Pathway: As discussed, glutamine is converted to glutamate by glutaminase (GLS), which is then deaminated by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) to form α-KG. This is a major source of α-KG in cells.
- Transamination Reactions: Glutamate can also be converted to α-KG through transamination with aspartate by the action of aminotransferases, which transfers the amino group to oxaloacetate, producing α-KG.
- Regulation of α-KG Production: 1) Regulation by Oxygen: In hypoxic conditions, the activity of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) is regulated by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs). The stabilization of HIF-1α under low oxygen levels induces the transcription of glutaminase and GDH, facilitating increased α-KG production under metabolic stress. 2) NAD/NADH Ratio: The NAD/NADH ratio also regulates α-KG metabolism. A high NAD⁺ to NADH ratio favors the conversion of glutamate to α-KG by glutamate dehydrogenase.
4.4 Nucleotide Synthesis
Glutamine is essential for nucleotide synthesis through its role as a nitrogen donor in the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines. This is especially crucial in rapidly proliferating cells such as those in tumors, the immune system, and during cell growth and repair.
- Purine Biosynthesis: Glutamine donates nitrogen to IMP (inosine monophosphate), a precursor for both purine adenine and guanine synthesis. The enzyme glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase catalyzes this reaction.
- AMP Kinase (AMPK): AMPK, a key energy-sensing kinase, modulates the activity of glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase to ensure that nucleotide synthesis is in sync with cellular energy status.
- Pyrimidine Biosynthesis: Glutamine is also involved in pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis. The enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPSII) uses glutamine to synthesize carbamoyl phosphate, a precursor for pyrimidine production.
- CPSII Regulation: CPSII is regulated by UTP (uridine triphosphate), which acts as a negative feedback inhibitor of the enzyme. High levels of UTP suppress the production of pyrimidines, ensuring balance with other nucleotide pools.
4.5 Redox Balance
Glutamine plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis by supporting the synthesis of glutathione (GSH), one of the major antioxidants in the cell. The conversion of glutamine to glutamate and its subsequent use in GSH synthesis is a key metabolic route for managing oxidative stress.
- Glutamate Cysteine Ligase (GCL): The enzyme GCL catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis, where glutamate combines with cysteine to form γ-glutamylcysteine, which is then converted to glutathione. GCL is regulated by NF-κB and Nrf2, two transcription factors that respond to oxidative stress and upregulate the expression of antioxidant genes, including GCL.
- Nrf2 Activation: In response to oxidative stress, Nrf2 activates the transcription of genes involved in antioxidant defense, including those involved in the synthesis of glutathione. Nrf2 itself is regulated by the Keap1 protein, which sequesters Nrf2 in the cytoplasm under normal conditions. Under oxidative stress, Keap1 is modified and releases Nrf2 to enter the nucleus and promote gene transcription.
Table 1. Summary of Key Proteins Involved in Metabolic Pathways
| Pathway | Enzyme/Protein | Function | Regulation |
| Glutaminolysis | Glutaminase (GLS, GLS2) | Converts glutamine to glutamate | Activated by c-Myc, inhibited by p53, repressed by miR-23 |
| Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH) | Converts glutamate to α-KG | Inhibited by GTP, activated by ADP and leucine | |
| TCA Cycle Integration | Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH1/IDH2) | Converts isocitrate to α-KG | Mutations in IDH1/IDH2 lead to oncogenic transformation via 2-HG production |
