ADNP Antibodies
Background
The activity-dependent neuroprotective protein encoded by the ADNP gene is a transcription factor that is crucial for neural development and cognitive function. This protein directly participates in chromatin remodeling, synaptic formation and DNA repair processes by regulating the expression of multiple target genes, and plays a core role in mitochondrial function. Clinically, ADNP gene mutations are directly related to Helsmoortel-Van der Aa Syndrome, and the typical manifestations of patients are intellectual disability and autism spectrum characteristics. This gene was first discovered by the team of Israeli scientist Ilan Gozes in 2007. The protein structure it encodes contains two highly conserved zinc finger domains and nine nuclear localization signals. This multi-domain characteristic provides an important model for studying neuroprotective mechanisms and greatly promotes the research progress of the molecular mechanisms of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Structure of ADNP
ADNP is a relatively large multifunctional protein with a molecular weight of approximately 140 kDa. This protein is composed of 1,102 amino acids, and its structural features are mainly reflected in multiple key functional domains.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 140 | 139.5 | 139.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains nine zinc finger structure and homologous special-shaped box structure domains | NBPF homolog, with highly conserved neuroprotective peptide fragments | Sequence is similar to human height, function domain structure |
The core functional region of this protein consists of two tandem PhD-type zinc finger domains, which can directly bind to the histone H3 tail and mediate the interaction with the chromatin remodeling complex. Its C-terminal contains a nuclear localization signal peptide, while the N-terminal region is responsible for binding to various partner proteins. The entire molecule forms a rigid spatial conformation through nine conserved zinc finger modules, which is crucial for its function as a transcriptional regulatory factor.
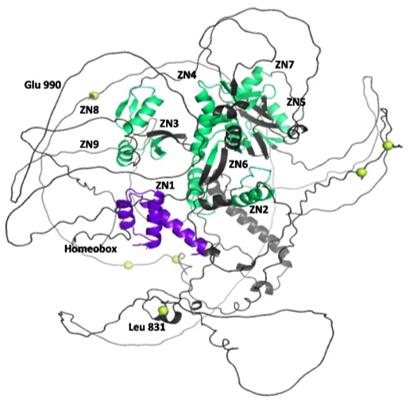 Fig. 1 3D structure of ADNP retrieved from Alphafold database.1
Fig. 1 3D structure of ADNP retrieved from Alphafold database.1
Key structural properties of ADNP:
- Contains nine highly conserved zinc-finger domains
- There is a mechanism of nuclear transfer mediated by nuclear localization signal
- Involved in transcriptional regulation through homeotypic box domains
- Form a stable β -folded lamellar and α -helical combined structure
Functions of ADNP
The core function of ADNP protein is to regulate neural development and maintain cellular homeostasis, and its mechanism of action covers multiple levels:
| Function | Description |
| Neurodevelopmental regulation | As a transcription factor, it directly activates or inhibits downstream target genes, guiding neuronal differentiation, migration and synaptic formation. |
| Chromatin remodeling | The interaction between zinc finger domains and chromatin modification complexes regulates epigenetic states and gene expression profiles. |
| DNA damage repair | Participate in maintaining genomic stability, is especially important in neurons, defects can lead to accelerate cell apoptosis. |
| Pathological association of autism | Insufficient haplodose is the main cause of Sheile-van der Wilde syndrome, and its clinical manifestations are characterized by intellectual disability and autism. |
| Mitochondrial function support | Regulating genes related to energy metabolism, influencing mitochondrial biosynthesis and function, and indirectly supporting neural activity. |
This protein functions in the form of a complex regulatory network through the nine zinc finger domains and nuclear localization signals it contains. The loss of its function has a much greater impact on the central nervous system than a defect in a single pathway, demonstrating its irreplaceable core position in the nervous system.
Applications of ADNP and ADNP Antibody in Literature
1. Sun X, Peng X, et al. "ADNP promotes neural differentiation by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 2984. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16799-0
The article indicates that ADNP stabilizes β-Catenin and enhances the Wnt signaling pathway by binding to β-Catenin and preventing it from binding to the Axin/APC degradation complex, thereby promoting neural induction and differentiation. The absence of ADNP can lead to the degradation of β-Catenin, causing neurodevelopmental abnormalities, which provides new insights into the pathological mechanism of ADNP syndrome.
2. Gozes, Illana. "The ADNP syndrome and CP201 (NAP) potential and hope." Frontiers in neurology 11 (2020): 608444. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.608444
The article indicates that ADNP syndrome is a rare autism spectrum disorder caused by de novo mutations in the ADNP gene. This mutation leads to neurological dysfunction, manifested as intellectual, social and motor disorders. Studies have shown that its active fragment CP201 can alleviate related symptoms in preclinical models, and clinical trials are planned to be conducted.
3. D’Incal, Claudio Peter, et al. "Chromatin remodeler Activity-Dependent Neuroprotective Protein (ADNP) contributes to syndromic autism." Clinical Epigenetics 15.1 (2023): 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-023-01450-8
The article indicates that the ADNP gene is one of the most common mutant genes causing Helsmoortel-Van der Aa syndrome (a syndromic type of autism). The proteins encoded by it mainly function by regulating chromatin remodeling. Abnormal ADNP function can trigger pleiotropic clinical features, which provides a mechanism-level explanation for understanding the complex manifestations of this syndrome.
4. Ferreira, Ana CF, et al. "Neuroprotective protein ADNP-dependent histone remodeling complex promotes T helper 2 immune cell differentiation." Immunity 56.7 (2023): 1468-1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2023.05.010
This study first discovered that ADNP is indispensable in the differentiation of Th2 cells and allergic immune responses. The mechanism lies in that ADNP can act as a key bridge, by recruiting chromatin remodeling complexes (such as CHD4 and BRG1), to activate the chromatin accessibility of type 2 cytokine gene loci, thereby driving the specialization of immune cells.
5. Maugeri, Grazia, et al. "Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP): An overview of its role in the eye." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.21 (2022): 13654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113654
This study indicates that ADNP and its derivative NAP are widely expressed in ocular tissues such as the retina and cornea. Studies have shown that NAP possesses neuroprotective, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties, and has demonstrated good safety in clinical trials. It is expected to become a potential candidate drug for the treatment of various eye diseases.
Creative Biolabs: ADNP Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality ADNP antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom ADNP Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our ADNP antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- D’Incal, Claudio Peter, et al. "Chromatin remodeler Activity-Dependent Neuroprotective Protein (ADNP) contributes to syndromic autism." Clinical Epigenetics 15.1 (2023): 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-023-01450-8
Anti-ADNP antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-F11R Recombinant Antibody (402) (CBMAB-0026-WJ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








