LAG3 Antibodies
Background
LAG3 is an important immune checkpoint protein, mainly expressed on the surface of activated T cells, and negatively regulates T cell function through interactions with other molecules. The transmembrane protein encoded by this gene contains multiple immunoglobulin-like domains, which can bind to ligands such as MHC class II molecules and inhibit the excessive activation of T cells to maintain immune homeostasis. LAG3 often synergistically interacts with PD-1 in the tumor microenvironment, leading to T cell exhaustion. This discovery has facilitated the development of novel cancer immunotherapies. After being first identified by Frederic Triebel's team in 1990, LAG3 quickly became a research hotspot in tumor immunotherapy. Its inhibitor Relatlimab was approved by the FDA in 2022, becoming the world's first clinical drug targeting LAG3. In-depth research on the mechanism of action of LAG3 not only promotes the development of combined immunotherapy, but also provides new ideas for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and chronic infections.
Structure of LAG3
LAG3 is a transmembrane immune checkpoint protein with a molecular weight of approximately 45-50 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies slightly depending on the degree of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rhesus monkey |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~50 | ~45 | ~49 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Sample containing four Ig domain structure, intracellular section contains KIEELE conservative motif | Highly homologous to humans and functionally similar | The similarity to the human LAG3 protein sequence is over 90% |
LAG3 is composed of 498 amino acids, and its extracellular region contains four immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains (D1-D4), among which the D1 domain is responsible for binding to MHC class II molecules. The transmembrane region of this protein anchors it to the cell membrane, while the intracellular segment contains a unique "KIEELE" signaling motif that mediates immunosuppressive function. LAG3 plays a key role in tumor immune escape and autoimmune diseases by regulating the T-cell activation threshold. Its inhibitory function depends on the interaction with ligands (such as FGL1, Galectin-3, etc.), and this mechanism has become an important target for cancer immunotherapy.
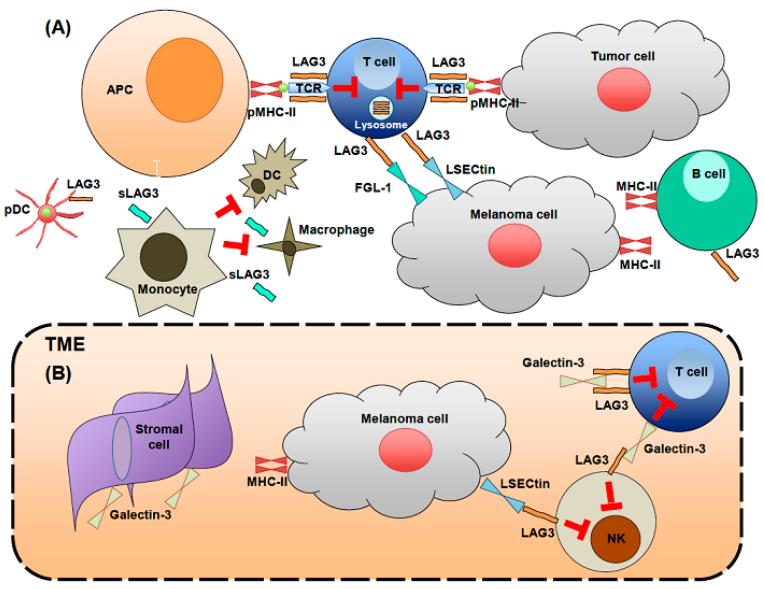 Fig. 1 LAG3 biology on immune cells.1
Fig. 1 LAG3 biology on immune cells.1
Key structural properties of LAG3:
- The extracellular region composed of Ig-like domains
- Transmembrane regions and intracellular signal motifs
- Ligand binding interface
- Disulfide bonds stabilize the structure
- Glycosylation modification site
Functions of LAG3
LAG3, as a key immune checkpoint molecule, mainly negatively regulates T cell activity to maintain immune homeostasis and also plays a significant role in tumor immune escape. Its multi-functionality is reflected in the following aspects:
| Function | Description |
| T-cell inhibition | Inhibitory signals are transmitted through the intracellular KIEELE motif to upregulate the T-cell activation threshold and prevent excessive immune responses. |
| Regulation of immune escape | Synergistic action with PD-1 in the tumor microenvironment leads to T cell depletion and promotes tumor immune escape. |
| Ligand-mediated regulation | Binding to MHC Class II molecules, FGL1 and Galectin-3 ligands, it triggers downstream immunosuppressive signaling pathways. |
| Autoimmunity prevention | Reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases by inhibiting the activation of autoreactive T cells. |
| Infection immune regulation | Regulating T cell function in chronic viral infections affects the efficiency of pathogen clearance. |
The discovery of this gene provides a key target for the development of novel immune combination therapies (such as LAG3/PD-1 dual blocking), and the FDA's approval of anti-LAG3 monoclonal antibody in 2022 marks an important breakthrough in this field.