| α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (OGDH) | Converts α-KG to succinyl-CoA in TCA cycle | Inhibited by ATP, NADH; activated by Ca²⁺, ADP | |
| Fumarase (FH) | Converts fumarate to malate | Mutations associated with hereditary cancers | |
| Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH) | Converts succinate to fumarate | Inhibited by fumarate accumulation in certain tumors | |
| α-KG Production | Aminotransferases (GOT1/GOT2) | Convert glutamate to α-KG via transamination | Regulation by cellular redox status and metabolic demand |
| Branched-Chain Aminotransferases (BCAT1/2) | Convert branched-chain amino acids to α-KG | BCAT1 is upregulated in certain cancers | |
| Nucleotide Synthesis | Glutamine-PRPP Amidotransferase (PPAT) | First step in purine biosynthesis | Inhibited by GMP, AMP (negative feedback) |
| Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase II (CPSII) | First step in pyrimidine synthesis | Inhibited by UTP, activated by PRPP | |
| Redox Balance | Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase (GCL) | Rate-limiting enzyme for glutathione synthesis | Upregulated by Nrf2, inhibited by oxidative stress |
| Glutathione Synthase (GSS) | Catalyzes final step of glutathione synthesis | Controlled by availability of glutamate, cysteine, glycine | |
| Cell Signaling | mTORC1 (mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1) | Integrates nutrient signals from glutamine | Activated by glutamine via SLC1A5 and Rag GTPases |
| AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) | Regulates energy balance, inhibits glutaminolysis | Activated by ATP depletion, inhibits mTORC1 | |
| Hypoxia & Tumor Metabolism | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) | Regulates metabolic adaptation to hypoxia | Stabilized in low oxygen, promotes glutamine uptake |
| c-Myc | Oncogenic transcription factor that increases glutaminolysis | Upregulates ASCT2, GLS, and glutamine metabolism |
5. Glutamine Metabolism in Specialized Functions
5.1 T Cell Metabolism
T cells depend on glutamine metabolism for their activation processes as well as their proliferation and effector functions. Glutamine supplies critical intermediates needed for energy production and nucleotide synthesis while maintaining redox balance which together support strong immune responses. The proper use of glutamine by T cells is critical for the immune system to function effectively during periods of immune challenge.
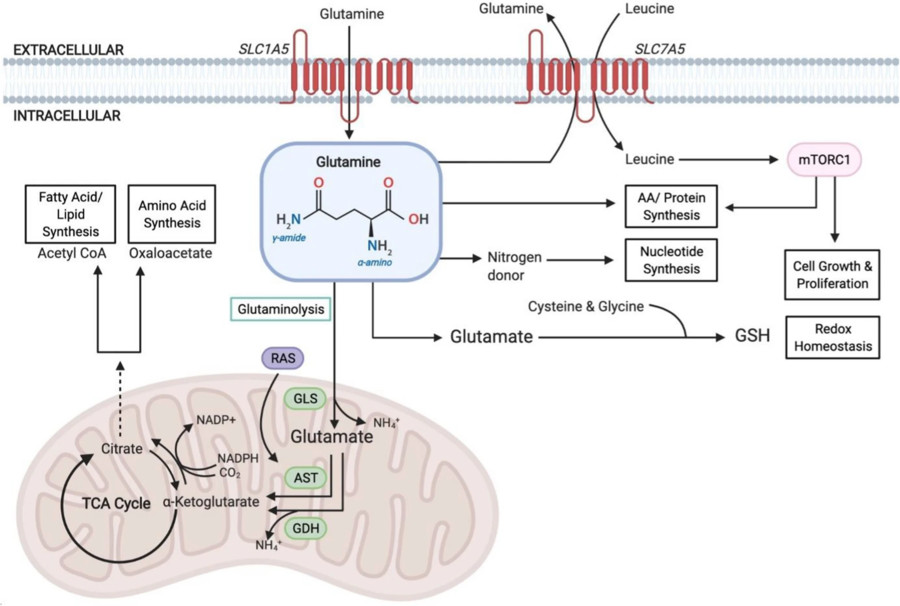 Fig. 4 The role of glutamine in cancer.3, 4
Fig. 4 The role of glutamine in cancer.3, 4
5.2 Hypoxic Conditions
Cells shift their metabolic processes under hypoxic conditions to survive in environments with low oxygen. The metabolic pathway of glutaminolysis becomes essential under hypoxic conditions as it provides necessary energy and maintains metabolic intermediates through glutamine metabolism. Glutamine maintains cellular redox balance to shield cells from oxidative harm when oxygen levels are depleted.
5.3 Lactate Production
Cancer cells demonstrate the Warburg effect by preferring glycolysis and lactate production regardless of oxygen presence which makes the interaction between glutamine metabolism and lactate generation particularly important to study. Glutamine generates intermediates for glycolysis and TCA pathways to support energy production when oxygen availability is restricted.
5.4 NADPH Generation
Glutamine metabolism forms a fundamental pathway which generates NADPH used as an essential cofactor in biosynthetic processes and antioxidant defense mechanisms. The generation of NADPH through fatty acid synthesis and reactive oxygen species detoxification establishes glutamine as essential for cellular metabolism and protection from oxidative stress.
