LAMP1 Antibodies
Background
LAMP1 is a highly glycosylated type I transmembrane protein, mainly distributed in the lysosomal membrane and endosome-lysosomal transport pathway of eukaryotic cells. This protein plays a core role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis and degrading metabolism by regulating the integrity of lysosomes, participating in autophagy processes, and mediating intracellular membrane transport. Its gene was first identified in 1987 and has become a landmark research object in organelle biology due to its crucial role in lysosomal biogenesis. The typical structural features of LAMP1 include highly conserved intracellular domains and a large number of glycosylated extracellular regions. This special conformation not only protects the lysosomal membrane from enzymatic damage but also participates in the regulation of cell adhesion and immune responses. Recent studies have found that the abnormal expression of LAMP1 is closely related to various pathological processes such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer metastasis and pathogen infection, making it an important object for disease mechanism research and targeted therapy development.
Structure of LAMP1
LAMP1 is a relatively large type I transmembrane protein. Its molecular weight varies between approximately 110 and 130 kDa due to high glycosylation, and this value can differ depending on the species and the degree of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~120 | ~110 | ~110-120 | ~120 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Human CD107a has a typical cavity structure | High homology with rat and a slightly different glycosylation pattern | Highly similar to mice | Conservative tyrosine motif |
This protein is composed of approximately 385 amino acids. Its structural features include a large, highly glycosylated lumenal domain, a single transmembrane domain, and a relatively short cytoplasmic tail. Its cavity structure is mainly composed of β -folds, which are responsible for protecting the lysosomal membrane from enzymatic hydrolysis. The cytoplasmic tail contains a typical tyrosine motif (G-Y-E-Q-F), which is used to mediate the interaction with the cell kernel transport mechanism and regulate the lysosomal movement and membrane fusion process.
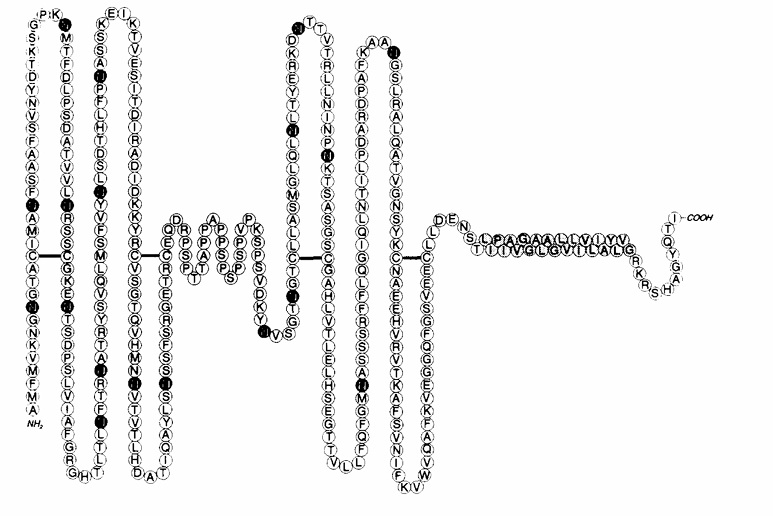 Fig. 1 Schematic model of h- lamp-1 polypeptide.1
Fig. 1 Schematic model of h- lamp-1 polypeptide.1
Key structural properties of LAMP1:
- Large highly glycosylated luminal domain structures
- Single anchor across a membrane structure domain is due to the lysosome membrane
- Cytoplasmic tail contains GYEQI tyrosine motif
Functions of LAMP1
The main function of LAMP1 is to maintain the integrity of lysosomes and participate in the degradation of intracellular substances. In addition, it also involves a variety of cellular processes, including autophagy regulation, cell adhesion and immune response.
| Function | Description |
| Lysosomal membrane protection | The lysosomal membrane is protected from degradation by internal acidic hydrolases through a highly glycosylated cavity structure. |
| Regulation of autophagy process | Involved in autophagy body with the lysosome fusion process, is the key to the degradation cell autophagy and the content of media. |
| Intracellular transport | Mediate membrane transport and interorganelle material exchange in the endosome-lysosomal system. |
| Cell adhesion and migration | Through the extracellular domain, it participates in intercellular interactions and affects the metastasis of cancer cells and the movement of immune cells. |
| Antigen presentation and immune regulation | Effect in immune cells MHC class II molecules and antigen processing of transportation, to participate in the immune response regulation. |
LAMP1 protein is often used as a marker of lysosomes due to its localization and functional characteristics. It is widely expressed in various cells, but its expression is often significantly upregulated in tumor cells and activated immune cells.
