CD38 Antibodies
Background
CD38 is a multifunctional type II transmembrane glycoprotein that plays central roles in immune regulation, cellular metabolism, and calcium signaling. First identified in the early 1980s as a T-cell activation marker, CD38 is now known to be widely expressed in hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic tissues. High levels are found on plasma cells, activated T and B lymphocytes, monocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells, while lower expression occurs in non-immune tissues such as airway epithelia and pancreatic β-cells. The therapeutic importance of CD38 has grown dramatically in the past decade, particularly in oncology. As a uniformly expressed marker on plasma cells, CD38 is a validated therapeutic target in multiple myeloma, leading to the development of monoclonal antibodies. Beyond hematologic malignancies, CD38 is also implicated in solid tumors, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, and aging, making it one of the most extensively studied immunological proteins in recent years.
Structure of CD38
CD38 is a single-chain glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 45 kDa. It is classified as a type II transmembrane protein, meaning its N-terminal tail resides inside the cytoplasm, while the C-terminal extracellular domain carries the enzymatic and receptor functions.
Structural domains:
- N-terminal cytoplasmic tail (~20 amino acids): Short, with no known catalytic activity, but important for anchoring.
- Single transmembrane domain (~20 amino acids): Anchors the protein to the membrane.
- Extracellular domain (~260 amino acids): Contains the active site responsible for NAD+ hydrolysis and cyclization. This region is heavily glycosylated, stabilizing the protein and modulating ligand recognition.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Monkey/Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | ~45 | ~43 | ~44 | ~45 |
| Primary Structural Notes | High expression on plasma cells; major therapeutic target | Conserved sequence, minor efficiency differences | Comparable to mouse | Structurally conserved |
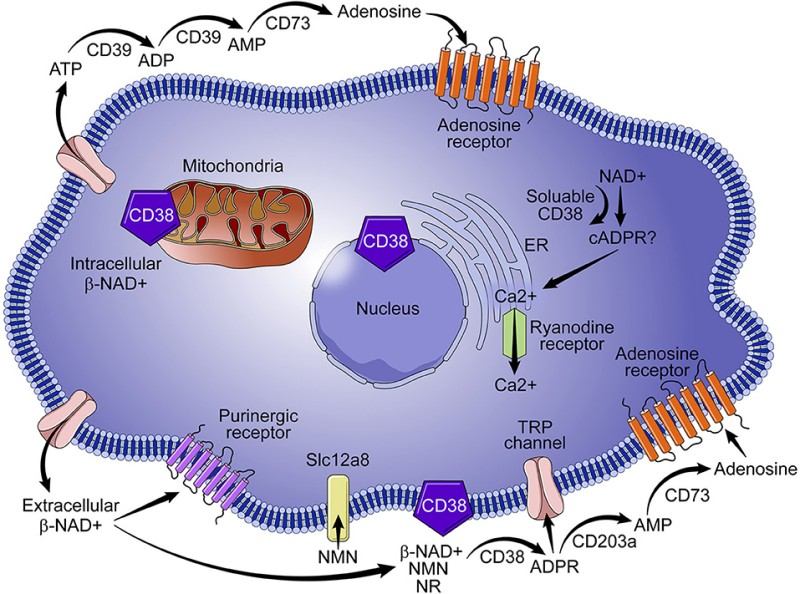 Fig. 1 Role of CD38 in NAD+ metabolism.1
Fig. 1 Role of CD38 in NAD+ metabolism.1
Key structural features of CD38:
- Type II transmembrane orientation (short cytoplasmic N-terminus, large extracellular C-terminus).
- Catalytic extracellular domain with ADP-ribosyl cyclase and NAD+ hydrolase activity.
- Oligomerization into dimers or tetramers enhances enzymatic efficiency.
- Post-translational glycosylation critical for protein folding, trafficking, and activity.
- Conserved glutamate residues in the catalytic site required for NAD+ metabolism.
Functions of CD38
| Function | Description |
| NAD+ Metabolism | Hydrolyzes NAD+ to generate cADPR and NAADP, potent calcium-mobilizing messengers that regulate intracellular calcium release. |
| Immune Activation | Functions as a receptor on T and B lymphocytes, influencing cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine secretion. |
| Plasma Cell Marker | Highly expressed on plasma cells, making it a diagnostic marker in diseases such as multiple myeloma and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. |
| Metabolic Regulation | CD38 is the main NADase in mammalian tissues, lowering intracellular NAD+ levels and linking CD38 activity to aging, insulin resistance, and metabolic decline. |
| Tumor Immunology | In tumor microenvironments, CD38 contributes to immunosuppression by enhancing adenosine production, promoting T-cell exhaustion and tumor immune evasion. |
Applications of CD38 and CD38 Antibody in Literature
1. Lokhorst, Henk M., et al. "Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma." New England Journal of Medicine 373.13 (2015): 1207-1219. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1506348
This landmark clinical trial introduced daratumumab, the first-in-class anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, as an effective therapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
2. Zeidler, Julianna D., et al. "The CD38 glycohydrolase and the NAD sink: implications for pathological conditions." American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology (2022). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00451.2021
Demonstrates CD38 as the dominant enzyme regulating systemic NAD⁺ metabolism, with implications for aging and metabolic syndrome.
3. Morandi, Fabio, et al. "CD38: a target for immunotherapeutic approaches in multiple myeloma." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 2722. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02722
Reviews CD38 expression across Multiple Myeloma and solid tumors, highlighting rationale for immunotherapy.
4. Chini, Eduardo N. "CD38 as a regulator of cellular NAD: a novel potential pharmacological target for metabolic conditions." Current pharmaceutical design 15.1 (2009): 57-63. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161209787185788
Explores the role of CD38 on the control of cellular NAD levels which indicates that CD38 may serve as a pharmacological target for multiple conditions.
Company A: CD38 Antibodies for Research
Company A specializes in the production of high-quality CD38 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CD38 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CD38 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Hogan, Kelly A., Claudia CS Chini, and Eduardo N. Chini. "The multi-faceted ecto-enzyme CD38: roles in immunomodulation, cancer, aging, and metabolic diseases." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 1187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01187
Anti-CD38 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ADAM29 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179787) (CBMAB-A1149-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC25 Recombinant Antibody (CBLC132-LY) (CBMAB-C9786-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASB9 Recombinant Antibody (1D8) (CBMAB-A0529-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOSB Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-3593) (CBMAB-F2522-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-CBL Recombinant Antibody (D4E10) (CBMAB-CP0149-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTN4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-6075) (CBMAB-0020CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B3 Recombinant Antibody (1E9) (CBMAB-A4021-YC)

-
Rat Anti-ABCC11 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179001) (CBMAB-A0236-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCNH Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1054) (CBMAB-C1111-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0216) (CBMAB-0217-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








