CCR6 Antibodies
Background
The CCR6 gene encodes a cell surface protein belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor family, which is mainly expressed in immune cells such as memory T cells, B cells and dendritic cells. This protein specifically binds to its ligand CCL20, thereby mediating the directional migration of immune cells and playing a key role in processes such as intestinal mucosal immunity, inflammatory responses, and lymphocyte homing. This gene was first identified in 1997. The clarification of its structure and function has provided an important foundation for understanding the immune mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, cancer metastasis and infectious diseases. Research on the CCR6-CCL20 axis has become an important direction for developing targeted treatments for various immune-related diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
Structure of CCR6
The protein encoded by the CCR6 gene is a G protein-coupled receptor with a molecular weight of approximately 41 kDa. This receptor belongs to the chemokine receptor family, and its size varies slightly among different species due to the degree of glycosylation and minor sequence differences. The following is a comparison of some species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 41 | About 40.5 | About 40.8 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Containing 352 amino acids, glycosylation sites N | Amino acid sequence homology is high and ligand-binding domains are highly conserved | Across the membrane area structure similar to the height of mice and humans |
The primary structure of this protein contains seven transmembrane α -helical domains, which is a characteristic of it as a G protein-coupled receptor. Its N-terminal extracellular region is crucial for the specific recognition and binding to its only known natural ligand, CCL20. The key secondary and tertiary structures together form a hydrophobic pocket to stabilize the ligand-receptor interaction, among which the specific amino acid residues on the third transmembrane region and the second extracellular loop are directly involved in the initiation of signal transduction.
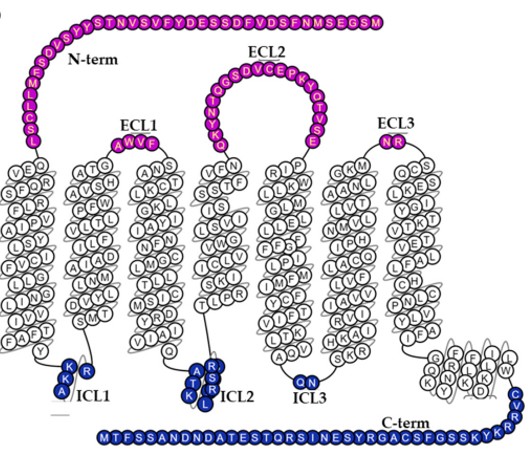 Fig. 1 CCR6 Topology: A Snake Helix Box Diagram.1
Fig. 1 CCR6 Topology: A Snake Helix Box Diagram.1
Key structural properties of CCR6:
- Classic sevenfold transmembrane α-helical domain
- Extracellular N-terminal and three extracellular loop CCL20 ligand binding domain
- Intracellular C side and three cell inner ring to participate in the G protein signal transduction
- Conserved disulfide bonds in the second extracellular loop are essential for maintaining receptor conformation
Functions of CCR6
The main function of the protein encoded by the CCR6 gene is to mediate the directional migration of immune cells and play a core role in mucosal immunity and tissue homeostasis. However, it is also involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including the development of inflammatory diseases and cancer metastasis.
| Function | Description |
| Cell chemotaxis | As a specific receptor for the chemokine CCL20, it guides lymphocytes, dendritic cells and other cells expressing CCR6 to migrate to the inflammatory site or mucosal tissue. |
| Mucosal immunity | Regulating the homing and localization of immune cells in mucosal sites such as the intestines and skin is the key to maintaining the defense function of the mucosal barrier. |
| Inflammatory regulation | Participate in the pathogenesis of various chronic inflammatory diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease). |
| Cancer metastasis | In some cancers, the CCR6-CCL20 axis can promote the migration of tumor cells and their metastasis to specific organs such as the liver and lymph nodes. |
| Immune tolerance | By regulating the migration of regulatory T cells (TreGs), it participates in the establishment and maintenance of immune tolerance. |
The signal transduction of CCR6 mainly relies on its coupling with Gαi protein, which inhibits intracellular cAMP levels and activates pathways such as MAPK, thereby driving cytoskeletal rearrangement and directional movement. The expression of its ligand CCL20 is often induced by pro-inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α, IL-1β), which makes the CCR6-CCL20 axis an important bridge connecting innate immunity and adaptive immunity.
Applications of CCR6 and CCR6 Antibody in Literature
1. Gómez-Melero, Sara, and Javier Caballero-Villarraso. "CCR6 as a potential target for therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of inflammatory diseases." Antibodies 12.2 (2023): 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020030
The article indicates that the CCR6/CCL20 signaling axis is involved in the processes of various diseases such as cancer and autoimmune diseases, and is an important therapeutic target. At present, no drugs targeting CCR6 have been approved. Developing antibodies against this receptor may become a potential new strategy to replace small molecules.
2. Kadomoto, Suguru, Kouji Izumi, and Atsushi Mizokami. "The CCL20-CCR6 axis in cancer progression." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.15 (2020): 5186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155186
The article indicates that the CCL20-CCR6 signaling axis not only participates in inflammatory diseases but also drives progression in various cancers such as liver cancer and intestinal cancer by directly promoting cancer and reshaping the tumor microenvironment, making it a highly promising therapeutic target.
3. Ranasinghe, Ranmali, and Rajaraman Eri. "Modulation of the CCR6-CCL20 axis: a potential therapeutic target in inflammation and cancer." Medicina 54.5 (2018): 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina54050088
The article indicates that the CCR6-CCL20 axis is a key target for inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Sixteen potential inhibitors have been identified globally, including antibodies and small molecule drugs. However, there is still a lack of efficient and safe new therapies, and the research and development prospects are broad.
4. Das, Mahasweta, et al. "CCL20-CCR6 axis modulated traumatic brain injury-induced visual pathologies." Journal of Neuroinflammation 16.1 (2019): 115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1499-z
Research has revealed that the CCL20-CCR6 axis mediates retinal degeneration and neuroinflammation after repetitive brain trauma (rTBI). Knockout of CCR6 or the use of CCL20 neutralizing antibodies can both alleviate the injury, confirming that this pathway is a potential target for the treatment of traumatic visual impairment.
5. Schumacher, David, et al. "CCR6 deficiency increases infarct size after murine acute myocardial infarction." Biomedicines 9.11 (2021): 1532. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111532
Research has found that in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, CCR6 deficiency can aggravate the decline of cardiac function and inflammation. In particular, CCR6-positive cells originating from the bone marrow play a key protective role, suggesting that enhancing this pathway may be a potential therapeutic direction.
Creative Biolabs: CCR6 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CCR6 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CCR6 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CCR6 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Gómez-Melero, Sara, and Javier Caballero-Villarraso. "CCR6 as a potential target for therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of inflammatory diseases." Antibodies 12.2 (2023): 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib12020030
Anti-CCR6 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 (Phosphorylated S473) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505430) (PTM-CBMAB-0067LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y185) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443434) (PTM-CBMAB-0001YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BLK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0618) (CBMAB-0621-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FLT1 Recombinant Antibody (11) (CBMAB-V0154-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOH Recombinant Antibody (4D9A4) (CBMAB-A3249-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CDK7 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C1783) (CBMAB-C3221-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








