RPIA Antibodies
Background
RPIA is a metabolic enzyme protein widely expressed in various tissues, mainly involved in the pentose phosphate pathway. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of riboketose-5-phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate, providing essential precursors for nucleotide synthesis and nucleic acid metabolism, and plays an important role in maintaining the basic functions of cells. Its abnormal activity is associated with various diseases. For instance, mutations in the RPIA gene can lead to ribose 5-phosphoisomerase deficiency, which affects neural development. The three-dimensional structure of this protein was analyzed by crystallography in the early 21st century, revealing its conserved (α/β) 8-barrel-shaped catalytic structure characteristics. Continuous research on RPIA has deepened people's understanding of the regulation of glucose metabolism, the mechanism of enzyme function, and the molecular basis of related genetic diseases.
Structure of RPIA
RPIA is a metabolic enzyme with a molecular weight of approximately 32 kDa. Its precise molecular weight varies slightly among different species due to differences in amino acid sequences.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 32.1 | 32.0 | 32.2 | 32.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Conservative TIM barrel structure, with His99 in the active center | His99 and others are of the same origin | His99 and others are of the same origin | Similar active centers |
This protein is composed of approximately 311 amino acids and forms a classic (α/β) 8-barrel three-dimensional structure (TIM barrel structure) through the folding of its primary structure. The protein structure contains a catalytic center located at the C-terminal of the barrel structure. Its conserved histidine (His99) and glutamic acid residues constitute the key active sites, directly participating in substrate binding and catalytic reactions. The function of RPIA relies on a complete hydrophobic core and precise active pocket conformation to maintain efficient ribo5-phosphate synthesis capacity.
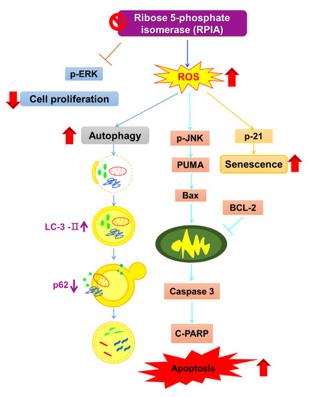 Fig. 1 RPIA Suppression Triggers Cell Death and Senescence.1
Fig. 1 RPIA Suppression Triggers Cell Death and Senescence.1
Key structural properties of RPIA:
- Classical (α/β)8 bucket structure (TIM bucket)
- Hydrophobic core to maintain the overall conformational stability
- Conservative active center (including key histidine residues) catalytic isomerization reaction substrates
Functions of RPIA
The main function of RPIA is to catalyze the isomerization of riboketose-5-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway, generating ribose-5-phosphate. In addition, it also plays a key role in cellular metabolic balance, oxidative stress response and nucleotide biosynthesis.
| Function | Description |
| Nucleotide synthesis | The generated ribose 5-phosphate is an essential precursor for de novo synthesis of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides and is crucial for cell proliferation and genetic material replication. |
| Metabolic balance | Linking glycolysis with the pentose phosphate pathway, regulating the supply of NADPH and ribose, maintaining cellular REDOX homeostasis and biosynthetic requirements. |
| Oxidative stress protection | By supporting the pentose phosphate pathway and promoting NADPH generation, it provides reducing power for the glutathione reduction system and helps eliminate reactive oxygen species. |
| Cellular energy supply | The catalytic reaction to provide alternative paths to sugar metabolism, help maintain cells under specific conditions of flow of energy metabolism. |
| Disease association | Loss-of mutations in RPIA can lead to ribose 5-phosphoisomerase deficiency, affecting neural development and presenting as intellectual disability and white matter lesions. |
Like many metabolic enzymes, the activity of RPIA is precisely regulated by substrate concentration, product feedback and cellular energy state to ensure that metabolic fluxes meet the physiological needs of cells. Its function is relatively single, mainly concentrated at the hub position of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Applications of RPIA and RPIA Antibody in Literature
- Szwarc, Maria M., et al. "Steroid receptor coactivator-2 controls the pentose phosphate pathway through RPIA in human endometrial cancer cells." Scientific reports 8.1 (2018): 13134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31372-y
Research has found that in endometrial cancer cells, knockdown of SRC-2 or RPIA can both inhibit cell proliferation and reduce the metabolic activity of glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation and pentose phosphate pathways, indicating that SRC-2 affects glucose metabolism pathways by regulating RPIA.
- Nieh, Yu-Chin, et al. "Suppression of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase a induces ROS to activate autophagy, apoptosis, and cellular senescence in lung cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.14 (2022): 7883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147883
Research has found that in lung cancer, the expression of RPIA protein is elevated. Inhibiting RPIA can lead to an increase in reactive oxygen species levels, thereby activating autophagy, apoptosis and senescence processes of cells, and thus inhibiting the proliferation of lung cancer cells. This provides a new idea for the treatment of lung cancer.
- Shen, Wen-Chi, et al. "Reduced ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A-1 expression in specific neurons and time points promotes longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans." Antioxidants 12.1 (2023): 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010124
Research has found that in nematodes, specifically knocking down the rpia-1 gene can extend lifespan and improve health levels. The mechanism involves activating autophagy and the AMPK pathway, as well as reducing TOR signaling, especially with significant effects in glutamatergic or cholinergic neurons.
- Chou, Yu-Ting, et al. "Identification of a noncanonical function for ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A promotes colorectal cancer formation by stabilizing and activating β-catenin via a novel C-terminal domain." PLoS Biology 16.1 (2018): e2003714. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2003714
The article indicates that the expression of RPIA is significantly elevated in colorectal cancer. Its non-classical function is to enter the cell nucleus, bind APC to β-catenin, thereby stabilizing β-catenin and promoting tumorigenesis. Targeting its C-terminal non-enzymatic active region may provide a new therapeutic strategy.
- Ancer-Rodríguez, Jesús, et al. "Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis—Key Players in the Lung Aging Process." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.14 (2024): 7867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147867
The article indicates that during the aging process of the lungs, the imbalance between cell proliferation and apoptosis is an important factor leading to related diseases. RPIA, p16 and others are involved in the regulation of this process, but their complete signaling pathways have not been fully elucidated at present and further research is needed.
Creative Biolabs: RPIA Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality RPIA antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom RPIA Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our RPIA antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Nieh, Yu-Chin, et al. "Suppression of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase a induces ROS to activate autophagy, apoptosis, and cellular senescence in lung cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.14 (2022): 7883. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147883
Anti-RPIA antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CR3022) (CBMAB-CR014LY)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CAT Recombinant Antibody (724810) (CBMAB-C8431-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-dsRNA Recombinant Antibody (2) (CBMAB-D1807-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-14-3-3 Pan Recombinant Antibody (V2-9272) (CBMAB-1181-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP8 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0987) (CBMAB-C2424-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-APOA1 Monoclonal Antibody (CBFYR0637) (CBMAB-R0637-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AZGP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-007) (CBMAB-Z0012-WJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






