SMAD4 Antibodies
Background
SMAD4 gene encodes a key intracellular signal transduction protein, which is mainly involved in the regulation of TGF-β signaling pathway. This protein translocates into the cell nucleus by forming a complex, directly activating the transcription of specific target genes, thereby regulating life activities such as cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. SMAD4 plays a core role in embryonic development and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. This gene was first identified as the pancreatic cancer tumor suppressor gene DPC4 in 1996. Subsequent studies have found that its mutations are closely related to various genetic diseases (such as juvenile polyposis syndrome) and malignant tumors (such as colorectal cancer). As a central regulator of the TGF-β pathway, the study of the molecular mechanism of SMAD4 has greatly promoted our understanding of the fields of cell signal transduction, tumorigenesis and developmental biology.
Structure of SMAD4
SMAD4 is a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 52 kDa, and its size is relatively conserved among different species. This protein is composed of 552 amino acids and has two typical conserved domains, MH1 and MH2. It forms homologous or heterologous complexes through its tertiary structure and participates in signal transduction. The special ring structure and surface hydrophobic region in the MH2 domain play a key role in oligomerization and transcriptional activation.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | Fruit fly |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 52.0 | 51.8 | 51.5 | 51.2 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Complete MH1 and MH2 domains | Highly conserved amino acid sequence | Retain the core functional areas | Structure is relatively simplified |
The MH1 domain of SMAD4 is responsible for DNA binding, while the MH2 domain mediates interactions and oligomerization with other SMAD proteins. Its junction region contains nuclear localization signals that regulate the nuclear cytoplasmic shuttle of proteins. The stability and function of this protein are precisely regulated by various post-translational modifications.
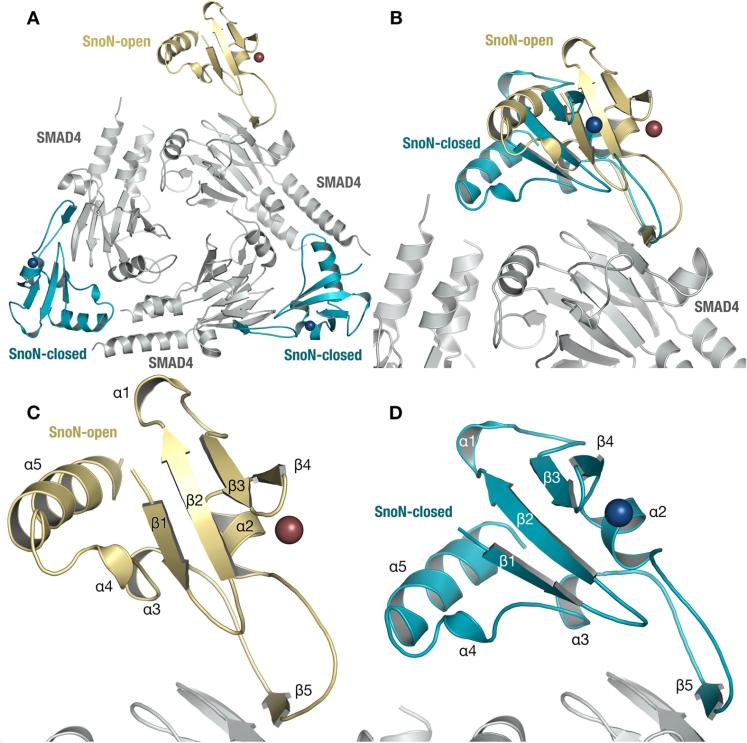 Fig. 1 Overall Structure of SnoN-SMAD4.1
Fig. 1 Overall Structure of SnoN-SMAD4.1
Key structural properties of SMAD4:
- Contains two highly conserved functional domains, MH1 and MH2
- MH2 structure domain mediated oligomerization and transcription complex is formed
- Specific recognition of DNA sequences through MH1 domains (GTCT elements)
- The linker region contains nuclear localization signals (NLS) to regulate nuclear and cytoplasmic shuttle
- Protein stability is regulated by post-translational modifications such as ubiquitination
Functions of SMAD4
The core function of the SMAD4 gene is to mediate the signal transduction of the TGF-β superfamily and regulate the transcription of target genes. In addition, it is also involved in a variety of important biological processes such as cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction and embryonic development.
