LAYN Antibodies
Background
The LAYN gene encodes a transmembrane protein called Layilin, which is mainly expressed in immune cells and epithelial cells. It participates in regulating cell adhesion and migration processes by acting as a cell surface receptor, especially when combined with extracellular matrix components such as hyaluronic acid, it can affect the recombination of the cytoskeleton and signal transduction. Research has found that LAYN plays a significant role in T-cell activation and the immune regulation of the tumor microenvironment, and its expression level is related to the prognosis of certain cancers and the response to immunotherapy. The functional research of this gene has deepened people's understanding of the immune regulatory mechanism and provided potential targets for the treatment strategies of related diseases.
Structure of LAYN
The molecular weight of the Layilin protein encoded by the LAYN gene is approximately 70-75 kDa. This value may fluctuate slightly depending on different species or the splicing method of the transcript.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 70-75 | 68-73 | 69-74 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains an extracellular lectin domain and an intracellular FERM binding domain | High homology with human, structure conservation | Have similar domain compositions |
This protein is composed of approximately 535 amino acids, and its extracellular region contains a lectin domain responsible for recognizing extracellular matrix components such as hyaluronic acid. The intracellular segment interacts with cytoskeletal regulatory proteins through the FERM binding domain, forming a bridge connecting the extracellular environment and the intracellular skeleton. This structural characteristic enables Layilin to sense mechanical signals and regulate cell morphology and movement.
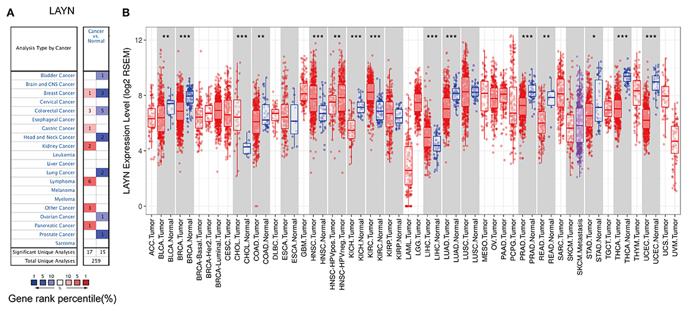 Fig. 1 LAYN expression levels in different types of human cancers.1
Fig. 1 LAYN expression levels in different types of human cancers.1
Key structural properties of LAYN:
- Extracellular C-type lectin domain, responsible for recognizing ligands such as hyaluronic acid
- Single-pass transmembrane domains connect extracellular and intracellular regions
- Intracellular section contains FERM combining structural domain
Functions of LAYN
The main function of the Layilin protein encoded by the LAYN gene is to act as a cell surface receptor to mediate the interaction between cells and the matrix. Its specific functions include:
| Function | Description |
| Regulation of cell adhesion | The recognition of hyaluronic acid through the extracellular lectin domain mediates the initial adhesion of cells to the extracellular matrix. |
| Regulation of cell migration | Through the intracellular FERM domain, the cytoskeleton is connected to affect cell morphological changes and migration movement. |
| Regulation of immune response | In the T cell surface expression, participate in the immune synapse formation and signal regulating T cell activation. |
| Mechanical signal transduction | As a mechanoreceptor, it converts the physical properties of the extracellular matrix into intracellular biochemical signals. |
| Impact of tumor progression | Regulate the invasion and metastasis processes of cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment. |
Layilin plays a core regulatory role in development, immune response and disease occurrence by integrating extracellular matrix signals with intracellular skeleton recombination. Its functional mechanism reflects the key bridging role of transmembrane receptors in connecting the intracellular and extracellular environments.
Applications of LAYN and LAYN Antibody in Literature
1. Pan, Jing-Hua, et al. "LAYN is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric and colon cancers." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00006
The article indicates that high expression of the LAYN gene is significantly associated with a poor prognosis in patients with colon cancer and gastric cancer. Studies have shown that LAYN can regulate the infiltration levels of immune cells such as CD8+ T cells and macrophages, and can serve as a potential prognostic biomarker.
2. Cao, Liangbin, Lingling Zhu, and Li Cheng. "ncRNA‐Regulated LAYN Serves as a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bioinformatics Analysis." BioMed research international 2022.1 (2022): 5357114. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5357114
The study has for the first time revealed that in hepatocellular carcinoma, LAYN is regulated by the HCG18/miR-148a axis, and its high expression is closely related to immune cell infiltration and poor prognosis of patients, and is expected to become a new immune biomarker and therapeutic target.
3. Chen, Qingjuan, et al. "The prognostic value of LAYN in HPV-related head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its influence on immune cell infiltration." Discover Oncology 15.1 (2024): 57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-024-00913-5
The study has for the first time revealed that in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, high expression of LAYN indicates a poor prognosis, and this is particularly significant in HPV-negative patients. Studies have found that LAYN is closely related to immunosuppressive phenomena such as M2-type macrophages and T-cell exhaustion, and can serve as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for HPV-related head and neck cancer.
4. Bäckryd, Emmanuel, et al. "Eleven neurology-related proteins measured in serum are positively correlated to the severity of diabetic neuropathy." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 17068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-66471-6
Research has demonstrated that LAYN is one of the 11 interrelated serum proteins in the study of diabetic neuropathy. This group of proteins is positively correlated with the severity of neuropathy and is expected to become a new biomarker for evaluating the condition.
5. Yang, Biaolong, et al. "Low-dose anti-VEGFR2 therapy promotes anti-tumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma by down-regulating the expression of layilin on tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells." Cellular Oncology 45.6 (2022): 1297-1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00718-0
This study reveals that in the combination of low-dose anti-angiogenic drugs and immunotherapy, the down-regulation of the LAYN gene in CD8+T cells can enhance their cytotoxic function, thereby improving the anti-tumor immune effect. LAYN can serve as a potential biomarker for combined immunotherapy of lung cancer.
Creative Biolabs: LAYN Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LAYN antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LAYN Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LAYN antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Pan, Jing-Hua, et al. "LAYN is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric and colon cancers." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00006
Anti-LAYN antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-CD24 Recombinant Antibody (ALB9) (CBMAB-0176CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-ATF4 Recombinant Antibody (D4B8) (CBMAB-A3872-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BSN Recombinant Antibody (219E1) (CBMAB-1228-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-FLI1 Recombinant Antibody (CBXF-0733) (CBMAB-F0435-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-DMD Recombinant Antibody (D1190) (CBMAB-D1190-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (H14) (CBMAB-E1341-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMOT Recombinant Antibody (CBYC-A564) (CBMAB-A2552-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACVR1C Recombinant Antibody (V2-179685) (CBMAB-A1041-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CCDC6 Recombinant Antibody (CBXC-0106) (CBMAB-C5397-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABCA3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-178911) (CBMAB-A0145-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD1C Recombinant Antibody (L161) (CBMAB-C2173-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ABL2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179121) (CBMAB-A0364-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BRD3 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0801) (CBMAB-0804-YY)

-
Rabbit Anti-AKT3 Recombinant Antibody (V2-12567) (CBMAB-1057-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-8-oxoguanine Recombinant Antibody (V2-7697) (CBMAB-1869CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AFM Recombinant Antibody (V2-634159) (CBMAB-AP185LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot








