EGR1 Antibodies
Background
EGR1 is a zinc finger transcription factor, mainly existing in various tissue cells of vertebrates. This protein can bind to the promoter region of a specific gene and participate in key biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis by regulating the expression of downstream target genes. In neural development and immune responses, EGR1 maintains intracellular homeostasis balance by rapidly responding to external stimuli. This gene was first identified in 1988. As a member of the immediate early gene family, its expression changes have become an important molecular marker for studying cellular stress responses. Its multi-level regulatory mechanism provides a key molecular basis for understanding gene transcriptional regulation, signal transduction pathways and the occurrence and development of diseases.
Structure of EGR1
The molecular weight of the protein encoded by the EGR1 gene is approximately 53-57 kDa. The specific value varies among different species, mainly due to the differences in amino acid composition and post-transcriptional modifications. The following table shows a comparison of the molecular characteristics of EGR1 protein in different species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Chicken | Zebrafish |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 56.5 | 55.2 | 55.8 | 54.1 | 52.3 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains three C2H2-type zinc finger domains | Highly conserved zinc finger structure | DNA binding domains are highly homologous | The core functional domains are similar | Basic transcriptional regulation and control function |
The EGR1 protein is composed of 533 amino acids. Its core structure consists of three concatenated Cys2-His2 type zinc finger modalities. These domains form stable spatial conformations through zinc ion coordination, enabling it to specifically recognize and bind to the GC-rich sequence in the promoter region of the target gene. Each zinc finger unit coordinates with zinc ions through conserved cysteine and histidine residues to form an independent DNA-binding unit, while the connection sequences between adjacent zinc fingers provide structural flexibility. This modular design enables EGR1 to act as an early response transcription factor, rapidly responding to extracellular signals and initiating the expression regulation of downstream genes.
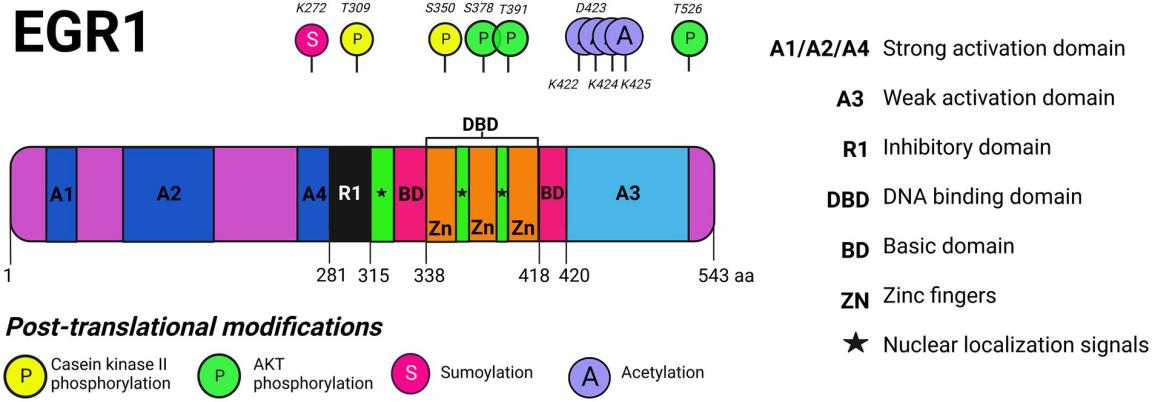 Fig. 1 EGR1 protein domains and post-translational modifications.1
Fig. 1 EGR1 protein domains and post-translational modifications.1
Key structural properties of EGR1:
- Contains three highly conserved C2H2 -type zinc finger domains
- Each zinc finger is coordinated with zinc ions by cysteine and histidine residues
- Zinc finger module form helical structure
- Basic amino acid area is responsible for the verification and protein interactions
Functions of EGR1
The main function of the EGR1 gene is to act as an immediate early response transcription factor, participating in the regulation of cell stress, proliferation and differentiation. In addition, it also involves a variety of pathophysiological processes, including neural plasticity, immune regulation and tumorigenesis.
| Function | Description |
| Gene transcriptional regulation | As a transcription factor, it binds to the GC-rich sequence in the promoter region of the target gene to activate or inhibit the expression of downstream genes. |
| Cellular stress response | In cell growth factor, damage or stress signals to stimulate rapid express, start the adaptive response. |
| Regulation of neural plasticity | Participate in learning and memory-related signaling pathways, regulate synaptic plasticity and neuronal functional remodeling. |
| Immune and inflammatory regulation | Expressed in immune cells, regulating the inflammatory factors and immune response process. |
| Tumors have a dual effect | In different cancer suppressor or its effect on promoting cancer, involved in regulating the cell cycle, apoptosis, and invasion and metastasis. |
The activation of EGR1 is characterized by its rapidness and transitivity. Its expression level often significantly increases within tens of minutes after stimulation and then rapidly returns to the baseline. This dynamic expression pattern makes it a key molecular bridge connecting extracellular signals with long-term adaptive gene expression.
