LCN2 Antibodies
Background
The LCN2 gene encodes a secretory protein called lipocalin 2 (also known as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin), which is mainly expressed in neutrophils, adipocytes and various epithelial cells. This protein participates in the regulation of iron homeostasis, innate immune response and inflammatory response by binding to small hydrophobic molecules (such as iron carriers), especially playing a key role in bacterial infection and metabolic stress processes. It was first identified in human neutrophils in 1993. Subsequent studies have revealed the significant role of LCN2 in various pathophysiological processes, including metabolic syndrome, kidney injury and tumor progression. The three-dimensional structure of this gene product features typical lipocalin folding characteristics. Its specific interaction mechanism with ligands has become an important model for studying molecular recognition and cell signal transduction, providing key clues for understanding cross-regulation of immune metabolism.
Structure of LCN2
LCN2 is a relatively small secreted protein with a molecular weight of approximately 22-25 kDa. This weight may vary slightly among different species or under different glycosylation modification states.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 25 | About 22-23 | About 23 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contain a signal peptide and a N - connection glycosylation sites | Amino acid sequences are highly conserved and glycosylation patterns may differ | High sequence homology with human LCN2 |
Lipocalin 2 is composed of approximately 200 amino acids, and its tertiary structure presents a typical lipocalin "β -barrel" folding pattern, forming a central hydrophobic cavity. The protein structure is composed of eight antiparallel β -folded plates to form a barrel-shaped main body and is connected to the ligand-binding pocket through a flexible ring region. Its ligand binding function depends on the key amino acid residues in the hydrophobic cavity, which can specifically bind iron carriers (such as enterobacteritin) to small hydrophobic molecules, thereby playing a core role in innate immunity and iron metabolism.
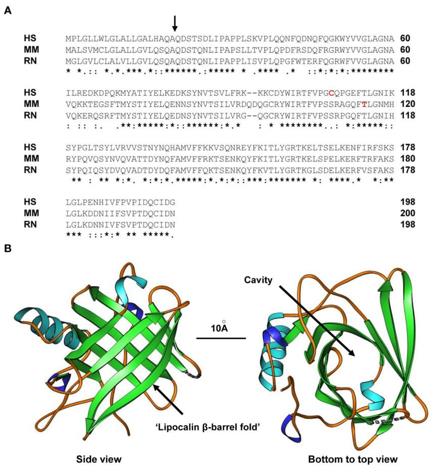 Fig. 1 Structure of LCN2.1
Fig. 1 Structure of LCN2.1
Key structural properties of LCN2:
- Typical lipocalin "β-barrel" folding structure
- Central hydrophobic ligand binding cavity
- Disulfide bonds stabilize the structure
- Flexible loop zone
Functions of LCN2
The core function of LCN2 (lipocalin 2) is to participate in the transport of iron ions and immune regulation, and it plays a key role in various pathophysiological processes.
| Function | Description |
| Steady-state regulation of iron | By binding to iron carriers of bacterial origin (such as enterobacteritin) or combining with iron transporters, it mediates the intake or excretion of iron within cells and regulates the balance of iron metabolism in the body. |
| Innate immune response | As an acute-phase response protein, it seizes the iron essential for bacterial growth through the "nutritional immunity" strategy during bacterial infection, directly inhibiting the proliferation of pathogens. |
| Inflammation and cellular stress | In a variety of tissue damage, such as kidneys, liver, and metabolic diseases (such as obesity, diabetes) expression, signal amplification and participate in inflammation cells protection/damage control. |
| Regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis | By influencing intracellular iron levels and activating related signaling pathways (such as EGFR and MAPK), it participates in regulating the survival, proliferation and apoptosis processes of epithelial cells. |
| Metabolic regulation | Expressed in adipose tissue and the liver, it is closely related to processes such as insulin resistance and lipid metabolism disorders, and is a key molecule connecting metabolism and inflammation. |
Unlike single-function storage proteins, LCN2 exerts complex and multi-directional regulatory effects in different cellular and tissue environments through its ligand binding ability, and its expression level is often regarded as a biomarker of inflammation and metabolic imbalance.
Applications of LCN2 and LCN2 Antibody in Literature
1. Wang, Dong, et al. "LCN2 secreted by tissue-infiltrating neutrophils induces the ferroptosis and wasting of adipose and muscle tissues in lung cancer cachexia." Journal of hematology & oncology 16.1 (2023): 30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-023-01429-1
The article highlights myoglobin as a key factor in rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury and introduces a high-affinity recombinant rabbit anti-myoglobin monoclonal antibody with broad species reactivity and strong diagnostic potential, potentially serving as a neutralizing antibody for RM-related diseases.
