HMMR Antibodies
Background
The HMMR gene encodes a protein called Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor, which plays a core role in cell mitosis, cell migration, and hyaluronan-mediated signaling pathways. It participates in various tissue development and repair processes by maintaining spindle stability and promoting cell movement, and has received extensive attention especially in the research of breast tissue function regulation and tumor cell invasiveness. This gene was first identified in 1998. Subsequent studies have revealed that its overexpression is closely related to the metastasis risk of various cancers, such as breast cancer and colorectal cancer, and thus it is regarded as a potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker. The in-depth exploration of HMMR not only broadens our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of the cell cycle, but also provides an important molecular basis for the study of dynamic cell interactions in the tumor microenvironment.
Structure of HMMR
The protein encoded by the HMMR gene is a hyaluronic acid-mediated motor receptor (HMMR, also known as RHAMM) with a molecular weight of approximately 85 kDa. There are certain differences in the molecular weight of this protein among different species, mainly due to the diversity of subtype splicing and post-translational modifications.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat | Bovine |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 85 | 84 | 83.5 | 86 |
This protein contains approximately 724 amino acids and has a complex multi-domain configuration, including a microtubule binding domain at the N-terminal and a hyaluronic acid binding domain at the C-terminal. Its tertiary structure forms a specific flexible conformation, which can dynamically bind tubulin to hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix. A key central coiled helical domain mediates homodimerization, while the basic amino acid cluster at its C-terminal directly binds to the hyaluronic acid chain through electrostatic interaction, thereby coordinating the signal transduction between the cytoskeleton and the microenvironment during cell division and migration.
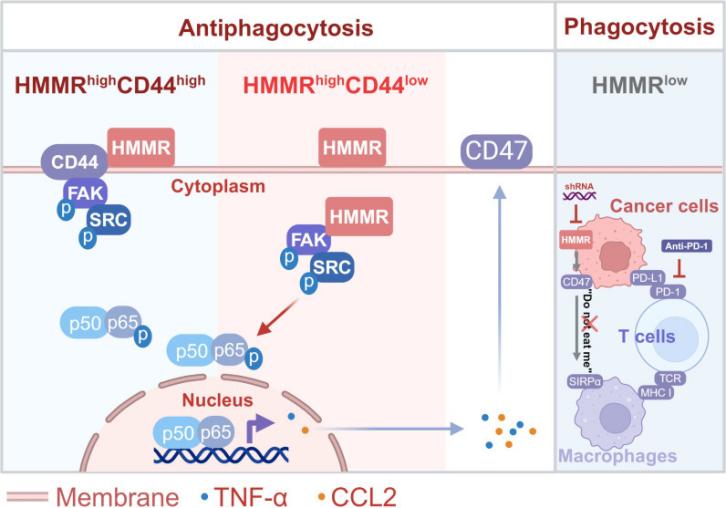 Fig. 1 HMMR Activates FAK/SRC to Trigger Immune Evasion in Liver Cancer.1
Fig. 1 HMMR Activates FAK/SRC to Trigger Immune Evasion in Liver Cancer.1
Key structural properties of HMMR:
- With multiple function structure domain
- Coiled-helix structures mediate protein dimerization
- Alkaline amino acid-rich region
Functions of HMMR
The core function of HMMR protein is to regulate cell mitosis and movement, and it also participates in various pathophysiological processes, especially playing a key role in tumor progression.
| Function | Description |
| Mitotic regulation | By combining microtubules to ensure the correct assembly of the spindle and the precise separation of chromosomes, genomic stability is maintained. |
| Cell migration promotion | Mediates hyaluronic acid signal transduction, enhances cell motility, and participates in wound repair and cancer cell invasion. |
| Association with tumor progression | Expression, in a variety of cancers by activated ERK signaling pathway and angiogenesis in tumor metastasis. |
| Hyaluronic acid signal transduction | As a hyaluronic acid receptor, it regulates the dynamic interaction between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. |
| Participation in tissue development | Guide the directional migration and localization of cells during embryonic development and the morphogenesis of specific tissues (such as the mammary gland). |
The functional activity of HMMR is highly dependent on its subcellular localization - regulating microtubule dynamics in the cytoplasm and mediating hyaluronic acid signaling on the cell surface. This dual localization mechanism enables it to integrate internal and external signals and coordinate complex cellular behaviors.
