MRC1 Antibodies
Background
The MRC1 gene encodes a protein that exists on the surface of macrophages as a pattern recognition receptor and is mainly involved in endocytosis and immune regulation. This protein mediates pathogen clearance and cell debris disposal by recognizing and binding to specific carbohydrate structures, and plays a key role in maintaining internal environmental homeostasis. Research has found that MRC1 plays a regulatory role in anti-inflammatory responses, and its expression changes are closely related to the progression of infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and HIV. This gene was first identified through cDNA library screening in 1990. Its unique carbohydrate recognition domain characteristics make it an important representative of the C-type lectin family. As a classic model in innate immunity research, MRC1 continuously provides important theoretical basis for research fields such as immune recognition mechanisms and host-pathogen interactions.
Structure of MRC1
The protein encoded by the MRC1 gene is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 162 kDa. The molecular weight of this protein will show certain differences in different cell types due to the varying degrees of glycosylation modification.
| Species | Human | Mouse | Rat |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | About 162 | About 160 | About 161 |
| Primary Structural Differences | Contains an extracellular C-type lectin domain | With the human MRC1 highly homology | Structure domain composition similar to humans |
This protein is composed of 1,439 amino acid residues, and its extracellular region contains multiple functional domains that jointly mediate ligand recognition. Its C-type lectin domain is a key region for recognizing specific carbohydrate ligands and can bind to sugar structures such as mannose in a calcium ion-dependent manner. This domain coordinates with calcium ions through conserved amino acid residues (such as Glu and Asn), and then interacts with sugar ligands. This mechanism is crucial for pathogen recognition and endocytosis.
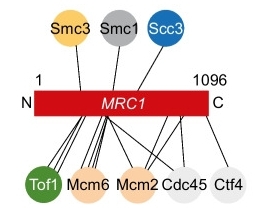 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of Mrc1 and its cohesin crosslinks.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of Mrc1 and its cohesin crosslinks.1
Key structural properties of MRC1:
- Complex multi-domain extracellular regions
- Characteristic C-type lectin recognition domain
- Transmembrane anchoring and intracellular signal transduction module
Functions of MRC1
The main function of the protein encoded by the MRC1 gene is to participate in immune recognition and endocytosis. Meanwhile, this protein also plays a key role in a variety of physiological processes, including immune regulation and tissue repair.
| Function | Description |
| Pathogen identification | The immune response is initiated by specifically recognizing sugar structures such as mannose and fucose on the surface of pathogens through the C-type lectin domain. |
| Endocytosis | Mediate the phagocytosis and clearance of foreign substances such as pathogens and apoptotic cells, and maintain the stability of the internal environment of the tissue. |
| Immune regulation | By regulating cytokine secretion and T cell activation, it participates in anti-inflammatory responses and prevents excessive immune damage. |
| Antigen presentation | Assist in presenting the processed antigen to T cells and link the innate immune and adaptive immune responses. |
| Tissue repair | In the condition of the infection in the extracellular matrix remodeling and tissue regeneration process, promote restoration of the damage. |
The ligand binding characteristics of this protein are manifested as a broad-spectrum carbohydrate recognition mode. Compared with the epitopes of antibodies that specifically recognize a single antigen, its mode of action is more inclined to the typical features of pattern recognition receptors - responding to the threat of multiple pathogens by recognizing specific molecular patterns. This localization makes it an important part of the innate immune defense system.
Applications of MRC1 and MRC1 Antibody in Literature
1. Huang, Linxi, et al. "Mrc1+ macrophage-derived IGF1 mitigates crystal nephropathy by promoting renal tubule cell proliferation via the AKT/Rb signaling pathway." Theranostics 14.4 (2024): 1764. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.89174
This study found through single-cell sequencing that in glyalate-induced crystal nephropathy, Mrc1+ macrophages promote the proliferation of renal tubular cells by secreting IGF1 and activating the AKT/Rb signaling pathway, thereby alleviating kidney injury. This provides a potential therapeutic target for crystalline nephropathy.
2. Poyuan, et al. "Mrc1-dependent chromatin compaction represses DNA double-stranded break repair by homologous recombination upon replication stress." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 630777. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.630777
This study reveals that under replication stress, Mrc1 induces global chromatin compression in a way that is independent of its partner proteins. This structural change hinders DNA terminal excision enzymes from approaching the damage site, thereby inhibiting homologous recombination repair and maintaining genomic stability.
3. Gellon, Lionel, et al. "Mrc1 and Tof1 prevent fragility and instability at long CAG repeats by their fork stabilizing function." Nucleic acids research 47.2 (2019): 794-805. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1195
This study reveals that when replication forks encounter CAG repeat sequences, the "fork stabilization" function of Mrc1 (independent of its checkpoint function) is crucial for preventing DNA breaks. This protective effect is particularly crucial in long repeat sequences, while the role of Tof1 is more sequence-specific.
4. Yu, Keesun, et al. "Characterization of splenic MRC1hiMHCIIlo and MRC1loMHCIIhi cells from the monocyte/macrophage lineage of White Leghorn chickens." Veterinary research 51.1 (2020): 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13567-020-00795-9
Two subsets of monocytes/macrophages were found in the spleen of chickens in this study: MRC1loMHCIIhi cells are good at antigen presentation and secretion of inflammatory factors; MRC1hiMHCIIlo cells, on the other hand, possess stronger phagocytic, migratory and bactericidal capabilities, and their proportions increase under inflammatory conditions, with clear functional differentiation.
5. Shrestha, Sudikchya, et al. "Replisome-cohesin interactions provided by the Tof1-Csm3 and Mrc1 cohesion establishment factors." Chromosoma 132.2 (2023): 117-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-023-00797-4
This study reveals that Mrc1 and Tof1-Csm3 regulate the chromosomal cohesin complex through direct and multi-faceted protein-protein interactions, thereby directly promoting the establishment of sister chromatid adhesions during DNA replication. This function is independent of their known replication-related roles.
Creative Biolabs: MRC1 Antibodies for Research
Creative Biolabs specializes in the production of high-quality MRC1 antibodies for research and industrial applications. Our portfolio includes monoclonal antibodies tailored for ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and other diagnostic methodologies.
- Custom MRC1 Antibody Development: Tailor-made solutions to meet specific research requirements.
- Bulk Production: Large-scale antibody manufacturing for industry partners.
- Technical Support: Expert consultation for protocol optimization and troubleshooting.
- Aliquoting Services: Conveniently sized aliquots for long-term storage and consistent experimental outcomes.
For more details on our MRC1 antibodies, custom preparations, or technical support, contact us at email.
Reference
- Shrestha, Sudikchya, et al. "Replisome-cohesin interactions provided by the Tof1-Csm3 and Mrc1 cohesion establishment factors." Chromosoma 132.2 (2023): 117-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-023-00797-4
Anti-MRC1 antibodies
 Loading...
Loading...
Hot products 
-
Mouse Anti-DISP2 Monoclonal Antibody (F66A4B1) (CBMAB-1112CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-AK4 Recombinant Antibody (V2-180419) (CBMAB-A1891-YC)

