CYP1B1 Antibodies
Background
CYP1B1 is an important member of the cytochrome P450 enzyme family, mainly distributed in extrahepatic tissues of vertebrates, such as the lungs, mammary glands and prostate. This enzyme can metabolize a variety of endogenous and exogenous compounds, participate in the biotransformation of steroid hormones, and play a key role in the activation process of exogenous toxins and drug precursors. Due to its abnormally high expression in tumor tissues being closely related to the progression of various cancers, CYP1B1 was first identified in 1994 and quickly became a research hotspot in targeted cancer therapy. The analysis of its three-dimensional structure has deepened people's understanding of substrate specificity and catalytic mechanisms, providing a structural basis for the development of selective inhibitors, and holds significant value for tumor treatment and toxicological research.
Structure of CYP1B1
CYP1B1 protein is a cytochrome P450 enzyme of approximately 60.2 kDa. There are slight differences in its molecular weight among different species, mainly due to the changes in amino acid sequences caused by gene polymorphisms.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 60.2 | About 59.8 | About 60.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | There are multiple known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). | Sequences are highly conserved and are often used in model studies | CYP1B1 is expressed with humans have high homology |
CYP1B1 is composed of 543 amino acids and forms a typical P450 protein folding structure. Its three-dimensional structure core is composed of multiple α -helicles and β -folds, forming a hydrophobic active pocket that can accommodate various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and steroid hormones and other substrates. The protein structure contains a non-covalently bound heme cofactor, which is the center of its catalytic function. Key active site residues, such as cysteine adjacent to heme, are responsible for transferring electrons and activating molecular oxygen, thereby completing the single oxygenation reaction of the substrate. The substrate specificity of this enzyme is jointly determined by the shape of its active pocket and the interaction of key amino acids.
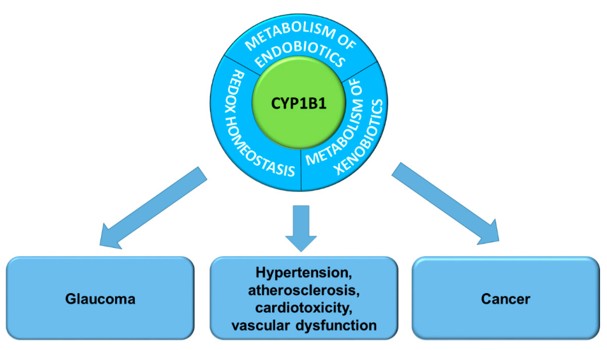 Fig. 1 Cytochrome P450 1B1 functions and its association with pathogenesis of diseases.1
Fig. 1 Cytochrome P450 1B1 functions and its association with pathogenesis of diseases.1
Key structural properties of CYP1A2:
- Typical P450 fold structure, containing alpha helix and beta sheet
- Hydrophobic active pockets to accommodate a variety of substrates
- Heme cofactor (iron protoporphyrin IX) is the catalytic active center
- Key cysteine residues (Cys470) and heme iron ligand
Functions of CYP1B1
The main function of the CYP1A2 gene is to metabolize a variety of endogenous and exogenous compounds. However, it also plays a key role in individual drug response differences and disease susceptibility.
| Function | Description |
| Metabolism of exogenous substances | Metabolizing approximately 10% of commonly used drugs (such as caffeine and clozapine) and activating precarcinogens (such as aromatic amines) is an important mediator in drug interactions. |
| Endogenous substance regulation | Arachidonic acid, steroids and bioconversion of endogenous material such as cholic acid, affect the steady state. |
| Sources of individual differences | There are significant polymorphisms (such as 1F, 1K, etc.) in its genes, resulting in a 60-fold difference in enzyme activity among the population, which is one of the main genetic factors for individual differences in drug efficacy and toxicity. |
| Disease association | Abnormal enzyme activity is associated with the risk of various diseases, including certain cancers (such as liver cancer), Parkinson's disease and gestational hypertension. |
| Biomarker | The level of its induced expression, such as the rate of caffeine metabolism, is often used as a clinical measure of the overall activity of the hepatic CYP450 enzyme system. |
The enzymatic kinetics of CYP1A2 follows the typical Mie equation, but its substrate binding curve may exhibit allosteric characteristics due to the presence of multiple binding sites, which explains its broad substrate specificity in metabolizing a variety of structurally distinct compounds.