| Function | Description |
| Signal transduction | As a key mediator of the TGF-β/BMP pathway, it receives extracellular signals and forms transcriptional complexes that transfer into the nucleus. |
| Transcriptional regulation | Binding to DNA-binding elements, such as GTCT sequences, in the nucleus activates or inhibits downstream target gene expression. |
| Cell cycle regulation | Induce the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors such as p21, promoting cell arrest in the G1 phase. |
| Apoptosis induction | Under specific conditions, pro-apoptotic genes can be activated to participate in the clearance of abnormal or damaged cells. |
| Embryonic development | Regulating mesodermal formation, organogenesis and cell differentiation is of vital importance to the development of early embryos. |
The signal response of SMAD4 is environmentally dependent, and its function can vary significantly due to differences in cell type, cofactors, and mutation status, which is fundamentally different from the allosteric regulation of hemoglobin.
Applications of SMAD4 and SMAD4 Antibody in Literature
1. Shan, Hui, et al. "Exploring the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SMAD4 in colorectal cancer." Cancer Biology & Therapy 25.1 (2024): 2392341. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2024.2392341
The article indicates that SMAD4 is a key transcription factor in the TGF-β signaling pathway and plays a dual role in the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer. This article explores its function and potential as a therapeutic target.
2. Shi, An‐da, et al. "SMAD4 regulates the progression of cholangiocarcinoma by modulating the expression of STING1." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 27.17 (2023): 2547-2561. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17857
This study explores the mechanism by which SMAD4 affects tumor progression in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) through transcriptional regulation of STING1. The expressions of SMAD4 and STING1 were both downregulated and significantly correlated. The low expression of both indicates a poor prognosis for the patient. SMAD4 silencing may promote the development of CCA by inhibiting the STING1-mediated immune response.
3. Du, Xing, et al. "SMAD4 activates Wnt signaling pathway to inhibit granulosa cell apoptosis." Cell death & disease 11.5 (2020): 373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2578-x
This study focuses on the role of the 5'-UTR variant SMAD4-201 of the SMAD4 gene in colorectal cancer. Research has found that the relative abundance of SMAD4-201 in cancer cell lines and cancer tissues is significantly higher than that in non-cancer tissues (p=0.001), suggesting that it may become a potential diagnostic biomarker for colorectal cancer, but further verification is still needed.
4. Babic, Tamara, et al. "SMAD4–201 transcript as a putative biomarker in colorectal cancer." BMC cancer 22.1 (2022): 72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09186-z
This study reveals that SMAD4, as an effector of the TGF-β pathway, mediates the interaction between TGF-β and the Wnt signaling pathway in granulosa cells by directly activating FZD4 transcription and regulating the lncRNA/miRNA network, promoting apoptosis and follicular atresia, and providing a new target for the treatment of reproductive diseases.
5. Igalouzene, Ramdane, et al. "SMAD4 TGF-β–independent function preconditions naive CD8+ T cells to prevent severe chronic intestinal inflammation." The Journal of clinical investigation 132.8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI151020
This study focuses on the epigenetic mechanism through which SMAD4 pre-regulates the expression of TGF-β target genes in CD8+ T cells, inhibits inflammatory factors and enhances IL-7 responses, thereby preventing the occurrence of intestinal inflammation. This mechanism does not rely on TGF-β signaling, providing a new therapeutic approach for inflammatory bowel disease.
Creative Biolabs: SMAD4 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SMAD4 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SMAD4 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SMAD4 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Walldén, Karin, Tomas Nyman, and B. Martin Hällberg. "SnoN stabilizes the SMAD3/SMAD4 protein complex." Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 46370. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46370
Anti-SMAD4 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rat Anti-C5AR1 Recombinant Antibody (8D6) (CBMAB-C9139-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BPGM Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1806) (CBMAB-2155-YY)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BACE1 Recombinant Antibody (CBLNB-121) (CBMAB-1180-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-55272) (CBMAB-H0819-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Human Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Recombinant Antibody (CBC05) (CBMAB-CR005LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CARD11 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0811) (CBMAB-C0866-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






