CTSB Antibodies
Background
The CTSB gene encodes cathepsin B, a cysteine protease mainly located in lysosomes, which is responsible for protein degradation and processing within vertebrate cells. This enzyme participates in key physiological processes such as autophagy, antigen presentation and tissue remodeling by hydrolyzing peptide bonds. Meanwhile, its abnormal expression is closely related to tumor metastasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Since its identification in mammalian tissues in the 1960s, tissue protease B has become a typical model for the study of lysosomal function. The conformational change mechanism from zymogenase activation to mature enzymes provides an important paradigm for the study of protease function regulation, promoting a deeper understanding of the intracellular microenvironment's regulation of enzyme activity and the mechanism of protease action in pathological networks.
Structure of CTSB
Cathepsin B encoded by the CTSB gene is a lysosomal protease with a molecular weight of approximately 37-38 kDa. There are slight differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to the different amino acid compositions in the precursor peptide and zymogen regions.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 37.8 | 37.5 | 37.6 | 37.9 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains precursor peptides and heavy and light chains | 80% homology to humans | Active site highly conservative | Enzyme original area is slightly different |
This protein is composed of 333 amino acids, and its spatial structure shows a typical papain folding pattern. The active center of the mature enzyme is composed of the Cys29-His199-Asn219 triad, a characteristic structure responsible for catalyzing substrate hydrolysis. The N-terminal precursor peptide of the protein is automatically removed during the activation process, and at the same time, a mature active site fissure is formed through structural rearrangement. This mechanism effectively prevents endogenous non-specific proteolysis within the cell.
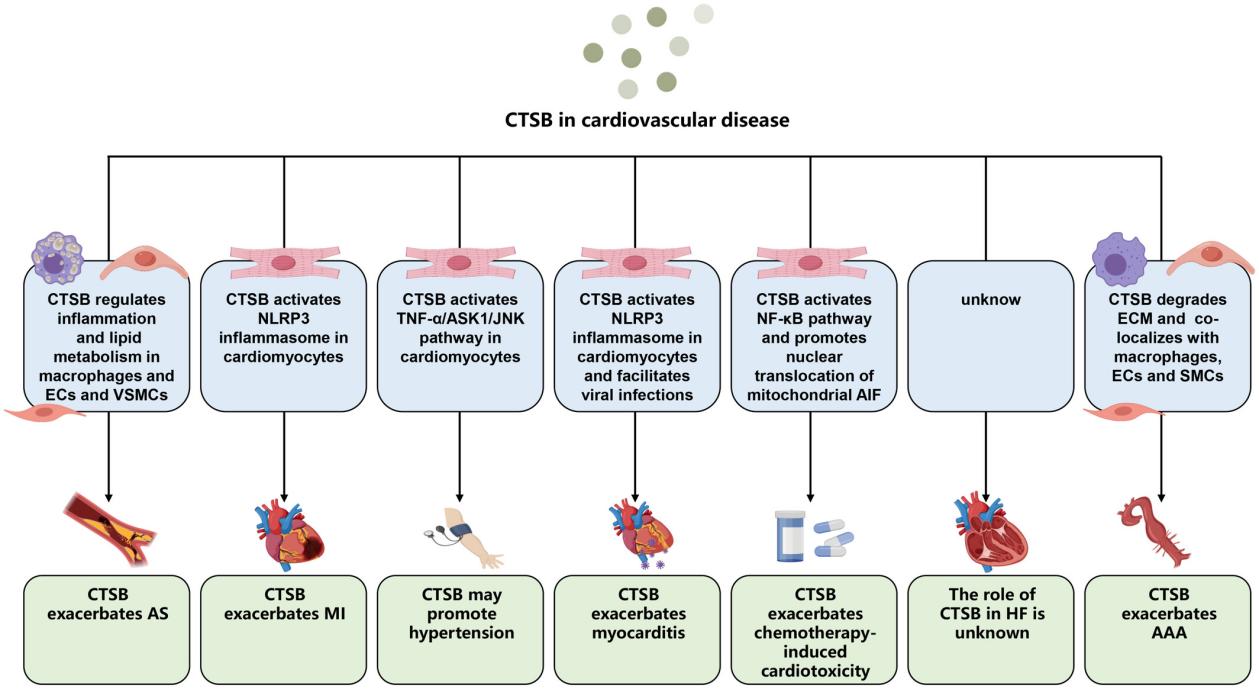 Fig. 1 CTSB function in cardiovascular diseases.1
Fig. 1 CTSB function in cardiovascular diseases.1
Key structural properties of CTSB:
- Papain protein-like folding structure
- Active fissures composed of heavy chains and light chains
- The catalytic triplet (Cys-His-Asn) is responsible for substrate hydrolysis
- Automatic removal of precursor peptide in enzyme activation process
Functions of CTSB
The main function of cathepsin B encoded by the CTSB gene is to degrade proteins within lysosomes. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including extracellular matrix remodeling, antigen presentation and tumor invasion.