Applications of CYP1B1 and CYP1B1 Antibody in Literature
1. Chen, Congcong, et al. "CYP1B1 inhibits ferroptosis and induces anti-PD-1 resistance by degrading ACSL4 in colorectal cancer." Cell death & disease 14.4 (2023): 271. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05803-2
The article indicates that CYP1B1 promotes the degradation of ACSL4 through the 20-HETE/PKC/FBXO10 pathway, inhibits ferroptosis in colorectal cancer and weakens the anti-PD-1 efficacy. Its high expression suggests a poor prognosis and can serve as a potential target for immunotherapy sensitization.
2. Liu, Chang, et al. "The AKR1C1–CYP1B1–cAMP signaling axis controls tumorigenicity and ferroptosis susceptibility of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma." Cell Death & Differentiation 32.3 (2025): 506-520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-024-01407-1
The article indicates that high expression of AKR1C1 in ECC suggests a poor prognosis. It down-regulates CYP1B1 through ubiquitination degradation and AHR transcriptional inhibition, and then inhibits ferroptosis through the cAMP-PKA pathway. Targeting this axis can work in synergy with ferroptosis inducers to inhibit tumor growth.
3. Zhu, Yin, et al. "CYP1B1 Mediates Cigarette Smoke–Induced Lipid Accumulation in Alveolar Type 2 Cells." The FASEB Journal 39.18 (2025): e71062. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202501439RR
Research has found that cigarette smoke drives abnormal lipid accumulation and promotes mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis by up-regulating the expression of CYP1B1 in alveolar type II epithelial cells. Targeted inhibition of CYP1B1 may provide a new strategy for treating lipid metabolism disorders in COPD.
4. Ye, Tao, et al. "CYP1B1‐AS1 Is a Novel Biomarker in Glioblastoma by Comprehensive Analysis." Disease markers 2021.1 (2021): 8565943. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8565943
Studies have found that eRNA CYP1B1-AS1 is strongly correlated with CYP1B1 gene expression in various cancers such as glioblastoma. Its overexpression affects prognosis through immune inflammation-related pathways and may serve as a potential prognostic marker for cancers such as GBM.
5. Hollis, Paul R., et al. "CYP1B1 augments the mesenchymal, claudin-low, and chemoresistant phenotypes of triple-negative breast cancer cells." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.17 (2022): 9670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179670
Research has found that in breast cancer, high expression of CYP1B1 is associated with a malignant phenotype. Down-regulation of CYP1B1 can reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition, inhibit cell invasion and metastasis, increase the expression of tight junction proteins, and enhance the sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs, suggesting that it is a potential target for combination therapy.
Creative Biolabs: CYP1B1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality CYP1B1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom CYP1B1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our CYP1B1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Mikstacka, Renata, and Zbigniew Dutkiewicz. "New perspectives of CYP1B1 inhibitors in the light of molecular studies." Processes 9.5 (2021): 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050817
Anti-CYP1B1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-APCS Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A663) (CBMAB-A3054-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALOX5 Recombinant Antibody (33) (CBMAB-1890CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKR1B1 Antibody (V2-2449) (CBMAB-1001CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BLNK Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0623) (CBMAB-0626-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD8 Recombinant Antibody (C1083) (CBMAB-C1083-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMIGO2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0756) (CBMAB-C2192-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC5 Recombinant Antibody (6E4) (CBMAB-CP2646-LY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (BA0013) (CBMAB-0272CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-FOXL1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0845) (CBMAB-F0462-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