2. Huang, Zixian, et al. "Silencing LCN2 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by reducing EGFR signal activation and recycling." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 42.1 (2023): 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02618-z
Research has found that lipocalin 2 (LCN2) is highly expressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma and activates downstream pathways by binding to and promoting the recycling of EGFR. Inhibiting LCN2 can effectively block EGFR signaling, suppress tumor growth and metastasis, and provide a new target for treatment.
3. Huang, Zhixin, et al. "Tumor-secreted LCN2 impairs gastric cancer progression via autocrine inhibition of the 24p3R/JNK/c-Jun/SPARC axis." Cell Death & Disease 15.10 (2024): 756. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-024-07153-z
Research has found that the expression of LCN2 in gastric cancer is associated with a good prognosis. LCN2 inhibits tumor proliferation and metastasis by binding to the receptor 24p3R, inhibits the JNK/c-Jun pathway, and down-regulates the expression of SPARC, thereby providing a new target for treatment.
4. Ren, Kaixuan, et al. "Synergistic effects of LCN2 and TWEAK on the progression of psoriasis." Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2025): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-025-01292-9
Research has found that in psoriasis, LCN2 binds to Fn14 and forms a positive feedback loop with TWEAK, synergistically activating the MAPK pathway and intensifying keratinocyte inflammation and epidermal hyperplasia, which is a key mechanism for disease progression.
5. Wang, Li, et al. "Microglial Lcn2 knockout enhances chronic intracerebral hemorrhage recovery by restoring myelin and reducing inflammation." Theranostics 15.10 (2025): 4763. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.109440
Research has found that during the chronic stage of cerebral hemorrhage, Lcn2 derived from microglia inhibits M2 polarization and down-regulates Gdf-1 through the JAK/STAT pathway, hindering the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and myelin repair. Inhibiting Lcn2 can promote the recovery of neurological function.
Creative Biolabs: LCN2 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality LCN2 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom LCN2 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our LCN2 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Schröder, Sarah K., et al. "Lipocalin 2 receptors: facts, fictions, and myths." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1229885. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1229885
Anti-LCN2 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-AAV-5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-503417) (CBMAB-V208-1369-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CHRNA9 Recombinant Antibody (8E4) (CBMAB-C9161-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ATM Recombinant Antibody (2C1) (CBMAB-A3970-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO2 Recombinant Antibody (85F11) (CBMAB-0276CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ATP5F1A Recombinant Antibody (51) (CBMAB-A4043-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-ACLY Recombinant Antibody (V2-179314) (CBMAB-A0610-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-C5b-9 Recombinant Antibody (aE11) (CBMAB-AO138LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Rat Anti-ADAM10 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179741) (CBMAB-A1103-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-BZLF1 Recombinant Antibody (BZ.1) (CBMAB-AP705LY)

-
Mouse Anti-COL12A1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C3117) (CBMAB-C4560-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180546) (CBMAB-A2070-YC)

-
Rat Anti-4-1BB Recombinant Antibody (V2-1558) (CBMAB-0953-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-ASTN1 Recombinant Antibody (H-9) (CBMAB-1154-CN)

-
Mouse Anti-ARG1 Recombinant Antibody (CBYCL-103) (CBMAB-L0004-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-HTLV-1 gp46 Recombinant Antibody (CBMW-H1006) (CBMAB-V208-1154-FY)

-
Rabbit Anti-ABL1 (Phosphorylated Y245) Recombinant Antibody (V2-505716) (PTM-CBMAB-0465LY)

-
Mouse Anti-DLL4 Recombinant Antibody (D1090) (CBMAB-D1090-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CD247 Recombinant Antibody (6B10.2) (CBMAB-C1583-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-AMACR Recombinant Antibody (CB34A) (CBMAB-CA034LY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