-
Rabbit Anti-B2M Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-0059) (CBMAB-0059-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-Acetyl-α-Tubulin (Lys40) Recombinant Antibody (V2-623485) (CBMAB-CP2897-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-FN1 Monoclonal Antibody (71) (CBMAB-1241CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADGRE5 Recombinant Antibody (V2-360335) (CBMAB-C2088-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CD83 Recombinant Antibody (HB15) (CBMAB-C1765-CQ)

-
Mouse Anti-CAPZB Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-C0944) (CBMAB-C2381-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-CECR2 Recombinant Antibody (CBWJC-2465) (CBMAB-C3533WJ)

-
Mouse Anti-ADIPOR2 Recombinant Antibody (V2-179983) (CBMAB-A1369-YC)

-
Mouse Anti-CIITA Recombinant Antibody (CBLC160-LY) (CBMAB-C10987-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CASP7 Recombinant Antibody (10-01-62) (CBMAB-C2005-LY)

-
Mouse Anti-CDKL5 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-1629) (CBMAB-C1689-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-ENO1 Recombinant Antibody (8G8) (CBMAB-E1329-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD46 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYC-0076) (CBMAB-C0085-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-DES Monoclonal Antibody (440) (CBMAB-AP1857LY)

-
Mouse Anti-BRCA2 Recombinant Antibody (CBYY-1728) (CBMAB-2077-YY)

-
Mouse Anti-EPO Recombinant Antibody (CBFYR0196) (CBMAB-R0196-FY)

-
Mouse Anti-CD2AP Recombinant Antibody (BR083) (CBMAB-BR083LY)

-
Mouse Anti-EMP3 Recombinant Antibody (CBFYE-0100) (CBMAB-E0207-FY)

- AActivation
- AGAgonist
- APApoptosis
- BBlocking
- BABioassay
- BIBioimaging
- CImmunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections
- CIChromatin Immunoprecipitation
- CTCytotoxicity
- CSCostimulation
- DDepletion
- DBDot Blot
- EELISA
- ECELISA(Cap)
- EDELISA(Det)
- ESELISpot
- EMElectron Microscopy
- FFlow Cytometry
- FNFunction Assay
- GSGel Supershift
- IInhibition
- IAEnzyme Immunoassay
- ICImmunocytochemistry
- IDImmunodiffusion
- IEImmunoelectrophoresis
- IFImmunofluorescence
- IGImmunochromatography
- IHImmunohistochemistry
- IMImmunomicroscopy
- IOImmunoassay
- IPImmunoprecipitation
- ISIntracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
- LALuminex Assay
- LFLateral Flow Immunoassay
- MMicroarray
- MCMass Cytometry/CyTOF
- MDMeDIP
- MSElectrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
- NNeutralization
- PImmunohistologyp-Paraffin Sections
- PAPeptide Array
- PEPeptide ELISA
- PLProximity Ligation Assay
- RRadioimmunoassay
- SStimulation
- SESandwich ELISA
- SHIn situ hybridization
- TCTissue Culture
- WBWestern Blot






