CAPG Antibodies
Background
The CAPG gene encodes an actin regulator called macrophage cap protein, which is mainly present in the cytoplasm and nucleus of mammals. This protein regulates the dynamics of the cytoskeleton by capping the positive end of actin filaments, influencing key physiological processes such as cell movement, cytoplasmic division and immune response. In tumor research, CAPG has attracted much attention due to its promoting effect on the migration and invasion of cancer cells, and its expression level is closely related to the metastatic potential of malignant tumors such as breast cancer and lung cancer. This gene was first identified in 1992. Subsequent studies gradually revealed that it has both nuclear regulatory functions and can be involved in gene transcription and chromatin remodeling. As the intersection point of cytoskeleton and epigenetic regulation, CAPG provides an important perspective for understanding the molecular mechanisms of cell motility and malignant transformation.
Structure of CAPG
CAPG is a cytoskeleton-related protein with a molecular weight of approximately 38.5 kDa. This value shows subtle differences among different species, mainly due to species-specific variations in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 38.5 | 38.3 | 38.6 | 38.4 |
This protein is composed of 348 amino acids, and its tertiary structure contains three typical actin binding domains. The core functional region of CAPG contains specific motifs that interact with the positive end of actin filaments and regulates the dynamic assembly of the cytoskeleton through a "capping" mechanism. The nuclear locus sequence at the N-terminal of the protein enables it to shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nucleus, while the acidic region at the C-terminal is responsible for direct binding to actin. This structural characteristic enables CAPG to play a key role in maintaining cell morphology and movement.
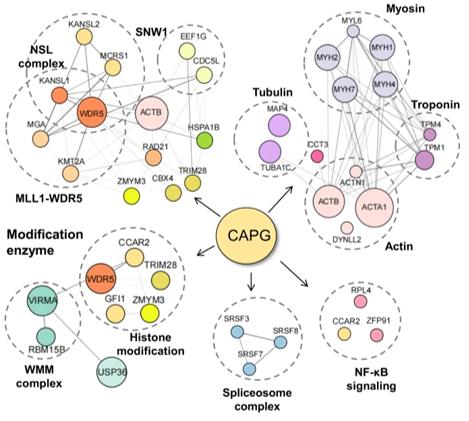 Fig. 1 Connection of CAPG with multiple protein complexes.1
Fig. 1 Connection of CAPG with multiple protein complexes.1
Key structural properties of CAPG:
- Contains three conserved actin-binding domains
- Flexible C-terminal sequence with nuclear localization signal
- Positively charged surface area is responsible for the combined with actin filament
Functions of CAPG
The core function of CAPG protein is to regulate the dynamic assembly of actin cytoskeleton. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of key physiological processes such as cell movement and nuclear activity.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of cell movement | By capping the ends of actin filaments, the formation of pseudopodia and the direction of cell migration are controlled. |
| Cytoplasmic division assistance | At the end of cell division, it helps with the precise assembly and positioning of the contraction ring. |
| Intraconuclear regulation | After entering the cell nucleus, it affects the transcriptional activity of genes and the remodeling of chromatin structure. |
| Promotion of tumor metastasis | In a wide variety of cancer cells increased, thus enhancing their ability of invasion and metastasis. |
| Participation in immune response | Regulate the chemotactic movement and phagocytic function of immune cells such as macrophages. |
Unlike single-function structural proteins, CAPG operates in a concentration-dependent mode: at low concentrations, it only delays actin assembly, while at high concentrations, it completely blocks elongation. This dynamic regulatory mechanism enables it to flexibly adapt to the demands of different cellular states.
Applications of CAPG and CAPG Antibody in Literature
1. Song, Runjie, et al. "A novel polypeptide CAPG-171aa encoded by circCAPG plays a critical role in triple-negative breast cancer." Molecular cancer 22.1 (2023): 104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01806-x
Research has found that the circular RNA circCAPG is highly expressed in TNBC and can be translated into CAPG-171aa protein. It promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating the MEKK2 pathway, and its generation is regulated by SLU7. It is expected to become a prognostic marker and a new therapeutic target for TNBC.
2. Kulkarni, Roshan, et al. "CAPG: comprehensive allopolyploid genotyper." Bioinformatics 39.1 (2023): btac729. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac729
This study developed the CAPG genotyping tool, which is specifically designed for heteropolyploid plants. It can more accurately distinguish homologous sequences and identify genotypes through double-reference genome alignment, effectively solving the problem of excessively high heterozygous false positives in existing methods.
3. Long, Yan, et al. "CAPG is a novel biomarker for early gastric cancer and is involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway." Cell death discovery 10.1 (2024): 15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01767-6
This study for the first time reveals that actin CAPG is highly expressed in early gastric cancer and can promote the malignant progression of cancer cells. Its mechanism of action is related to the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, suggesting that it can serve as a novel biomarker for early gastric cancer.
4. Fu, Ying, et al. "CapG promoted nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell motility involving Rho motility pathway independent of ROCK." World Journal of Surgical Oncology 20.1 (2022): 347. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-022-02808-7
Research has found that actin regulatory protein CapG is highly expressed in poorly differentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma and can enhance cancer cell migration and invasion by promoting myosin light chain phosphorylation. This effect is independent of the ROCK and Rac1 pathways.
5. Ma, Qian, et al. "Super-enhancer-associated gene CAPG promotes AML progression." Communications biology 6.1 (2023): 622. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04973-1
Studies have found that the super enhancer-related gene CAPG is highly expressed in AML and predicts a poor prognosis. It promotes leukemia progression by regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. In animal models, knocking down Capg can inhibit tumors and prolong survival.
Creative Biolabs: CAPG Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CAPG antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CAPG Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CAPG antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ma, Qian, et al. "Super-enhancer-associated gene CAPG promotes AML progression." Communications biology 6.1 (2023): 622. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04973-1
Anti-CAPG antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (D73H4) (CBMAB-A2314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CAMK2A Recombinant Antibody (BA0032) (CBMAB-0137CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AGK Recombinant Antibody (V2-258056) (CBMAB-M0989-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR-0120) (CBMAB-R0120-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