5.5 Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Research findings indicate that glutamine metabolism affects both mitochondrial function and their production. Glutamine metabolism demonstrates significant influence over mitochondrial functionality and mitochondrial production. High energy demand tissues like muscle tissue, neurons and immune cells rely heavily on this role. Cells adapt to varying energy requirements through glutamine's modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis.
6. Related Products
Creative Biolabs is a trusted provider of high-quality glutamine metabolism-related antibodies for research applications. We offer custom antibodies targeting key components of the glutamine-glutamate cycle, glutaminolysis, and glutamine transporters. Our products are optimized for various techniques, including Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, supporting researchers in advancing their studies.
| CAT# | Products | Specificity | Antibody Isotype |
| CBMAB-0814-LY | Mouse Anti-ZNF384 Recombinant Antibody (1C11) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-0815-LY | Mouse Anti-ZNF384 Recombinant Antibody (1E8) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-0349CQ | Rabbit Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (BA0124) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-0350CQ | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (BA0405) | Sheep, Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-0351CQ | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (BA0404) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Common fruit fly, Zebrafish | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-0365CQ | Rabbit Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (BA0068) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-0212-CN | Mouse Anti-Transglutaminase Recombinant Antibody (4C1) | Guinea pig, Human, Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-0233-CN | Mouse Anti-LMX1B Recombinant Antibody (50.5A5) | Chicken, Mouse, Planaria | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-1679-YC | Mouse Anti-UBE2K Monoclonal Antibody (701316) | Human, Mouse | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-1949CQ | Mouse Anti-DGLUCY Recombinant Antibody (C-7) | Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-1570-CN | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (27D10) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-1571-CN | Rabbit Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (7H9L16) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-1574-CN | Mouse Anti-HAP1 Recombinant Antibody (1B6) | Rat, Mouse, Monkey | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-1581-CN | Mouse Anti-HTR2B Recombinant Antibody (4A4) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-1582-CN | Mouse Anti-HTR2B Recombinant Antibody (4F3) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-M0001-WJ | Rat Anti-MAGI2 Recombinant Antibody (13F10) | Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-W0025-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (1A12) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-W0043-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-W0072-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-208) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-W0076-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (2H4) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-W0087-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (3B12) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-W0112-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-212) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-W0119-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (4H383) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-W0131-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (5G11A5) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-W0142-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (6F-H2) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0158-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (9F523) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0159-WJ | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CAN-R9(IHC)-56-2) | Mouse, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-W0196-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-042) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-W0238-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-087) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-W0276-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-127) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-W0309-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJW-165) | Mouse, Rat, Human | |
| CBMAB-W0322-WJ | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (D6M6S) | Human | |
| CBMAB-W0376-WJ | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (RMWT1-1) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-W0377-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (rWT1/857) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0378-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (SPM361) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0381-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (WLMT1-1) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0382-WJ | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (WT1/1434) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-W0383-WJ | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (WT1/1434R) | Human | IgG, κ |
| CBMAB-W0384-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (WT1/857) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-W0385-WJ | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (WT1/857 + 6F-H2) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-U0124-FY | Mouse Anti-UBE2K Recombinant Antibody (CBFYU-124) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-U0125-FY | Mouse Anti-UBE2K Recombinant Antibody (757C3a) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-D0031-YC | Mouse Anti-ATN1 Recombinant Antibody (2C10) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-D1297-YC | Mouse Anti-DNAJB6 Recombinant Antibody (2C11-C1) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-D1299-YC | Mouse Anti-DNAJB6 Recombinant Antibody (2D12-B9) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-D1300-YC | Mouse Anti-DNAJB6 Recombinant Antibody (1A5) | Human | IgG2a, λ |
| CBMAB-D1664-YC | Mouse Anti-DR1 Recombinant Antibody (D-1) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-D1665-YC | Mouse Anti-DR1 Recombinant Antibody (R594.1.1A12) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-D1666-YC | Rabbit Anti-DR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-401) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-D2183-YC | Mouse Anti-POLG Recombinant Antibody (3H16) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-D2184-YC | Rabbit Anti-POLG Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-495) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-E2079-FY | Rat Anti-GATD3A (AA 1-281) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-1451) | Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-0027-YY | Mouse Anti-ATN1 (AA 320-400) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0027) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-Z0542-WJ | Mouse Anti-ZNF384 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-198) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-Z0543-WJ | Mouse Anti-ZNF384 Recombinant Antibody (3545C5a) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0379-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2537) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H0385-FY | Mouse Anti-HAP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0689) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0554-FY | Mouse Anti-HTR2B (AA 1-57) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2497) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-H0755-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2538) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H0756-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2543) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H0757-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2539) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H1264-FY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0393) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H1266-FY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0395) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H1267-FY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-0396) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3512-FY | Mouse Anti-HTR2B (AA 1-56) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2498) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H3513-FY | Mouse Anti-HTR2B (AA 199-359) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2499) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-H3542-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 181-810) Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3268) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3543-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3269) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-H3544-FY | Rabbit Anti-HTT (AA 584-601, 650-666, 82-99) Recombinant Antibody (3H2L4) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3545-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1247-1646) Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3270) | Human, Mouse | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-H3546-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (4H105) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3547-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3271) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3548-FY | Rabbit Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (D7F7) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3549-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (N-terminus) Recombinant Antibody (H.F5) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3550-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 997-1276) Recombinant Antibody (HDA3E10) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3551-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1844-2131) Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYH-3272) | Human, Mouse, Rabbit | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3553-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2528) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3554-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2529) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3555-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1844-2131) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2530) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3556-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 2703-2911) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2531) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3557-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 2146-2541) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2532) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3558-FY | Rat Anti-HTT (AA 549-679) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2533) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3559-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 81-191) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2534) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H3560-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1247-1646) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2535) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-H3561-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2536) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3562-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1171-1177) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2540) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H3563-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2541) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3564-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 181-810) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2542) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3565-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2544) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-H3566-FY | Rabbit Anti-HTT (N-terminus) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2545) | Human | |
| CBMAB-H3568-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 1524-1627) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2547) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-H3569-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 81-190) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2548) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3570-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 544-552) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2549) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3571-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT (AA 2703-2911) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2550) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H3572-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2551) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3573-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2552) | Human, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3896-FY | Rabbit Anti-UBE2K Recombinant Antibody (D27C4) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Cattle | IgG |
| CBMAB-H3897-FY | Mouse Anti-UBE2K (AA 1-40) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-2828) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-L0162-YJ | Mouse Anti-SLC7A8 Recombinant Antibody (3F10) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-L0163-YJ | Mouse Anti-SLC7A8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJL-106) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-L1898-YJ | Mouse Anti-LMX1B Recombinant Antibody (CBYJL-1891) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-L1899-YJ | Rabbit Anti-LMX1B Recombinant Antibody (CBYJL-1892) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G0533-LY | Rabbit Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2823) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G0534-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-133) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G0540-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2826) | Sheep, Rat, Human, Mouse, | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G0541-LY | Rabbit Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-2827) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G0542-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-136) | Sheep | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3887-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (5B7) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3888-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (5C4) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3891-LY | Rabbit Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (6H5L15) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3892-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1309) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3893-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1310) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3894-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1311) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3895-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1312) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-G3897-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS2 Recombinant Antibody (585CT26-3-1) | Human | IgM |