Applications of HMMR and HMMR Antibody in Literature
1. Wu, Hong, et al. "HMMR triggers immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by inactivation of phagocyte killing." Science advances 10.23 (2024): eadl6083. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adl6083
This study reveals that HMMR activates NF-κB signaling by forming FAK/SRC complexes, maintains the CD47 "Don't Eat me" signal, and helps liver cancer cells escape immune phagocytosis. The absence of HMMR can promote phagocytosis and enhance the anti-PD-1 efficacy. Patients with HMMRhighCD47high have a poorer prognosis. Targeting HMMR provides a new strategy for immunotherapy of liver cancer.
2. Guo, Kaixuan, et al. "HMMR promotes prostate cancer proliferation and metastasis via AURKA/mTORC2/E2F1 positive feedback loop." Cell death discovery 9.1 (2023): 48. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01341-0
This study reveals that HMMR drives the progression of prostate cancer by inhibiting the ubiquitination and degradation of AURKA protein, thereby activating the mTORC2/AKT signaling pathway. The transcription factor E2F1 activated by this pathway can feed back to promote HMMR transcription, forming a vicious positive feedback loop. HMMR thus becomes a potential intervention target for prostate cancer.
3. Jaskuła, Kinga, et al. "Cardiovascular effects mediated by hmmr and cd44." Mediators of Inflammation 2021.1 (2021): 4977209. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4977209
Current research shows that hyaluronic acid receptors HMMR (also known as RHAMM) and CD44 play important roles in cardiovascular diseases. They jointly participate in the disease processes such as myocardial infarction by mediating chronic inflammation, influencing cell migration and tissue repair, and are potential new therapeutic targets.
4. Shang, Junyi, et al. "HMMR potential as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of cancer—speculation based on a pan-cancer analysis." Frontiers in Surgery 9 (2023): 998598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2022.998598
The article indicates that pan-cancer analysis reveals that HMMR is generally upregulated in various cancers, and high expression is significantly associated with poor prognosis in patients. HMMR is closely related to tumor staging, immune cells and checkpoints, participates in key oncogenic pathways, and is expected to become a potential biomarker for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
5. He, Zhengcheng, et al. "Hyaluronan mediated motility receptor (HMMR) encodes an evolutionarily conserved homeostasis, mitosis, and meiosis regulator rather than a hyaluronan receptor." Cells 9.4 (2020): 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040819
The article indicates that HMMR is not only a hyaluronic acid receptor but also a key cell cycle regulatory protein. It precisely regulates cell division by interacting with mitotic kinases and motor proteins. Its dysfunction can drive tumorigenesis. This mechanism is independent of hyaluronic acid signaling, making it an important oncogene.
Creative Biolabs: HMMR Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality HMMR antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom HMMR Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our HMMR antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Wu, Hong, et al. "HMMR triggers immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by inactivation of phagocyte killing." Science advances 10.23 (2024): eadl6083. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adl6083
Anti-HMMR antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-ACTB Recombinant Antibody (V2-179553) (CBMAB-A0870-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C1QC Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0600) (CBMAB-C0654-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CA9 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-2079) (CBMAB-C0131-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-BIRC7 Recombinant Antibody (88C570) (CBMAB-L0261-YJ)

-
Rat Anti-AChR Recombinant Antibody (V2-12500) (CBMAB-0990-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-CD33 Recombinant Antibody (6C5/2) (CBMAB-C8126-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATG5 Recombinant Antibody (9H197) (CBMAB-A3945-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-DMPK Recombinant Antibody (CBYCD-324) (CBMAB-D1200-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-AQP2 Recombinant Antibody (E-2) (CBMAB-A3358-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ALOX5AP Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-1219) (CBMAB-F0750-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-FAS2 Monoclonal Antibody (1D4) (CBMAB-0071-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ASH1L Monoclonal Antibody (ASH5H03) (CBMAB-1372-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-EIF4G1 Recombinant Antibody (2A9) (CBMAB-A2544-LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








