LYVE1 Antibodies
Background
LYVE1 (lymphatic endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is mainly expressed on the surface of lymphatic endothelial cells. This protein specifically binds to hyaluronic acid and participates in regulating the adhesion, migration and lymphangiogenesis of lymphatic endothelial cells, thereby maintaining interstitial fluid balance and immune cell transport. Its gene was first cloned and identified in 1999. As a specific marker of lymphatic vessel endothelium, LYVE1 plays a key role in pathophysiological processes such as tumor metastasis, inflammatory response and tissue repair. The structural and functional research of this receptor has deepened people's understanding of the association between the lymphatic system and diseases, especially in the mechanism of tumor lymphatic metastasis and the development of targeted treatment strategies, which is of great value.
Structure of LYVE1
LYVE1 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 41-43 kDa. Its molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to differences in the degree of glycosylation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 41 | About 40 | About 42 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains 322 amino acids, extracellular region one Link structure domain | Highly homologous, the Link domain is conserved | High sequence similarity to human LYVE1 |
This protein is composed of 322 amino acids, and its core structural feature is a Link module located in the extracellular region (similar to the domain of CD44), which is responsible for specifically recognizing and binding to hyaluronic acid. Its transmembrane domain anchors the protein to the cell membrane, while the shorter intracellular tail region is involved in signal transduction. The three-dimensional structure of the Link module forms a specific fold, constituting the hyaluronic acid binding pocket. This structural basis determines the specificity and function of its ligand binding.
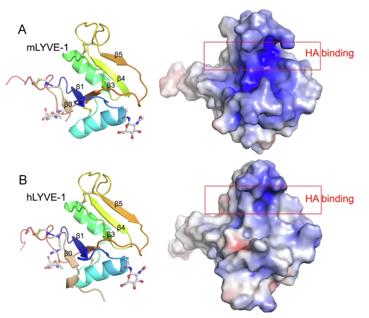 Fig. 1 X-ray crystallographic structures of unbound mLYVE-1 and hLYVE-1 HABDs.1
Fig. 1 X-ray crystallographic structures of unbound mLYVE-1 and hLYVE-1 HABDs.1
Key structural properties of LYVE1:
- Extracellular Link module domain (CD44-like folding)
- Specific hyaluronic acid binding pocket
- Type I single transmembrane anchoring structure
Functions of LYVE1
The main function of LYVE1 (lymphatic endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1) is to mediate the binding of lymphatic endothelial cells to hyaluronic acid, thereby regulating lymphangiogenesis and immune cell transport. Meanwhile, it is also involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes, including tumor metastasis and inflammatory responses.
| Function | Description |
| Hyaluronic acid binding | Specific recognition and based on hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix, involved in the stability of the lymphatic vessels and reshaping. |
| Lymphangiogenesis | Promote the adhesion and migration of lymphatic endothelial cells, and drive the formation of new lymphatic vessels during embryonic development and tissue repair. |
| Immune cells homing | Mediate the entry of dendritic cells and other immune cells into the lymphatic system through lymphatic vessels to initiate adaptive immune responses. |
| Regulation of tumor metastasis | As a major lymphatic endothelial marker, it often provides metastasis channels for tumor cells, and its expression level is related to the prognosis of various cancers. |
| Tissue fluid balance | The lymphatic endothelium participates in the absorption and drainage of interstitial fluid to maintain fluid balance. |
Compared with hyaluronic acid receptors such as CD44, LYVE1 has a higher affinity for hyaluronic acid and is more specific. Its expression is almost limited to the lymphatic endothelium, making it a key molecular marker for studying lymphatic system function and tumor lymphatic metastasis.
Applications of LYVE1 and LYVE1 Antibody in Literature
1. Hog, Pauline, et al. "Prostaglandin e2 boosts the hyaluronan-mediated increase in inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide by enhancing lyve1 expression." Biology 12.11 (2023): 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111441
Research has found that the hyaluronic acid receptor Lyve1 on the surface of macrophages plays a key role in the resolution of inflammation. Prostaglandin E2 enhances the expression of Lyve1 through the EP2 receptor signaling pathway, enabling this macrophage subpopulation to respond synergistically to the inflammatory stimulation of lipopolysaccharide and low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, and integrate extracellular matrix signals with inflammatory responses.
2. Anstee, Joanne E., et al. "LYVE-1+ macrophages form a collaborative CCR5-dependent perivascular niche that influences chemotherapy responses in murine breast cancer." Developmental cell 58.17 (2023): 1548-1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2023.06.006
Studies have found that in the spontaneous breast cancer model, tumor-associated macrophages expressing LYVE-1 are induced by IL-6 to form paravicular "nest" structures, which synergically inhibit CD8⁺T cell infiltration through CCR5 signaling and lead to chemotherapy resistance. Blocking this subset can enhance anti-tumor immunity and the efficacy of chemotherapy.
3. Feng, Zhenzhen, and Jiyuan Wu. "hsa_circ_0129047 Upregulates LYVE1 to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Sponging miR‐492." Disease Markers 2023.1 (2023): 6978234. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6978234
Studies have found that the circular RNA circ_0129047 is down-regulated in liver cancer. It inhibits tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by adsorbing miR-492 and relieving its inhibition of the target gene LYVE1, suggesting that this axis is expected to become a new therapeutic target for liver cancer.
4. Turiel, Guillermo, et al. "Single-cell compendium of muscle microenvironment in peripheral artery disease reveals altered endothelial diversity and LYVE1+ macrophage activation." Nature Cardiovascular Research (2025): 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-025-00709-y
This study found through single-cell sequencing that LYVE1hiMHCIIlow macrophages were dominant in the skeletal muscle of patients with lower extremity arterial disease and showed pro-inflammatory transformation. Endothelial cells influence their polarization through signals, providing new evidence for targeted therapy.
5. Liu, Jing, et al. "Serum soluble LYVE1 is a promising non-invasive biomarker of renal fibrosis: a population-based retrospective cross-sectional study." Immunologic Research 72.3 (2024): 476-489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-023-09448-3
The article indicates that the level of serum soluble LYVE1 is positively correlated with the degree of renal fibrosis. After being incorporated into the diagnostic model, the model's predictive ability for moderate to severe and severe renal fibrosis was significantly enhanced, and it is expected to become a novel biomarker for non-invasive diagnosis of renal fibrosis.
Creative Biolabs: LYVE1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LYVE1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LYVE1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LYVE1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Bano, Fouzia, et al. "Structure and unusual binding mechanism of the hyaluronan receptor LYVE-1 mediating leucocyte entry to lymphatics." Nature Communications 16.1 (2025): 2754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57866-8
Anti-LYVE1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-ALK (Phosphorylated Y1278) Recombinant Antibody (D59G10) (PTM-CBMAB-0035YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7719) (CBMAB-1898CQ)

-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD164 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0077) (CBMAB-C0086-FY)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys16) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623415) (CBMAB-CP1021-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AGO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634169) (CBMAB-AP203LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Rat Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (16) (CBMAB-E1578-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BAD (Phospho-Ser136) Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0138) (CBMAB-0139-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