Applications of LAG3 and LAG3 Antibody in Literature
1. Shi, An, et al. "Immune checkpoint LAG3 and its ligand FGL1 in cancer." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2022): 785091. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.785091
The article indicates that the interaction between LAG3 and FGL1 inhibits the tumor immune microenvironment, and its domain (D1/D2 of LAG3 and FD of FGL1) mediates the function. LAG3 is enriched on the surface of lymphocytes, while FGL1 is expressed on the cell membrane of breast cancer cells. The co-expression of the two enhances PD-1-mediated immunosuppression. Antibodies targeting LAG3 (such as relatlimab) have been used for melanoma, while the high expression of FGL1/LAG3 leads to resistance in EGFR-TKI and PD-1 treatment. This review provides new ideas for anti-cancer strategies.
2. Graydon, Colin G., Shifa Mohideen, and Keith R. Fowke. "LAG3's enigmatic mechanism of action." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2021): 615317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.615317
The article indicates that LAG3 is an important immune checkpoint, involved in tumors, infections and autoimmune diseases, but its mechanism of action remains unclear. This review explores the transcriptional and post-translational regulation of LAG3, ligand interactions (such as MHC-II and FGL1), and signaling mechanisms (unrelated to CD4). LAG3 mediates immunosuppression by inhibiting T cell activation and promoting depletion. Targeting LAG3 can enhance anti-tumor immunity, but its biological characteristics still require in-depth research.
3. Wu, Renzheng, et al. "LAG3 immune inhibitors: a novel strategy for melanoma treatment." Frontiers in Oncology 14 (2024): 1514578. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1514578
The article indicates that LAG3 inhibitors offer a new direction for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Although breakthroughs have been made in PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibitors, patients are prone to developing drug resistance. LAG3 promotes immune escape by inhibiting T cell function. Its inhibitors can restore T cell activity and work synergistically with existing immunotherapies. Targeting LAG3 is expected to overcome the problem of drug resistance and improve the therapeutic effect.
4. Solinas, Cinzia, et al. "LAG3: the biological processes that motivate targeting this immune checkpoint molecule in human cancer." Cancers 11.8 (2019): 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081213
The article indicates that LAG3, as an emerging immune checkpoint molecule, plays a key regulatory role in the tumor microenvironment. This article focuses on the expression characteristics of LAG3 in breast cancer and its clinical application prospects, including the progress of clinical trials of soluble LAG3 immunoglobulins and antagonists, providing new targets for tumor immunotherapy.
5. Ulase, Dita, et al. "LAG3 in gastric cancer: it's complicated." Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 149.12 (2023): 10797-10811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04954-1
This study, through the analysis of 580 gastric cancer samples, found that the distribution difference of LAG3 positive cells between the tumor center and the invasion frontier significantly affects prognosis. In primary gastric cancer, the survival period of the LAG3 high-expression group (tumor center ≥21.45 cells /mm², invasion frontier ≥208.50 cells /mm²) was significantly prolonged. In the neoadjuvant therapy group, high expression of LAG3 in the tumor center (≥12.62 cells /mm²) was an independent prognostic factor. The results indicated that a high density of LAG3 was associated with a good prognosis.
Creative Biolabs: LAG3 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LAG3 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LAG3 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LAG3 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Solinas, Cinzia, et al. "LAG3: the biological processes that motivate targeting this immune checkpoint molecule in human cancer." Cancers 11.8 (2019): 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081213
Anti-LAG3 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BHMT Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0547) (CBMAB-0550-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CAP219) (CBMAB-AP536LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1/AKT2/AKT3 (Phosphorylated T308, T309, T305) Recombinant Antibody (V2-443454) (PTM-CBMAB-0030YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGAP5 Recombinant Antibody (54/P190-B) (CBMAB-P0070-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BrdU Recombinant Antibody (IIB5) (CBMAB-1038CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-dsDNA Recombinant Antibody (22) (CBMAB-AP1954LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A950) (CBMAB-A4388-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CRTAM Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2235) (CBMAB-C2305-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








