KCNT1 Antibodies
Background
The KCNT1 gene encodes a sodium-activated potassium channel protein, which is mainly expressed in the central nervous system and heart tissue of mammals. This protein participates in the regulation of neuronal excitability and the maintenance of cardiac rhythm by regulating potassium ion flow, and plays a key role in maintaining the stability of cell membrane potential. It shows a significant mutation association in epileptic encephalopathy and arrhythmia-related diseases. In 2012, its pathogenicity was first confirmed by an international research team through whole exome sequencing. As a core regulatory unit in the process of neuronal hyperpolarization, the function-acquired mutation mechanism of this gene has become an important target for the development of antiepileptic drugs. The research on its complex gating mechanism continuously promotes dual breakthroughs in the theory and therapeutic strategies of ion channels.
Structure of KCNT1
KCNT1 is a large transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 130-140 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies among different species due to splicing variants.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~140 | ~138 | ~139 | ~140 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains Slob domains that regulate channel activity | Species-specific splicing exists in the C-terminal region | The transmembrane region is highly conserved | There are minor amino acid variations in the intracellular segment |
This protein is composed of approximately 1,200 amino acids, and its primary structure folds into a typical pore protein conformation containing six transmembrane segments (S1-S6). The uniqueness of KCNT1 lies in the fact that its cytoplasmic C-terminal contains a distinctive regulatory domain (RCK2). This domain regulates the opening of channels by sensing the concentrations of sodium ions and ATP within the cell, thereby precisely controlling the effervescence of potassium ions. The selective filter formed by its pore loop region ensures the efficient passage of potassium ions, while the S4 transmembrane segment serves as a voltage sensor, making the channel sensitive to changes in membrane potential.
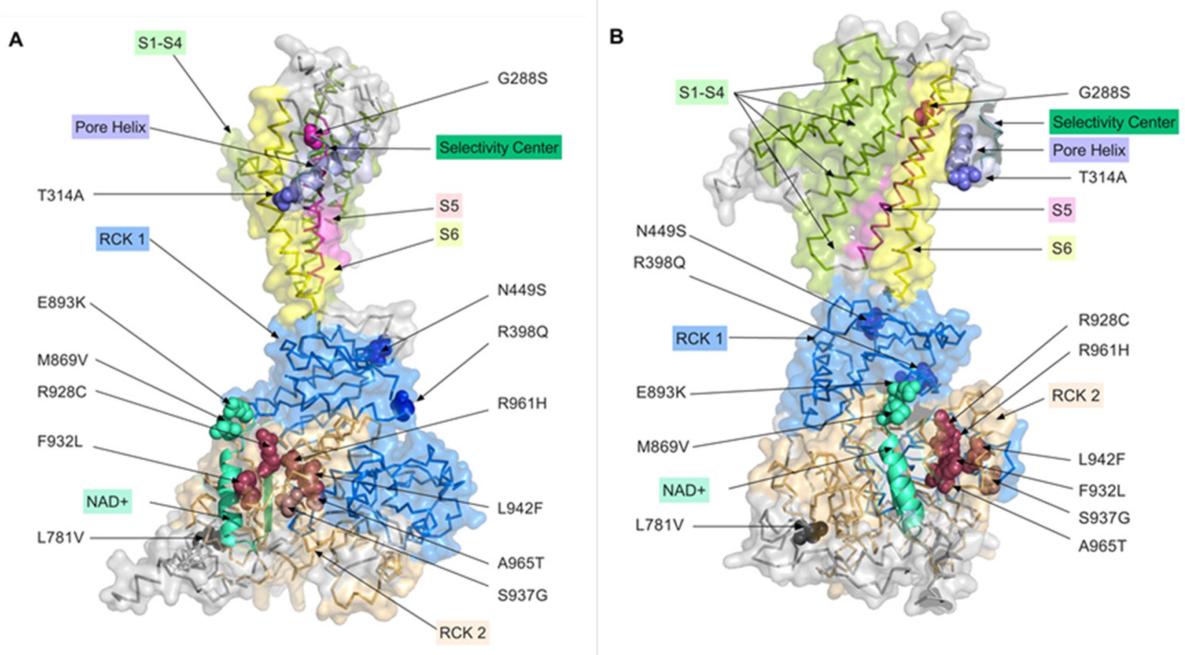 Fig. 1 Distribution of the studied mutations on the 3D model of the KCNT1 channel.1
Fig. 1 Distribution of the studied mutations on the 3D model of the KCNT1 channel.1
Key structural properties of KCNT1:
- Typical pore architecture consisting of six transmembrane domains (S1-S6)
- Unique intracellular RCK2 structure domain is responsible for sodium ions combine with ATP
- The P-loop forms a potassium ion-selective filter
Functions of KCNT1
The core function of the protein encoded by the KCNT1 gene is to regulate neuronal excitability, and its mutations are closely related to various neurological diseases.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of neuronal excitability | By generating hyperpolarized post-potentials, the repeated discharge of action potentials is effectively inhibited, maintaining the stability of neural circuits. |
| The mechanism of epilepsy | Gain-of-function mutations can enhance potassium currents, paradoxically causing network synchronization discharges and leading to malignant migratory partial epilepsy. |
| Associated with developmental encephalopathy | This gene mutation is the main cause of early-onset epileptic encephalopathy (such as EIMFS), often accompanied by severe psychomotor developmental delay. |
| Sleep cycle regulation | In the thalamic-cortical circuit, it participates in the stable maintenance of the sleep-wake cycle by regulating state transitions. |
| Exploration of drug targets | Quinidine and other drugs can provide a molecular basis for precision treatment by partially blocking the function of overactivated channels. |
The current-voltage relationship of this channel presents an inward rectification characteristic, and its activation process is simultaneously regulated by both membrane potential and intracellular sodium ion concentration. This characteristic is crucial for understanding its pathophysiological mechanism in epilepsy.
Applications of KCNT1 and KCNT1 Antibody in Literature