Applications of LAMP1 and LAMP1 Antibody in Literature
1. Qiu, Fen, and Chen. "LAMP1/2 as potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for brain lower grade glioma: A review." Medicine 102.33 (2023): e34604. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000034604
This study, based on the analysis of the TCGA database, found that LAMP1 was significantly upregulated in low-grade glioma (LGG) of the brain and was closely related to the poor prognosis of patients and immune cell infiltration. The expression level of LAMP1 is significantly correlated with histological subtypes, suggesting that it can serve as a potential prognostic marker for LGG.
2. Wang, bao, et al. "Research on the effect of LAMP1 in the development and progression of ccRCC and its potential mechanism with LC3C-mediated autophagy." Frontiers in Immunology 15 (2024): 1494005. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494005
The article indicates that LAMP1 is significantly lowly expressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and is closely related to a poor prognosis. Functional experiments have shown that LAMP1 can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. Its expression is regulated by LC3C and is related to the VHL status. LAMP1 can serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for ccRCC.
3. Zhang, Jiyuan, et al. "Lysosomal LAMP proteins regulate lysosomal pH by direct inhibition of the TMEM175 channel." Molecular cell 83.14 (2023): 2524-2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.06.004
The article indicates that LAMP1 and LAMP2 directly inhibit the activity of the ion channel TMEM175, regulate the pH homeostasis of lysosomes, and promote acidification to maintain the optimal hydrolase function. Disrupting this interaction leads to lysosomal alkalization and functional impairment. This discovery is of great significance to the physiological and disease mechanisms related to lysosomes.
4. Meca‐Laguna, Gabriel, et al. "Cell‐Surface LAMP1 is a Senescence Marker in Aging and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis." Aging Cell (2025): e70141. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.70141
The article indicates that LAMP1 is a novel membrane marker of cellular senescence, which is specifically highly expressed in senescent cells of humans and mice, and significantly increases with age and fibrosis models. LAMP1+ cells highly express typical aging markers such as p16 and p21. Antibody-drug conjugates targeting LAMP1 can effectively eliminate senescent cells and have potential for anti-aging treatment.
5. Rahmani, Zohra, et al. "Lamp1 deficiency enhances sensitivity to α-synuclein and oxidative stress in Drosophila models of Parkinson disease." International journal of molecular sciences 23.21 (2022): 13078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113078
The article indicates that LAMP1 plays a key protective role in Parkinson's disease (PD) models. Experiments on fruit flies have shown that the absence of LAMP1 aggravates motor deficits caused by oxidative stress and alpha-synuclein toxicity, while its reexpression can completely reverse the phenotype and may alleviate neurotoxicity by promoting non-pathogenic aggregation formation, suggesting that it has a protective mechanism against PD.
Creative Biolabs: LAMP1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LAMP1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LAMP1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LAMP1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Carlsson, Sven R., and Minoru Fukuda. "Structure of human lysosomal membrane glycoprotein 1: assignment of disulfide bonds and visualization of its domain arrangement." Journal of Biological Chemistry 264.34 (1989): 20526-20531. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)47094-4
Anti-LAMP1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AFDN Recombinant Antibody (V2-58751) (CBMAB-L0408-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADGRE4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-160163) (CBMAB-F0011-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADAM12 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179752) (CBMAB-A1114-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT2 (Phosphorylated S474) Recombinant Antibody (V2-556130) (PTM-CBMAB-0605LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C4B Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C2996) (CBMAB-C4439-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






