GPRC5D Antibodies
Background
GPRC5D is a G protein-coupled receptor, mainly expressed on the cell membrane surface, and specifically distributed in plasma cells and certain B lymphocyte subsets in the human body. The protein encoded by this gene regulates calcium ion homeostasis and cell differentiation processes by participating in cell signal transduction pathways. In recent years, it has received extensive attention due to its targeted value in the treatment of multiple myeloma. When researchers first identified the gene in 2004, they noted its unique seventh-transmembrane domain and structural similarity to rhodopsin receptors. The CAR-T therapy developed for GPRC5D has entered the clinical trial stage. The analysis of its ligand binding mechanism and downstream signaling pathways provides a new molecular basis for tumor immunotherapy.
Structure of GPRC5D
GPRC5D is a G protein-coupled receptor with a molecular weight of approximately 40 kDa, and its precise molecular weight varies among different species and transcriptional variants. This protein has a typical seventh-transmembrane domain, with its N-terminal located outside the cell and containing a cysteine-rich region, and its C-terminal located inside the cell and involved in signal transduction. The following is its comparison among different species:
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 39.8 | 40.2 | 40.1 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Long N-terminal domain, rich in cysteine | The N-terminal is relatively short, and the transmembrane region is highly conserved | The homology with mouse was up to 90% |
The secondary structure of GPRC5D is mainly composed of α -helix, and its extracellular domain forms a specific spatial conformation, which may be involved in ligand recognition. This receptor is classified as an orphan receptor, and its endogenous ligand remains unclear to date. Current research has found that GPRC5D is highly specifically expressed on the surface of plasma cells, and this characteristic makes it an important target for immunotherapy of multiple myeloma.
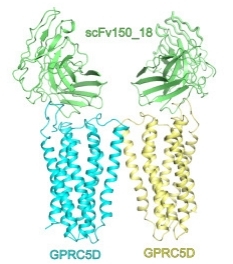 Fig. 1 The structural model of the GPRC5D and scFv150_18 complex.1
Fig. 1 The structural model of the GPRC5D and scFv150_18 complex.1
Key structural properties of GPRC5D:
- Typical seventh-transmembrane domains (GPCR A family characteristics)
- Extracellular section contains rich in cysteine structural domain
- Conserved DRY motif is located in the second intracellular ring, mediating G protein coupling
Functions of GPRC5D
The main function of the GPRC5D gene is to act as an orphan receptor to participate in cell signal transduction and differentiation regulation, especially playing a significant role in the immune system. Its specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Cell signal regulation | Transduction of extracellular signals through G protein-coupling mechanisms affects intracellular calcium ion levels and second messenger pathways. |
| Plasma cell differentiation and survival | High specificity in plasma cell surface expression that may regulate the differentiation and apoptosis process. |
| Tumor immune targets | As an important surface marker of multiple myeloma, it provides specific targets for immunotherapies such as CAR-T. |
| Maintain organizational homeostasis | In the lungs such as epithelial cell function regulation and tissue damage repair process. |
| Potential inflammatory regulatory function | May be related to GPCR family participation of the inflammatory response in the immune balance and fine-tuning. |
Although GPRC5D is classified as an orphan receptor and its ligand binding characteristics remain unclear, it is known that it participates in various physiological and pathological processes through autonomous or atypical activation methods, especially having significant application value in the field of tumor immunotherapy.
Applications of GPRC5D and GPRC5D Antibody in Literature
1. Rodriguez-Otero, Paula, et al. "GPRC5D as a novel target for the treatment of multiple myeloma: a narrative review." Blood cancer journal 14.1 (2024): 24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-023-00966-9
The article indicates that GPRC5D is an emerging immunotherapy target for multiple myeloma. Bispecific antibodies targeting GPRC5D and CAR-T therapy showed an overall response rate of ≥64% in early clinical trials. Although accompanied by adverse reactions in the skin and mouth, they were generally controllable. The application prospects of its combination with existing therapies are worthy of further exploration.
2. Lee, Holly, et al. "Mechanisms of antigen escape from BCMA-or GPRC5D-targeted immunotherapies in multiple myeloma." Nature medicine 29.9 (2023): 2295-2306. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02491-5
The article indicates that the biallelic mutation of GPRC5D is an important mechanism for the recurrence of multiple myeloma after T-cell redirection therapy against GPRC5D. Research has found that after treatment, GPRC5D protein down-regulation or clonal amplification leading to antigen loss through somatic events may occur, indicating that immune selection pressure drives antigen-negative recurrence. Attention should be paid to the impact of target mutations on the efficacy of antibodies.
3. Zhao, Juanjuan, et al. "Bispecific antibodies targeting BCMA, GPRC5D, and FcRH5 for multiple myeloma therapy: latest updates from ASCO 2023 Annual Meeting." Journal of Hematology & Oncology 16.1 (2023): 92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-023-01489-3
The article indicates that GPRC5D is a novel target for the treatment of multiple myeloma, and related bispecific antibodies (such as talquetamab) have shown potential in clinical trials. Despite the adverse reactions on the skin and in the mouth, its therapeutic effect is remarkable and the overall safety is controllable, providing a new treatment direction for patients with relapsed and refractory diseases.
4. Merz, Maximilian, et al. "Bispecific antibodies targeting BCMA or GPRC5D are highly effective in relapsed myeloma after CAR T-cell therapy." Blood cancer journal 14.1 (2024): 214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-024-01197-2
The article indicates that for multiple myeloma with recurrence after CAR-T treatment, studies have shown that GPRC5D-targeted bispecific antibodies (such as talquetamab) have significant efficacy, with an overall response rate of 79%. They can effectively improve the survival of patients with early recurrence and extramedullary lesions and are expected to become the standard rescue plan.
5. Yan, Sijia, et al. "Application of GPRC5D Targeting Therapy in Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma." Cancer Medicine 14.6 (2025): e70764. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.70764
The article indicates that GPRC5D, as a novel therapeutic target for multiple myeloma, its targeted therapy provides a new strategy for relapsed/refractory patients. This article systematically reviews the latest progress in targeted therapy for GPRC5D, providing references and directions for future research in this field.
Creative Biolabs: GPRC5D Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality GPRC5D antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom GPRC5D Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our GPRC5D antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Yan, Pengfei, et al. "The binding mechanism of an anti-multiple myeloma antibody to the human GPRC5D homodimer." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 5255. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49625-y
Anti-GPRC5D antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-ABIN2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179106) (CBMAB-A0349-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV8 Recombinant Antibody (V2-634028) (CBMAB-AP022LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AHCYL1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180270) (CBMAB-A1703-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCT6A/B Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0168) (CBMAB-C5570-CQ)

-
Rabbit Anti-ADRA1A Recombinant Antibody (V2-12532) (CBMAB-1022-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-BCL2L1 Recombinant Antibody (H5) (CBMAB-1025CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ALDOA Recombinant Antibody (A2) (CBMAB-A2316-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl SMC3 (K105/K106) Recombinant Antibody (V2-634053) (CBMAB-AP052LY)

-
Mouse Anti-APP Recombinant Antibody (5C2A1) (CBMAB-A3314-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys36) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623395) (CBMAB-CP0994-LY)

-
Rat Anti-FABP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-2299) (CBMAB-F1612-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DLC1 Recombinant Antibody (D1009) (CBMAB-D1009-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (G-3) (CBMAB-A3359-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-2C TCR Recombinant Antibody (V2-1556) (CBMAB-0951-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






