CD276 Antibodies
Background
CD276 (also known as B7-H3) is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the B7 costimulatory molecule family, which is widely expressed on the surface of various normal tissues and tumor cells. This protein plays a dual role in the immune checkpoint pathway by regulating the immune response activity of T lymphocytes - it can not only suppress excessive immune responses to maintain autoimmune tolerance, but also be utilized by tumor cells to achieve immune escape. Since its first identification by Chapoval et al. in 2001, CD276 has become an important research target in the field of tumor immunotherapy due to its abnormally high expression in malignant tumors such as lung cancer and prostate cancer. Its unique molecular structure and differentiated immunomodulatory functions continuously drive the development of innovative therapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and antibody-drug conjugates, providing a key theoretical basis for the study of immune regulatory mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment.
Structure of CD276
CD276 (B7-H3) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein. Its molecular weight varies among different species, mainly due to the different degrees of gene splicing and glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Crab-eating macaque |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~60-110 | ~55-100 | ~58-105 | ~62-108 |
| Primary Structural Differences | There are two main isomers, 4Ig and 2Ig | High homology with human and different glycosylation pattern | Extracellular domain highly conserved amino acid sequence | The structure closest to human protein |
This protein is composed of 316 amino acids (taking human 4Ig-B7-H3 as an example), and its extracellular segment contains immunoglobulin-like domains (IgV and IgC). These domains form stable dimers through disulfide bonds, which form the basis of interaction with ligands. Its intracellular segment is relatively short and lacks known clear signaling motifs. This feature suggests that it may transmit immunosuppressive signals by forming complexes with other membrane proteins. The hydrophobic α -helix in the transmembrane region is responsible for anchoring proteins to the cell membrane. Its complex N-link glycosylation modification not only affects the molecular weight of the protein, but also directly participates in regulating its specificity and affinity for binding to receptors.
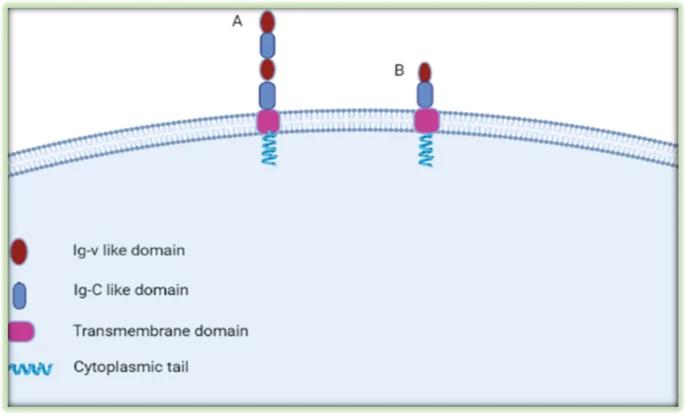 Fig. 1 Structure of B7-H3 Protein.1
Fig. 1 Structure of B7-H3 Protein.1
Key structural properties of CD276:
- Extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain (IgV-IgC)
- Homodimer configuration stabilized by disulfide bonds
- Highly glycosylated immunomodulatory interface
Functions of CD276
The main function of CD276 (B7-H3) is to act as a regulatory molecule in immune responses. However, its specific effects are environmentally dependent and show significant differences under physiological and pathological conditions.
| Function | Description |
| Immune co-regulation | In the tumor microenvironment, T cell activation and cytokine production are usually inhibited, but costimulatory activity may also be exhibited under specific inflammatory conditions. |
| Cell adhesion support | The extracellular immunoglobulin domain mediates cell-cell interactions and affects the migration and invasion of tumor cells. |
| Angiogenesis regulation | In a variety of solid tumors with high expression, by influencing the promote the formation of the tumor related to vascular endothelial cell function. |
| Metabolic reprogramming | Participating in the metabolic adaptation of the tumor microenvironment through indirect mechanisms may be related to the exhaustion of immune cell function. |
| Diagnostic markers | Its specific high expression pattern on the surface of various malignant tumor cells makes it a potential target for immunotherapy and a diagnostic marker. |
The interaction between CD276 and its ligands does not follow the typical affinity saturation model, but rather exhibits complex concentration dependence and microenvironment sensitivity, which reflects its functional plasticity in immune synapses and the complexity of regulation as an immune checkpoint molecule.
Applications of CD276 and CD276 Antibody in Literature
1. Zhou, Wu-Tong, and Wei-Lin Jin. "B7-H3/CD276: an emerging cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 701006. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.701006
The article indicates that CD276 (B7-H3) is an immunomodulatory protein of the B7 family, which is highly expressed in various tumors and participates in the regulation of the tumor microenvironment. It is a potential target for cancer immunotherapy. Multiple therapies based on CD276 have demonstrated good anti-tumor effects and safety in preclinical studies.
2. Cheng, Maosheng, et al. "CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 2818. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46735-5
This study reveals that CD276 is expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (Tams), promoting their cell burial by activating JUN transcription factors, thereby inhibiting T cell infiltration and weakening anti-tumor immunity. Combined blocking of CD276 and PD-1 can significantly inhibit tumor growth, providing a new target for combined immunotherapy.
3. Getu, Ayechew Adera, et al. "New frontiers in immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) research and drug development." Molecular Cancer 22.1 (2023): 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01751-9
This study reveals that CD276 (B7-H3) is specifically highly expressed in tumors. Besides its immune checkpoint function, it also drives malignant processes such as tumor proliferation, metastasis and metabolic reprogramming. Its significantly different expression pattern from normal tissues makes it a highly potential anti-cancer target. Recent research has made significant progress in both the mechanism of action and drug development.
4. Feng, Yang, et al. "Engineering CD276/B7-H3-targeted antibody-drug conjugates with enhanced cancer-eradicating capability." Cell reports 42.12 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113503
This study reveals that for the CD276 target, researchers have developed a novel antibody-drug conjugate, m276-SL-PBD. This drug, through multiple optimizations, can efficiently eliminate large triple-negative breast cancer tumors at extremely low doses. Its therapeutic index has significantly improved compared to previous generations of drugs, providing a promising targeted solution for the treatment of various solid tumors.
5. Liu, Shengzhuo, et al. "The role of CD276 in cancers." Frontiers in Oncology 11 (2021): 654684. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.654684
The article indicates that CD276 (B7-H3) is an abnormally expressed immune checkpoint molecule in malignant tumors, which drives tumor progression by promoting tumor cell proliferation, invasion and migration. Existing evidence indicates that the therapeutic strategy targeting CD276 shows great therapeutic potential in malignant tumors.
Creative Biolabs: CD276 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CD276 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD276 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD276 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Getu, Ayechew Adera, et al. "New frontiers in immune checkpoint B7-H3 (CD276) research and drug development." Molecular Cancer 22.1 (2023): 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01751-9
Anti-CD276 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CALR Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0763) (CBMAB-C0818-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AP2M1 (Phosphorylated T156) Recombinant Antibody (D4F3) (PTM-CBMAB-0610LY)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CSPG4 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYM-1050) (CBMAB-M1203-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