| Function | Description |
| Protein degradation | Hydrolysis of peptide bonds in the acidic environment of lysosomes is responsible for the removal of long-lived and discarded proteins in cells. |
| Antigen presentation | Exogenous or endogenous proteins are cleaved into short peptides for presentation by MHC Class II molecules to activate immune responses. |
| Extracellular matrix remodeling | Under specific conditions, it is secreted outside the cell, degrading components such as collagen and laminin, and affecting tissue repair and cancer cell metastasis. |
| Promotion of tumor invasion | By degrading the basement membrane and extracellular matrix components, physical channels are created for the local infiltration and distant metastasis of cancer cells. |
| Regulation of autophagy in cells | To assist in the autophagy-lysosome pathway degradation of captive cytoplasmic components, maintain cell metabolism balance. |
The optimal pH for the activity of cathepsin B is within the acidic range, which is consistent with its main localization in lysosomes. However, it still retains some enzymatic activity at neutral pH, and this characteristic is believed to be closely related to its pathological function outside the lysozyme.
Applications of CTSB and CTSB Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Yuting, et al. "CTSB promotes sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2023): 1053754. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1053754
This study, through a model of acute kidney injury caused by sepsis, found that cathepsin B (CTSB) plays a key role in renal cell apoptosis. Lps-induced activation of CTSB induces the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway; Inhibiting CTSB can alleviate cell damage. CTSB may become a new therapeutic target.
2. Li, Xiaoxun, et al. "CST6 protein and peptides inhibit breast cancer bone metastasis by suppressing CTSB activity and osteoclastogenesis." Theranostics 11.20 (2021): 9821. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.62187
This study reveals that in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury, cathepsin B (CTSB) is a key factor leading to renal cell death. Inhibiting the activity of CTSB can effectively alleviate cell damage by protecting mitochondrial function, indicating that it can serve as a new therapeutic target.
3. Peng, Sida, et al. "CTSB knockdown inhibits proliferation and tumorigenesis in HL-60 cells." International Journal of Medical Sciences 18.6 (2021): 1484. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.54206
This study reports for the first time that cathepsin B (CTSB) is highly expressed in adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and is associated with a poor prognosis for patients. Mechanically, knocking down CTSB can effectively inhibit the proliferation and tumorigenesis ability of leukemia cells by suppressing the AKT signaling pathway.
4. Ma, Kaiming, et al. "CTSB is a negative prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target associated with immune cells infiltration and immunosuppression in gliomas." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 4295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08346-2
Research has found that cathepsin B (CTSB) is highly expressed in malignant subtypes (such as mesenchymal type) gliomas and is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis. CTSB is closely related to the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment, especially positively correlated with the infiltration of immunosuppressive cells such as TAM and MDSC, suggesting that it can serve as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target.
5. Li, Cairui, et al. "CTSB nuclear translocation facilitates DNA damage and lysosomal stress to promote retinoblastoma cell death." Molecular Biotechnology 66.9 (2024): 2583-2594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-01042-0
This study reveals that cathepsin B (CTSB) exerts tumor suppressor effects in retinoblastoma through its nuclear translocation. After CTSB enters the nucleus, it inhibits BRCA1 and activates the STAT3/STING1 pathway, inducing DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, ferroptosis and autophagy, thereby inhibiting tumor progression.
Creative Biolabs: CTSB Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CTSB antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CTSB Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CTSB antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Cai, Zhulan, Shunyao Xu, and Chen Liu. "Cathepsin B in cardiovascular disease: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic strategies." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 28.17 (2024): e70064. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70064
Anti-CTSB antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BANF1 Recombinant Antibody (3F10-4G12) (CBMAB-A0707-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BMI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-P026) (CBMAB-P0108-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (P67.6) (CBMAB-C10189-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Rat Anti-CCR2 Recombinant Antibody (475301) (CBMAB-C1338-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CORO1A Recombinant Antibody (4G10) (V2LY-1206-LY806)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CFL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1771) (CBMAB-C1833-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








