GRB2 Antibodies
Background
GRB2 is a widely expressed cytoplasmic adaptor protein that mainly participates in the signal transduction process mediated by receptor tyrosine kinases. This protein recognizes phosphorylated tyrosine residues through its SH2 domain and uses two SH3 domains to recruit downstream effector molecules, thereby activating key signaling pathways such as RAS-MAPK to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. During embryonic development and tumorigenesis, GRB2 serves as the core medium for cellular communication by precisely coordinating the assembly of multi-protein complexes. GRB2, which was jointly identified by multiple research teams in the early 1990s, has become a classic model for studying the mechanism of cell signal transduction due to its pivotal function of connecting cell surface receptors with intracellular signal networks. Its modular structure and multivalent binding characteristics continuously provide an important theoretical framework for protein-protein interaction networks, dynamic assembly, and targeted therapeutic strategies.
Structure of GRB2
GRB2 is an intracellular adaptor protein with a molecular weight of approximately 25 kDa. Its molecular weight shows a high degree of conservation among different mammals, which is attributed to the precise localization of its functional domain.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 25.2 | 25.1 | 25.2 | 25.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Including SH2 1 and 2 SH3 domain structure | Completely conservative SH2 domain structure | The SH3 domain has a single amino acid substitution | The consistency with the human sequence reaches 99% |
This protein is composed of 217 amino acids, forming a unique modular three-dimensional architecture. The core structure of GRB2 consists of one SH2 domain and two SH3 domains, which form a specific spatial arrangement through flexible connecting peptides. Its SH2 domain can specifically recognize phosphorylated tyrosine residues, while the two SH3 domains are responsible for binding to proline-rich motifs. This unique structural combination enables GRB2 to simultaneously bridge upstream activated receptors and downstream effector molecules, playing a crucial molecular adapter role in signal transduction.
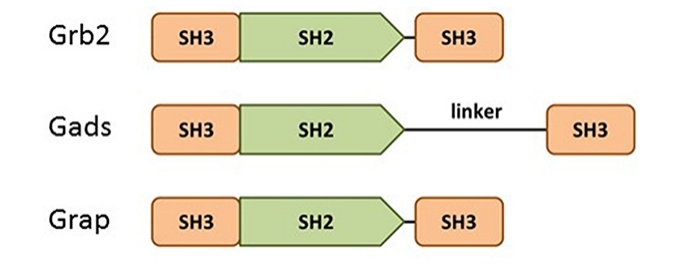 Fig. 1 Domain structure of the Grb2 family members: Grb2, Gads, and Grap.1
Fig. 1 Domain structure of the Grb2 family members: Grb2, Gads, and Grap.1
Key structural properties of GRB2:
- Modular domain composition
- Phosphotyrosine recognition mediated by the SH2 domain
- Proline-enriched motif binding driven by the double SH3 domain
Functions of GRB2
As a core adaptor protein for intracellular signal transduction, GRB2's function mainly lies in the precise assembly of signal complexes. This protein plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes by specifically recognizing phosphorylated tyrosine and proline-enriched motifs.
| Function | Description |
| Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling | By binding to the phosphorylated tyrosine site of the activated receptor through the SH2 domain, a downstream signaling cascade reaction is initiated. |
| Activation of the RAS-MAPK pathway | The SH3 domain is utilized to recruit the SOS1 guanylate exchange factor to the cell membrane, directly activating the RAS signaling molecule. |
| Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation | Integrate multiple signals such as growth factors and cytokines to regulate the cell cycle process and fate determination. |
| Regulation of immune response | Involved in T cell receptors and B cell receptor signal transduction, regulation of immune cell activation and function. |
| Cell migration and skeleton recombination | Linking adhesion spot kinase with downstream effector molecules affects cell motility and morphogenesis. |
The signal transduction mode of GRB2 exhibits typical "molecular switch" characteristics, in sharp contrast to the synergistic effects of multi-domain proteins. Its unique structural composition enables it to simultaneously recognize upstream activation signals and downstream effector molecules, playing an irreplaceable adapter role in both normal development and tumorigenesis, providing a key entry point for targeted therapy research.
Applications of GRB2 and GRB2 Antibody in Literature
1. Montero-Vergara, Jetsy, et al. "GRB2 is a BECN1 interacting protein that regulates autophagy." Cell Death & Disease 15.1 (2024): 14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-06387-7
Research has found that GRB2 is a novel binding protein of BECN1. It affects autophagy by regulating the activity of VPS34 kinase. In breast cancer models, inhibiting the function of GRB2 can reduce autophagy activity and suppress tumor growth, revealing a new function of GRB2 in regulating tumors through autophagy.
2. Zhou, Jie, et al. "RNF173 suppresses RAF/MEK/ERK signaling to regulate invasion and metastasis via GRB2 ubiquitination in hepatocellular carcinoma." Cell Communication and Signaling 21.1 (2023): 224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-023-01241-x
This study found that RNF173 can ubiquitinate and degrade GRB2, thereby inhibiting its downstream RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, and ultimately curbing the proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells.
3. Hou, Bolin, et al. "Grb2 binds to PTEN and regulates its nuclear translocation to maintain the genomic stability in DNA damage response." Cell Death & Disease 10.8 (2019): 546. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1762-3
This study reveals a new function of GRB2 in DNA damage responses. It maintains genomic stability by regulating the nuclear localization of the tumor suppressor protein PTEN and influencing the expression of the key protein Rad51 for homologous recombination repair.
4. Yablonski, Deborah. "Bridging the gap: modulatory roles of the Grb2-family adaptor, Gads, in cellular and allergic immune responses." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 1704. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01704
In this study, as a member of the GRB2 family, Gads serves as a key bridge connecting LAT and SLP-76 and is crucial for assembling the T-cell receptor signaling complex. Its function can be enhanced through dimerization or negatively regulated by the shearing of the linker region.
5. Ahmed, Zamal, et al. "Grb2 monomer–dimer equilibrium determines normal versus oncogenic function." Nature communications 6.1 (2015): 7354. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8354
Research has found that the activity of the adaptor protein GRB2 is regulated by its conformation: the monomer state can bind to SOS and activate MAPK signals to promote cancer, while the dimer state inhibits this process. Its monome-dimer conversion is like a molecular switch that controls the progression of cancer.
Creative Biolabs: GRB2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GRB2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GRB2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GRB2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yablonski, Deborah. "Bridging the gap: modulatory roles of the Grb2-family adaptor, Gads, in cellular and allergic immune responses." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 1704. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01704
Anti-GRB2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Rat Anti-CD300A Recombinant Antibody (172224) (CBMAB-C0423-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1C3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12560) (CBMAB-1050-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-APC Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A661) (CBMAB-A3036-YC)

-
Rat Anti-(1-5)-α-L-Arabinan Recombinant Antibody (V2-501861) (CBMAB-XB0003-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (DE2B4) (CBMAB-1122-CN)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL6 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0442) (CBMAB-0445-YY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (SN3) (CBMAB-C1037-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503416) (CBMAB-V208-1402-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDKL5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1629) (CBMAB-C1689-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