Applications of EGR1 and EGR1 Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Bin, et al. "The role of the transcription factor EGR1 in cancer." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2021): 642547. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.642547
The article indicates that Early growth response factor 1 (EGR1) is a transcription factor that participates in processes such as tissue damage and immune responses. Recent studies have found that it may regulate cell proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis in the occurrence and development of tumors. The specific mechanism remains to be clarified, providing a reference for clinical efficacy prediction and exploration of new targets.
2. Pan, Mingang, et al. "EGR1 suppresses HCC growth and aerobic glycolysis by transcriptionally downregulating PFKL." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 43.1 (2024): 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-024-02957-5
This study reveals that the expression of EGR1 is decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma. It inhibits tumor proliferation by suppressing aerobic glycolysis regulated by the PFKL gene. Animal and organoid experiments have confirmed that EGR1 gene therapy can inhibit tumor growth and enhance the efficacy of sorafenib, demonstrating its potential as a new target for liver cancer treatment.
3. Chen, Jian-Wen, et al. "Transient upregulation of EGR1 signaling enhances kidney repair by activating SOX9+ renal tubular cells." Theranostics 12.12 (2022): 5434. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.73426
This study reveals that in the early stage of acute kidney injury, the transcription factor EGR1 is rapidly upregulated. It accelerates the proliferation and repair of renal tubular cells by directly binding to the Sox9 gene promoter, promoting SOX9 expression and activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The deficiency of EGR1 can aggravate the damage, indicating that it is a potential therapeutic target for kidney protection.
4. Havis, Emmanuelle, and Delphine Duprez. "EGR1 transcription factor is a multifaceted regulator of matrix production in tendons and other connective tissues." International journal of molecular sciences 21.5 (2020): 1664.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051664
This study reveals that the transcription factor EGR1 is expressed in various connective tissues such as tendons and cartilages, and its core function lies in regulating the generation of extracellular matrix. It is involved in the development, homeostasis and repair processes of tissues and is closely related to fibrotic lesions, and thus is regarded as a potential target for anti-fibrotic treatment.
5. Woodson, Caitlin M., and Kylene Kehn-Hall. "Examining the role of EGR1 during viral infections." Frontiers in Microbiology 13 (2022): 1020220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020220
This study reveals that EGR1 is a multifunctional transcription factor that can be activated by various signals such as growth factors, cellular stress, and viral infections. As a convergence point of signal pathways, it plays a significant role in neural function and cancer. This article focuses on reviewing the direct and indirect regulatory roles of EGR1 in the replication process of DNA and RNA viruses.
Creative Biolabs: EGR1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality EGR1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom EGR1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our EGR1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Woodson, Caitlin M., and Kylene Kehn-Hall. "Examining the role of EGR1 during viral infections." Frontiers in Microbiology 13 (2022): 1020220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020220
Anti-EGR1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ESR1 Recombinant Antibody (Y31) (CBMAB-1208-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-CCN1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-3580) (CBMAB-C4816WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-AMH Recombinant Antibody (5/6) (CBMAB-A2527-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ANXA7 Recombinant Antibody (A-1) (CBMAB-A2941-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CTNND1 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-2414) (CBMAB-C2487-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL1A2 Recombinant Antibody (CF108) (V2LY-1206-LY626)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-NSUN6 Recombinant Antibody (D-5) (CBMAB-N3674-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP1B1 Recombinant Antibody (E4) (CBMAB-0463-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ALPL Antibody (B4-78) (CBMAB-1009CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ALB Recombinant Antibody (V2-363290) (CBMAB-S0173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EGR1 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJZ-100) (CBMAB-Z0289-WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ELAVL4 Recombinant Antibody (6B9) (CBMAB-1132-YC)

-
Rat Anti-CD34 Recombinant Antibody (MEC 14.7) (CBMAB-C10196-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








