GPNMB Antibodies
Background
GPNMB is a molecule that exists as a type II transmembrane glycoprotein and is widely expressed in melanocytes, osteoclasts and certain tumor cells. The protein encoded by this gene can play a dual role in tissue repair and the tumor microenvironment by participating in processes such as cell adhesion, differentiation and immune regulation. Especially in the research on diseases such as melanoma and triple-negative breast cancer, it has been found that GPNMB can not only affect tumor progression by regulating autophagy, but also serve as an important biomarker for targeted therapy. This gene was first identified in melanoma cells by a Japanese research team in 1995. The unique association mechanism between its extracellular segment domain and intracellular signal transduction remains an important model in the fields of tumor immunity and bone metabolism research to this day, providing a molecular theoretical basis for the development of precision medical strategies.
Structure of GPNMB
GPNMB is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 65-100 kDa. Its differences mainly stem from the varying degrees of glycosylation modification among species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 65-100 | 60-95 | 62-98 | 68-102 |
| Primary Structural Differences | With RGD motif and PKD domain structure | The RGD motif is conserved | High homology was found in the extracellular segment | Different number of glycosylation sites |
This protein is composed of 560 amino acids. Its extracellular segment contains an RGD cell adhesion motif and a PKD domain, while the intracellular segment has signal transduction functions. The secondary structure of GPNMB is mainly β -folding, which forms specific spatial conformations, enabling it to bind with ligands such as integrins. The special spatial arrangement of its extracellular segment not only mediates intercellular interactions but also participates in regulating melanin production and the balance of bone metabolism.
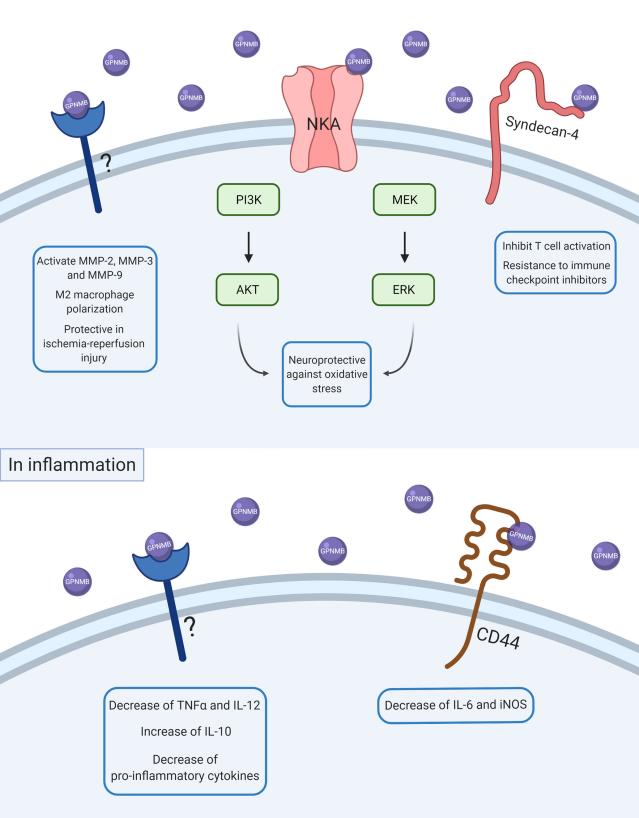 Fig. 1 Scheme of GPNMB intracellular signaling in physiological and inflammatory conditions.1
Fig. 1 Scheme of GPNMB intracellular signaling in physiological and inflammatory conditions.1
Key structural properties of GPNMB:
- By extracellular region, transmembrane region and intracellular short paragraph of type I transmembrane topology
- Extracellular region containing RGD cell adhesion die bodies and PKD domain structure
- Nearly membrane area exists since the cracking loci, can release soluble form
Functions of GPNMB
The core function of GPNMB is to participate in tissue repair and immune regulation, and at the same time play a dual role in tumor occurrence.