1. Di Matteo, Francesca, et al. "KCNT1 Channel Blockers: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective." Molecules 29.12 (2024): 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29122940
The article indicates that the KCNT1 potassium channel has become an important target for the treatment of epilepsy. At present, the development of blockers for this channel is still in its early stage. This paper systematically reviews the chemical structures and screening methods of the discovered KCNT1 blockers, and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of various research strategies.
2. Burbano, Lisseth Estefania, et al. "Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for KCNT1 encephalopathy." JCI insight 7.23 (2022): e146090. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.146090
This study developed a precise gene silencing therapy for developmental epileptic encephalopathy caused by KCNT1 gene mutations. By injecting KCNT1-targeted antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) into diseased mouse models, epileptic seizures were effectively controlled, behavioral abnormalities were improved, and survival periods were significantly prolonged, providing a new proof of concept for the treatment of KCNT1-related epilepsy.
3. Shore, Amy N., et al. "Heterozygous expression of a Kcnt1 gain-of-function variant has differential effects on somatostatin-and parvalbumin-expressing cortical GABAergic neurons." Elife 13 (2024): RP92915. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.92915
This study aimed to reveal the pathogenic mechanism of the KCNT1 functional gain mutation and found that this mutation had opposite effects on two types of inhibitory neurons, SST and PV, in the mouse cortex: the excitability of the former decreased, while that of the latter increased. This difference stems from the interaction with different ion channels, providing new cellular targets for precision treatment.
4. Rychkov, Grigori Y., et al. "Functional effects of epilepsy associated KCNT1 mutations suggest pathogenesis via aberrant inhibitory neuronal activity." International journal of molecular sciences 23.23 (2022): 15133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315133
This study systematically analyzed the functional effects of various KCNT1 mutations and found that most mutations would enhance channel current or the probability of opening, and the degree of change was positively correlated with the severity of neurological diseases. The results indicated that the gain-of-function mutation of KCNT1 might eventually lead to epileptic seizures by increasing resting potassium conductivity and inhibiting inhibitory neuronal activity.
5. Kim, Grace E., and Leonard K. Kaczmarek. "Emerging role of the KCNT1 Slack channel in intellectual disability." Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 8 (2014): 209. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00209
The article indicates that the potassium channel KCNT1 (Slack) is a key regulator of neuronal excitability. Abnormal function of this channel is associated with intellectual disability and childhood epilepsy. The mechanism involves interaction with fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) and affects delayed outward potassium current, making it an important target for neurological disease research.
Creative Biolabs: KCNT1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality KCNT1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom KCNT1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our KCNT1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Rychkov, Grigori Y., et al. "Functional effects of epilepsy associated KCNT1 mutations suggest pathogenesis via aberrant inhibitory neuronal activity." International journal of molecular sciences 23.23 (2022): 15133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315133
Anti-KCNT1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CARTPT Recombinant Antibody (113612) (CBMAB-C2450-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADV Recombinant Antibody (V2-503423) (CBMAB-V208-1364-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1A2 Recombinant Antibody (M7-PB-E9) (CBMAB-A4013-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






