SETDB1 Antibodies
Background
The SETDB1 gene encodes a histone methyltransferase, which is mainly present in the nuclei of higher eukaryotes. This enzyme specifically catalyzes the trimethylation modification of the ninth lysine of histone H3, thereby participating in the formation of heterochromatin structure and playing a key role in gene transcriptional silencing, maintaining genomic stability, and regulating embryonic development. Early research first reported its function in 1999, and subsequent studies further revealed the dual regulatory role of SETDB1 in maintaining stem cell pluripotency, neurodevelopment, and tumorigenesis. Its structure contains highly conserved SET domains and methylation modification recognition units. This modular feature makes it a classic model for epigenetic research, deepening people's understanding of the association between chromatin modification mechanisms and diseases.
Structure of SETDB1
SETDB1 is a histone methyltransferase with a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa. Its specific molecular weight may fluctuate slightly due to post-translational modifications or different transcriptional splicing variants.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~150 | ~148 | ~145 | ~160 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Participate in gene silencing, tumor regulation and nervous system development | It is crucial for maintaining the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells | Plays a key role in early embryonic development | With functions of conservative in heterochromatin formation |
This protein is composed of approximately 1,300 amino acids, and its core functional domain is the highly conserved SET domain at the C-terminal, which is responsible for catalyzing the trimethylation of lysine at position 9 of histone H3. The tertiary structure of proteins forms a specific binding pocket that can recognize and bind S-adenosylmethionine as a methyl donor, and precisely target specific regions of chromatin through its adjacent Tudor and MBD-like domains, thereby regulating gene expression.
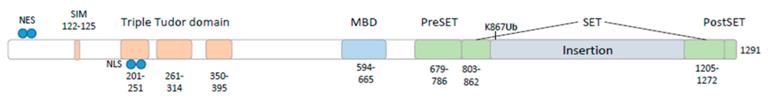 Fig. 1 Protein domain structure of SETDB1.1
Fig. 1 Protein domain structure of SETDB1.1
Key structural properties of SETDB1:
- Contains the highly conserved SET domain
- With Tudor structure domain and structure domain MBD samples
- The tertiary structure to form a combined with pockets
Functions of SETDB1
The main function of the SETDB1 protein is to act as a histone methyltransferase to catalyze gene silencing. However, it is also widely involved in a variety of key biological processes, including the maintenance of genomic stability, the determination of cell fate, and the occurrence and development of diseases.
| Function | Description |
| Transcriptional silencing | By catalyzing the trimethylation of lysine at position 9 of histone H3, heterochromatin formation is promoted, thereby inhibiting gene transcription. |
| Genomic stability | Silence transposons and repeat sequences in the genome to prevent their abnormal activation and maintain the integrity of genetic information. |
| Regulation of embryonic development | In early embryonic development has played a key role and pluripotent stem cells maintain, its expression disorders can lead to dysplasia. |
| Dual effects of tumors | In different cancer suppressor carcinoma, or the complex effect, such as in some tumor proto-oncogene in silence, in other promotion in tumor metastasis. |
| Regulation of neural function | Involved in nerve cell differentiation and function, associated with neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder. |
Unlike histone methyltransferases with broad substrate specificity, SETDB1 exhibits high specificity for the H3K9 site. This specificity makes it an exact "switch" in the epigenetic regulatory network, and its abnormal activity is closely related to a variety of developmental diseases and cancers.
Applications of SETDB1 and SETDB1 Antibody in Literature
- Fukuda, Kei, and Yoichi Shinkai. "SETDB1-mediated silencing of retroelements." Viruses 12.6 (2020): 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060596
The article indicates that SETDB1 is a histone methyltransferase that maintains genomic stability by silencing retrotransposions through catalyzing H3K9me3. It is highly expressed in various tumors and works in synergy with KAP1, HUSH complex, etc. to inhibit endogenous retroviruses. The methylation mediated by it can continue during replication.
- She X, Wu Q, et al. "SETDB1 methylates MCT1 promoting tumor progression by enhancing the lactate shuttle." Advanced Science 10.28 (2023): 2301871. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202301871
The article indicates that SETDB1 stabilizes MCT1 by methylating the K473 site of the MCT1 protein and blocking its autophagic degradation. This modification promotes glycolysis, lactate shuttle and M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer, which is associated with a poor prognosis for patients.
- Luo, Fei, et al. "LINC00115 promotes chemoresistant breast cancer stem-like cell stemness and metastasis through SETDB1/PLK3/HIF1α signaling." Molecular Cancer 23.1 (2024): 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-024-01975-3
Research has found that LINC00115 can act as a scaffold to link SETDB1 and PLK3, promoting the methylation of PLK3 and thereby stabilizing HIF1α. This feedback loop enhances the characteristics of breast cancer stem cells, leading to chemotherapy resistance and metastasis. Targeting this pathway is expected to become a new therapeutic strategy.
- K., Wang, T., et al. "Hepatocellular SETDB1 regulates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury through targeting lysine methylation of ASK1 signal." Research 6 (2023): 0256. https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0256
Research has found that SETDB1, in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury, activates the downstream JNK/p38 pathway by methylating ASK1, thereby exacerbating inflammation and apoptosis. Inhibiting SETDB1 can significantly alleviate liver injury, suggesting it as a potential therapeutic target.
- Johnson, Eleanor, Kiarash Salari, and Shujie Yang. "SETDB1: A perspective into immune cell function and cancer immunotherapy." Immunology 169.1 (2023): 3-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13619
Research has found that SETDB1, as a histone methyltransferase, is involved in the normal development and functional regulation of B cells and T cells. In tumor cells, its overexpression can help tumor immune escape by silencing reverse transcription elements, inhibiting interferon pathways, and other means, thereby affecting the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Creative Biolabs: SETDB1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SETDB1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SETDB1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SETDB1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
Anti-SETDB1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ARSA Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A799) (CBMAB-A3679-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-DLK1 Recombinant Antibody (9D8) (CBMAB-D1061-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0050) (CBMAB-0050-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (315304) (CBMAB-1214-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACO2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179329) (CBMAB-A0627-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CRYAB Recombinant Antibody (A4345) (CBMAB-A4345-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ADRB2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180026) (CBMAB-A1420-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARIH1 Recombinant Antibody (C-7) (CBMAB-A3563-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENPP1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0159) (CBMAB-E0375-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-180650) (CBMAB-A2186-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (2Q1282) (CBMAB-C1624-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179982) (CBMAB-A1368-YC)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