| CBMAB-G3917-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (1055) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3918-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (10K208) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3919-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (10K209) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-G3920-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (11A3.1) | Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3922-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (1F4) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3925-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (2B12) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3928-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (2Q56) | Sheep, Human, Mouse, Rat, | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3929-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (3004) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3930-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (3013) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3932-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (4H8C1D7) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3933-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (7711) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3935-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (8G9) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3937-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-3189) | Mouse, Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3940-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (GS-6) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-G3943-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1323) | Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3944-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1324) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3947-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1327) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G3948-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1328) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-G3949-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1329) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-G3952-LY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1332) | Mouse, Rat, Human, Zebrafish, | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-R0091-CN | Rabbit Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (CBCNR-175) | Mouse, Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-R1264-CN | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (20/Ran) | Human, Chicken, Dog, Mouse, Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-R1265-CN | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (6A2G5) | Mouse, Vert | IgG |
| CBMAB-R1266-CN | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (8D1A6) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-R1267-CN | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (8D1H12) | Human, Rat, Monkey | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-R1268-CN | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (ARAN1) | Mouse, Hamster, Cattle, Human, Frog | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-G3484-LY | Mouse Anti-GIGYF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-3170) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-G3896-LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1313) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-G0517-LY | Mouse Anti-QARS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-123) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-G3808-LY | Mouse Anti-QARS Recombinant Antibody (CBLG1-1276) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-R0109-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (62D9) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-R1327-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (15B57) | Human | |
| CBMAB-R1328-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (455517) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-R1329-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (4F12-3C6) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-R1330-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (9H175) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-R1331-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (AT62D9) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-R1333-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (CBCNR-201) | Mouse, Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-R1334-CN | Mouse Anti-RAP2B Recombinant Antibody (CBCNR-202) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-H3996-FY | Mouse Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-3449) | Sheep | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-H4069-FY | Mouse Anti-HAP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYH-3518) | Mouse, Rat, Monkey | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-H4150-FY | Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (2401C1a) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-F0468-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0879) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-F1093-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (FOXP2-73A/8) | Human, Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-F1157-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2030) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-F1801-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1953) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-F1953-CQ | Rabbit Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (D55H9) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-F1954-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (5C11A8) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-F2468-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 (AA 616-716) Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0878) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-F2469-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 (AA 657-684) Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0880) | Human | IgM |
| CBMAB-F3211-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0877) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-F3875-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3179) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-F3876-CQ | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3180) | Human | IgM |
| CBMAB-F4135-CQ | Rabbit Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1510) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-N2326-WJ | Mouse Anti-NFYA Recombinant Antibody (3F9) | Human, Rat | IgM, κ |
| CBMAB-N2328-WJ | Mouse Anti-NFYA Recombinant Antibody (G-2) | Human, Mouse, Rat | |
| CBMAB-N4353-WJ | Mouse Anti-UHRF2 Recombinant Antibody (C-10) | Human | |
| CBMAB-M1497-FY | Mouse Anti-MAGI2 (AA 519-628) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1338) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-M0430-FY | Mouse Anti-MAML2 Recombinant Antibody (MAML2/1302) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-M0632-FY | Mouse Anti-MAML2 (AA 796-895) Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-0504) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-M1513-FY | Rabbit Anti-MAML2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1354) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-T0936-YJ | Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-1868) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T0938-YJ | Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-1869) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T0939-YJ | Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-1870) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T0940-YJ | Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-1871) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T0941-YJ | Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-1872) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-T1209-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2110) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T1210-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2111) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-T1211-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (TBPB8A9) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-T1212-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (830CT4.3.3) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-T1213-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2112) | Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat, | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-T1214-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (1TBP18) | Human, Rat, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-T1215-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2113) | Human, Rat, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-T1216-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2114) | Human, Rat, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-T1217-YJ | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2115) | Human, Rat, Mouse | IgG |
| CBMAB-T1218-YJ | Rabbit Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2116) | Human, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-T2077-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2851) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-T2078-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2852) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T2079-YJ | Mouse Anti-Tgm2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2853) | Guinea pig | IgG3, κ |
