SOX17 Antibodies
Background
The SOX17 gene encodes a DNA-binding protein belonging to the SOX (SPERm-related HMG cassette) transcription factor family, which plays a core regulatory role in embryonic development and endodermal organ formation. It regulates the expression of downstream genes by specifically recognizing CCtgAT-like motifs, and plays a key role in the occurrence of the cardiovascular system, the development of bile ducts, and the maintenance of gastrointestinal homeostasis. Studies have shown that SOX17 is a specific marker for vascular endothelial cell differentiation and participates in the tumor suppression process through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This gene was first identified in 1993. Its mutations are closely related to congenital defects such as biliary atresia and pulmonary hypertension in humans. In recent years, it has been confirmed to be a key regulatory factor for the directional differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into the endoderm, providing an important theoretical basis for regenerative medicine research.
Structure of SOX17
SOX17 is a transcription factor with a molecular weight of approximately 42-44 kDa. This value may vary slightly due to differences in amino acid composition and transcript splicing patterns among different species.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Zebrafish | African clawed toad | Chicken |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 43.8 | 43.6 | 42.9 | 43.5 | 43.7 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains conserved HMG domain and transcriptional activation domain | 90% homology to humans | There are two collateral homologous genes | Highly expressed during embryonic development | Organize specificity isomer |
This protein is composed of 414 amino acids, and its core functional region is a highly conserved HMG domain. This domain adopts a special L-shaped three-dimensional conformation and achieves DNA recognition through the combination of α -helix and β -folding. At the molecular mechanism level, arginine at position 49 and lysine at position 76 in the HMG domain directly interact with the DNA double helix, inducing DNA to bend by approximately 80 degrees. This conformational change provides a structural basis for the assembly of transcriptional regulatory complexes.
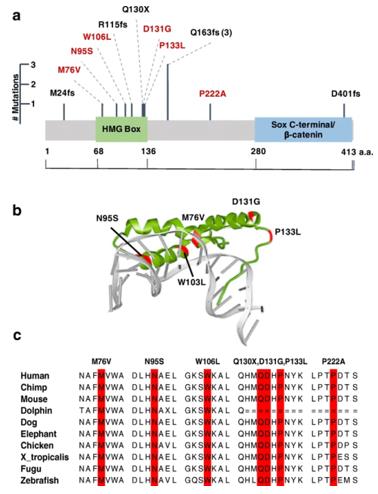 Fig. 1 Rare deleterious variants in SOX17.1
Fig. 1 Rare deleterious variants in SOX17.1
Key structural properties of SOX17:
- Contains the highly conserved HMG-box domain
- Specific binding is formed by inducing DNA bending through the HMG domain
- N-terminal and C-terminal regulatory regions are involved in transcriptional activation
Functions of SOX17
The core function of the SOX17 transcription factor is to regulate embryonic development and endodermal differentiation. Its main physiological functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Endodermal lineage orientation | By activating key genes such as Sox2/Foxa2, pluripotent stem cells are driven to differentiate into endodermal cells. |
| Regulation of cardiovascular development | Regulate the Notch1/Dll4 signaling axis to guide the specialization of arterial endothelial cells and vascular morphogenesis. |
| Formation of the bile duct system | Synergistic with Hhex/Hnf1β, promote the maturation and arrangement of intrahepatic bile duct precursor cells. |
| Wnt signal path modulation | By binding to the β-catenin complex, it not only enhances the Wnt activity in specific tissues but also exerts anti-cancer effects in tissues such as the colon. |
| Cell fate locking | Inhibit pluripotent genes through epigenetic modifications to ensure the irreversibility of the differentiation process. |
The binding of SOX17 to DNA exhibits a unique synergistic effect. The DNA bending induced by its HMG domain significantly enhances the recruitment efficiency of cofactors, a characteristic that places it at a pivotal position in the developmental regulatory network.
Applications of SOX17 and SOX17 Antibody in Literature
1. Zou X, Liu T, et al. "SOX17 is a critical factor in maintaining endothelial function in pulmonary hypertension by an exosome‐mediated autocrine manner." Advanced Science 10.14 (2023): 2206139. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202206139
Studies have shown that SOX17 inhibits the expression of NR4A3 and PCSK9 by regulating the autocrine effects of exosomes miR-224-5p and miR-361-3p, improves endothelial function, and delays the vascular remodeling process of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
2. Walters, Rachel, et al. "SOX17 enhancer variants disrupt transcription factor binding and enhancer inactivity drives pulmonary hypertension." Circulation 147.21 (2023): 1606-1621. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.061940
Research has found that risk variations of pulmonary arterial hypertension cause disease by affecting HOXA5/ROR-α binding, reducing endothelial SOX17 expression, and leading to cellular dysfunction. Existing drugs can reverse this transcriptional feature, providing new strategies for treatment.
3. Irie, Naoko, et al. "SOX17 is a critical specifier of human primordial germ cell fate." Cell 160.1 (2015): 253-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.013
Research has found that SOX17 is a key regulatory factor in the fate determination of human primordial germ cells, while BLIMP1 assists this process by inhibiting somatic genes. This reveals a new mechanism of human germ cell specialization that is significantly different from that of mouse models.
4. Zhu, Na, et al. "Rare variants in SOX17 are associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension with congenital heart disease." Genome medicine 10.1 (2018): 56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0566-x
The article indicates that genome-wide research has found that the transcription factor SOX17 is a new key risk gene for pulmonary arterial hypertension related to congenital heart disease (PAH-CHD), with approximately 3.2% of cases associated with its rare harmful variation. This gene also plays a role in idiopathic PAH.
5. Uchida, Aya, et al. "SOX17-positive rete testis epithelium is required for Sertoli valve formation and normal spermiogenesis in the male mouse." Nature communications 13.1 (2022): 7860. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35465-1
Research has found that the expression of the Sox17 gene in the testicular reticulum of mice is crucial for maintaining the "valve" structure of the output channel. The absence of Sox17 can lead to valve damage, fluid reflux and abnormal sperm development, revealing its new function in maintaining normal sperm maturation.
Creative Biolabs: SOX17 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality SOX17 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom SOX17 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our SOX17 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Zhu, Na, et al. "Rare variants in SOX17 are associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension with congenital heart disease." Genome medicine 10.1 (2018): 56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0566-x
Anti-SOX17 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APOE Recombinant Antibody (A1) (CBMAB-0078CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARHGDIA Recombinant Antibody (CBCNA-009) (CBMAB-R0415-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID1B Recombinant Antibody (KMN1) (CBMAB-A3546-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AOC3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0014) (CBMAB-0014-YY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DDC Recombinant Antibody (8E8) (CBMAB-0992-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC3 Recombinant Antibody (16E63) (CBMAB-C3367-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






