AHSG Antibodies
Background
AHSG (α 2-hs-glycoprotein) is a glycoprotein mainly synthesized by the liver and secreted into the plasma. It belongs to the cystatin superfamily and functions as a multifunctional regulatory factor in the body, participating in various physiological processes, including bone tissue mineralization, immune inflammatory responses, and the regulation of insulin signaling pathways. This protein can bind to calcium ions and hydroxyapatite, playing a significant role in bone metabolism. At the same time, it influences inflammatory responses and apoptosis by interacting with immune cells. The AHSG gene was first isolated and described in 1962. Subsequent studies on the tertiary structure of the protein it encodes have revealed its close association with mineralized tissues and metabolic diseases. Due to its significant correlation with diseases such as metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and vascular calcification, the structural and functional mechanisms of AHSG have always been an important direction in biomedical research, providing a key basis for understanding the role of glycoproteins in systemic physiological regulation.
Structure of AHSG
AHSG (α 2-hs-glycoprotein) is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 49 kDa. There are differences in its molecular weight and glycosylation modification among different species. The following is a comparison of AHSG characteristics of some species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 49 | 46 | About 50 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Two subunits, highly glycosylated | The structure of the sugar chain is slightly different from that of humans | Glycosylation patterns and mammalian conservation |
This protein is composed of two polypeptide chains (α chain and β chain) linked by disulfide bonds, and its tertiary structure belongs to the typical β -folded sandwich structure of the cystatin superfamily. AHSG contains multiple functional domains, among which two high-affinity regions bound to calcium ions (" calcium-binding bags ") can regulate the mineralization process; Another domain mediates interactions with cell surface receptors (such as integrins), participating in inflammation and metabolic regulation. Its N-terminal and C-terminal play a key role in maintaining the conformation and biological functions of proteins.
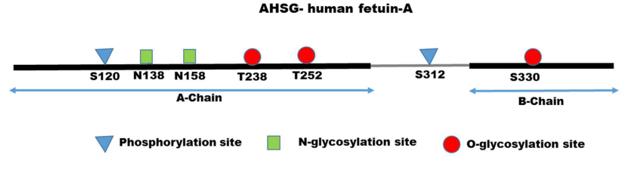 Fig. 1 Amino acid sequence of human fetuin-A.1
Fig. 1 Amino acid sequence of human fetuin-A.1
Key structural properties of AHSG:
- Typical cystatin -like β -folded sandwich structure
- Calcium ion bag structure domain maintain mineralized regulating function
- High glycosylation modification affects protein stability and receptor recognition
- Integrin-binding domains mediate cellular signal transduction and inflammatory regulation
Functions of AHSG
The main function of AHSG (α 2-hs-glycoprotein) is to act as a multifunctional regulatory protein in plasma. It is involved in a variety of physiological processes such as bone metabolism, inflammatory response and insulin signaling pathways.
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of Bone mineralization | By combining hydroxyapatite and calcium ions, it bidirectionally regulates the formation and absorption of bone tissue and inhibits abnormal calcification. |
| Inflammation Regulation | As an acute-phase reaction protein, it can regulate the activity of immune cells such as macrophages and influence the course of inflammatory responses. |
| Metabolic regulation | By interacting with insulin receptors, it affects insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism and is associated with type 2 diabetes. |
| Vascular Protection | Inhibiting the abnormal calcification and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells may play a protective role in vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. |
| Tissue repair | It accumulates at the injury site and participates in the tissue repair and regeneration process by regulating cell adhesion and proliferation. |
The functional status of AHSG is highly dependent on its post-translational glycosylation modification level, which directly affects its binding ability to different ligands (such as calcium ions and cell receptors), thereby enabling it to exert complex and precise regulatory effects in vivo.
Applications of AHSG and AHSG Antibody in Literature
- Ochieng, Josiah, et al. "Impact of Fetuin-A (AHSG) on tumor progression and type 2 diabetes." International journal of molecular sciences 19.8 (2018): 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082211
The article indicates that fetuin-A is synthesized by the liver and enters the bloodstream, with a concentration of approximately 0.2–0.8 mg/mL. The study found that it can inhibit insulin signal transduction and exacerbate type 2 diabetes, and can be abnormally secreted by various tumor cells to promote progression. The related autoantibodies may have early diagnostic value.
- Yue, Wanyong, et al. "The BHMT2/MAT1A/AHSG axis promotes M1 macrophage activation and exacerbates necrotizing enterocolitis." Scientific Reports 15.1 (2025): 39458. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-22915-1
The article indicates that in necrotizing enterocolitis, the BHMT2/MAT1A/AHSG axis of intestinal epithelial cells upregulates AHSG expression by regulating histone methylation, drives M1 macrophage polarization, exacerbates inflammation and tissue damage, and targeting this pathway may have therapeutic potential.
- Dong, Yufei, et al. "Alpha-2 Heremans Schmid Glycoprotein (AHSG) promotes the proliferation of bladder cancer cells by regulating the TGF-β signalling pathway." Bioengineered 13.6 (2022): 14282-14298. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2081465
Studies have confirmed that the expression of AHSG in bladder cancer tissues and urine is significantly elevated. This protein inhibits the TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway, promoting the proliferation of cancer cells and the transition from G1 to S phase, and may become a new biomarker for bladder cancer.
- Kazamia, Rafailia, et al. "Tissue and plasma proteomic profiling indicates AHSG as a potential biomarker for ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms." BMC cardiovascular disorders 23.1 (2023): 138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-023-03154-6
The study found that the concentration of AHSG protein in the plasma of patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms was significantly lower than that of healthy individuals, and it was also associated with various cardiovascular risk factors. This suggests that AHSG may serve as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of thoracic aortic aneurysms.
- Shi, Feiyu, et al. "Identification of serum proteins AHSG, FGA and APOA-I as diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer." Clinical proteomics 15.1 (2018): 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-018-9194-0
The research found that through proteomics technology, it was discovered that the levels of FGA, AHSG and APOA-I in the serum of gastric cancer patients were significantly abnormal. ELISA verification showed that these three substances were related to the tumor stage and burden, and could be potential serum markers for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Creative Biolabs: AHSG Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality AHSG antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom AHSG Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our AHSG antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Ochieng, Josiah, et al. "Impact of Fetuin-A (AHSG) on tumor progression and type 2 diabetes." International journal of molecular sciences 19.8 (2018): 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082211
Anti-AHSG antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (D6) (CBMAB-1240CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARID3A Antibody (A4) (CBMAB-0128-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACE2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179293) (CBMAB-A0566-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD63 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-1200) (CBMAB-C1467-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AP4E1 Recombinant Antibody (32) (CBMAB-A2996-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-58519) (CBMAB-L0166-YJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV9 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634029) (CBMAB-AP023LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCL18 Recombinant Antibody (64507) (CBMAB-C7910-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