| CBMAB-T2080-YJ | Mouse Anti-Tgm2 Recombinant Antibody (CUB7402) | Guinea pig | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T2081-YJ | Mouse Anti-Tgm2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2854) | Guinea pig | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T2082-YJ | Mouse Anti-Tgm2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2855) | Guinea pig, Dog, Human, Rabbit, | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T2092-YJ | Mouse Anti-Tgm2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2862) | Rat, Human, Guinea pig | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-T2098-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2868) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T2099-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2869) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-T2101-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2870) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-T2102-YJ | Mouse Anti-TGM4 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-2871) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-T3702-YJ | Mouse Anti-TOX3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-4237) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T3703-YJ | Mouse Anti-TOX3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-4238) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-T3704-YJ | Mouse Anti-TOX3 Recombinant Antibody (TOX3/1123) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-T3705-YJ | Mouse Anti-TOX3 Recombinant Antibody (TOX3/1124) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-T5090-YJ | Mouse Anti-TXNL4A Recombinant Antibody (CBYJT-5477) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-P2678-YC | Mouse Anti-PQBP1 Recombinant Antibody (3H7) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-P2679-YC | Mouse Anti-PQBP1 Recombinant Antibody (B-9) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-S0014-CQ | Mouse Anti-SLC38A1 Recombinant Antibody (S104-32) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S0893-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ (AA 269-362) Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-3608) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-S1142-CQ | Mouse Anti-SETD2 (AA 1787-2144) Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-3873) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S1292-CQ | Mouse Anti-SETD2 (AA 1787-2144) Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-4031) | Human | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-S2431-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-5214) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-S2669-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SLC38A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-5459) | Human, Mouse, Rat | |
| CBMAB-S2977-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (B92) | Human, Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S3251-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SETD2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0276) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, | |
| CBMAB-S3252-CQ | Mouse Anti-SETD2 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0277) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S3280-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0305) | Mouse | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S3281-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0306) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster, | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-S3419-CQ | Mouse Anti-SLC38A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0469) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-S3420-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SLC38A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-0470) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-S4153-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-1294) | Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-S4154-CQ | Rabbit Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-1295) | Mouse, Rat, Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-S5759-CQ | Mouse Anti-SFPQ Recombinant Antibody (CBXS-3013) | Human | |
| CBMAB-XB0071-YC | Mouse Recombinant Anti-ATXN7 Recombinant Antibody (1C1) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-C4985WJ | Rabbit Anti-GATD3A Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3721) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-C4581-CN | Mouse Anti-UHRF2 Recombinant Antibody (3A11) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-C4582-CN | Mouse Anti-UHRF2 Recombinant Antibody (CBCNC-765) | Human | |
| CBMAB-XB0568-YC | Recombinant Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (1H6) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-XB0570-YC | Recombinant Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (2C1) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-XB0573-YC | Recombinant Mouse Anti-HTT Recombinant Antibody (4E6) | Human, Mouse | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-XB1094-YC | Recombinant Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (1B12) | Human, Mouse | |
| CBMAB-XB1095-YC | Recombinant Mouse Anti-TAF4 Recombinant Antibody (2B9) | Human, Mouse | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A3156-LY | Mouse Anti-FOXP2 Recombinant Antibody (1F8) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-A4570-LY | Mouse Anti-ITCH Recombinant Antibody (1B8) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-A5175-LY | Mouse Anti-MAGI2 Recombinant Antibody (6C8) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-A6990-LY | Mouse Anti-PQBP1 Recombinant Antibody (1A11) | Human | IgG2a, κ |
| CBMAB-A9948-LY | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (1E2) | Human | IgG2b, κ |
| CBMAB-CP0840-LY | Rabbit Anti-GLUL Recombinant Antibody (D2O3F) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP2402-LY | Rabbit Anti-SETD2 Recombinant Antibody (D5T1Q) | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP2714-LY | Rabbit Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (D5G7Y) | Human, Monkey | IgG |
| CBMAB-CP3021-LY | Rabbit Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (D8I7F) | Human | IgG |
| CBMAB-MA263-YC | Mouse Anti-WT1 Recombinant Antibody (IHC685) | Human | |
| CBMAB-BR426LY | Mouse Anti-RAN Recombinant Antibody (5D5) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-CS365LY | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CB365) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AO078LY | Mouse Anti-ATXN1 Recombinant Antibody (2F5) | Human | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-CA267LY | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CB267A) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-CA268LY | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CB268A) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| CBMAB-AL403LY | Mouse Anti-WT1 (Autostainer Link 48) Recombinant Antibody (CB403) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-AL404LY | Mouse Anti-WT1 (Autostainer/Autostainer Plus) Recombinant Antibody (CB404) | Human | IgG1, κ |
| CBMAB-FT101LY | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (CF427) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG2a |
| CBMAB-AP415LY | Mouse Anti-AR Recombinant Antibody (CAP173) | Human, Rat | IgG1 |
| CBMAB-AP2560LY | Mouse Anti-GLS Recombinant Antibody (307) | Human | IgG2b |
| CBMAB-EN349-LY | Mouse Anti-ATXN2 Recombinant Antibody (EG317) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgM, κ |
| CBMAB-EN1902-LY | Rabbit Anti-HTR2B Recombinant Antibody (EG1589) | Human | IgG |
| V2LY-0624-LY245 | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (EC245) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
| V2LY-0624-LY246 | Mouse Anti-TBP Recombinant Antibody (EC246) | Human, Mouse, Rat | IgG |
References
- Jin, Jonghwa, et al. "Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 55.4 (2023): 706-715.
- Erb, Holger HH, et al. "Glutamine metabolism and prostate cancer." Cancers 16.16 (2024): 2871.
- Endicott, Molly, Michael Jones, and Jonathon Hull. "Amino acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in cancer: a review." Amino Acids 53.8 (2021): 1169-1179.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