| Function | Description |
| Cell adhesion and migration | The cell-matrix interaction is mediated through the RGD motif, influencing the migration and localization of various cells such as melanocytes and osteoblasts. |
| Immune regulation | Regulating the T-cell activation threshold in antigen-presenting cells, its soluble form can inhibit excessive inflammatory responses. |
| Tissue repair | Promote the fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition, in the process of wound healing and bone remodeling play a key role. |
| Tumor-promoting effect | The activation of PI3K/Akt pathway enhances tumor cell survival and promotes angiogenesis and distant metastasis. |
| Tumor suppressive function | In certain contexts, it can induce autophagy and enhance chemotherapy sensitivity, demonstrating an environment-dependent tumor suppressor effect. |
The functional spectrum of GPNMB shows "spatiotemporal specificity": under physiological conditions, it mainly mediates the maintenance of tissue homeostasis, while in the pathological microenvironment, it may transform into a cancer-promoting or cancer-suppressing factor. This functional paradox makes it a pivotal molecule for cross-disciplinary research.
Applications of GPNMB and GPNMB Antibody in Literature
1. Saade, Marina, et al. "The role of GPNMB in inflammation." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 674739. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.674739
The article indicates that GPNMB is a glycoprotein highly expressed in macrophages and microglia, and it is closely related to inflammatory and neuroinflammatory processes. At present, there is controversy over its effect in research. Most believe that it has anti-inflammatory functions and promotes the resolution of inflammation, but there is also evidence suggesting that it may exert pro-inflammatory effects. This article reviews the dual role of GPNMB in inflammation.
2. Gillett, Drew A., et al. "Progranulin and GPNMB: interactions in endo-lysosome function and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease." Journal of Neuroinflammation 20.1 (2023): 286. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-023-02965-w
The article indicates that GPNMB interacts with granular protein precursors (PGRN) to jointly regulate endosome-lysosome function, immunity and inflammatory responses. The two are closely related in neurodegenerative diseases and are potential therapeutic targets that may delay the progression of the disease.
3. Neal, Matthew L., et al. "The glycoprotein GPNMB attenuates astrocyte inflammatory responses through the CD44 receptor." Journal of neuroinflammation 15.1 (2018): 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1100-1
The article indicates that GPNMB, through its receptor CD44, inhibits the inflammatory response of astrocytes in the Parkinson's disease model, reduces the production of factors such as nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species and IL-6, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects. This study reveals a new mechanism by which GPNMB has anti-neuroinflammation effects.
4. King, Emily M., et al. "Gpnmb and Spp1 mark a conserved macrophage injury response masking fibrosis-specific programming in the lung." JCI insight 9.24 (2024): e182700. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.182700
Research has found that the macrophage subpopulation expressing GPNMB is a conserved response after lung injury and exists in both fibrotic and non-fibrotic models. This subpopulation itself is not sufficient to drive fibrosis, and the key to fibrosis lies in the persistent presence of recruiting macrophages and the dynamic imbalance in their programming.
5. Wang, Jing, et al. "Macrophage-derived GPNMB trapped by fibrotic extracellular matrix promotes pulmonary fibrosis." Communications Biology 6.1 (2023): 136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04333-5
Research has found that in pulmonary fibrosis, GPNMB derived from macrophages is captured by the diseased extracellular matrix and activates fibroblasts through the CD44/Serpinb2 pathway, thereby driving the fibrotic process. This mechanism provides potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Creative Biolabs: GPNMB Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GPNMB antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GPNMB Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GPNMB antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Han, Jun, et al. "Effect of changes in the structure of myoglobin on the color of meat products." Food Materials Research 4.1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.48130/fmr-0024-0003
Anti-GPNMB antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALX1 Recombinant Antibody (96k) (CBMAB-C0616-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (HIS50) (CBMAB-C10123-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXA3 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-0377-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCN2 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2383) (CBMAB-C2456-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








